In “What Is The Aquatic Plant Yellow Floating Heart”, you will embark on a scholarly exploration of a unique aquatic flora. You are invited to traverse the nuanced ecosystem of the Yellow Floating Heart, a plant often overlooked yet filled with fascinating ecological implications. You will acquire a comprehensive understanding of its botanical characteristics, evolutionary secrets, and the role it plays within its aquatic environment. Renowned for its unparalleled beauty and adaptability, the Yellow Floating Heart holds a wealth of knowledge that enriches our comprehension of biodiversity and environmental science. This structured analysis will enhance your botanical knowledge and further ignite your interest in the vast wonders of nature.
Overview of Yellow Floating Heart
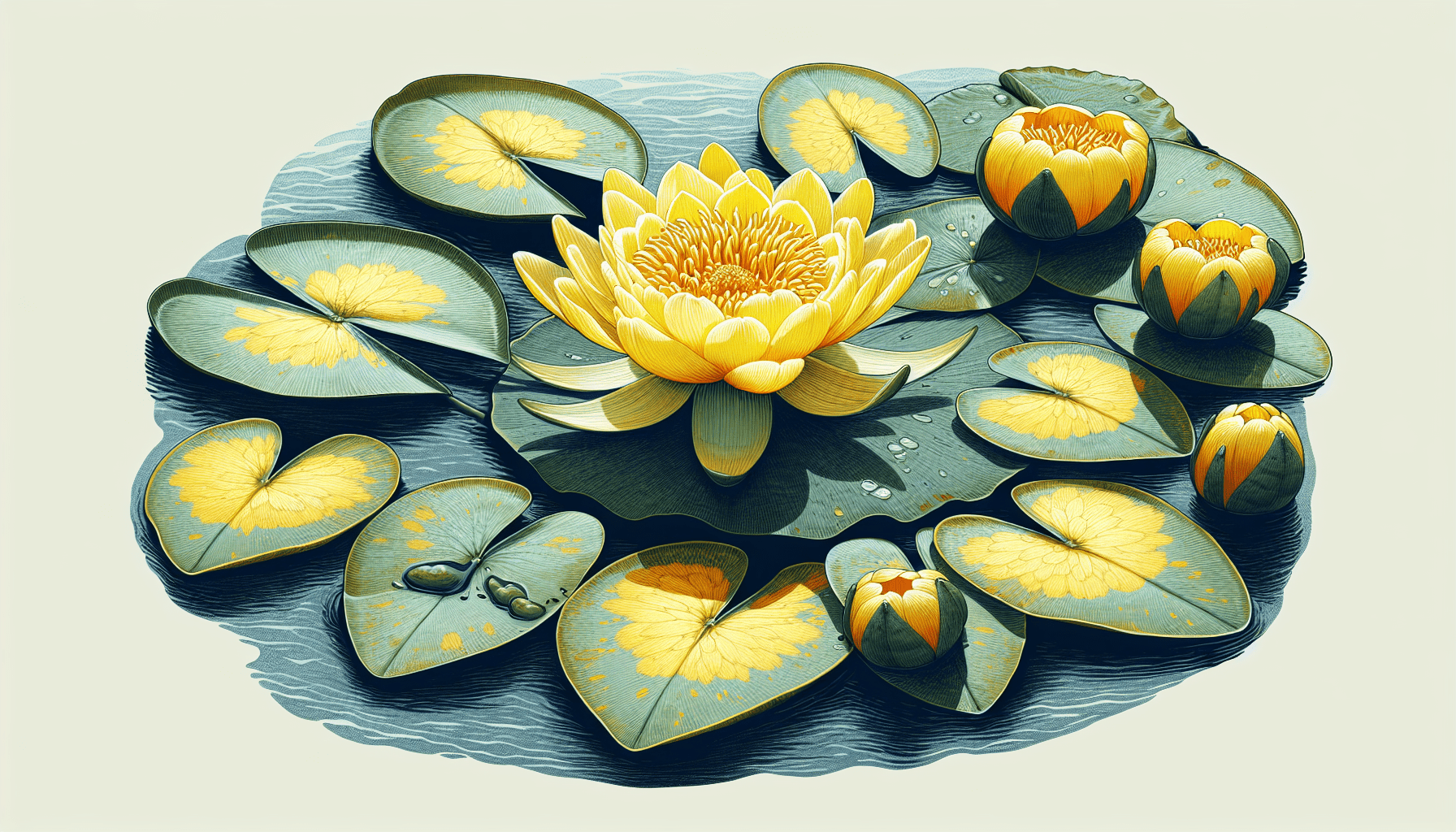
The Yellow Floating Heart, known scientifically as Nymphoides peltata, is an aquatic plant that resides in the family of Menyanthaceae. This species is noted for its striking yellow flowers and its broad, heart-shaped leaves.
Native to parts of Asia and Europe, the Yellow Floating Heart has spread widely through human activity and is now found in numerous regions across the globe, including North America and Australasia. However, it’s thrive best in its original, natural habitats.
The Yellow Floating Heart is a perennial plant identifiable by its bright yellow flowers and the characteristic heart shape of its leaves. The flowers, which bloom from June to September, have five petals each and are fringed at the margins. The leaves, on the other hand, are typically dark green and waxy. They float on the water’s surface, with stems attached in the centre – an attachment style termed as peltate.
Habitat and Growing Conditions
The Yellow Floating Heart is an adaptable species and thrives in a variety of aquatic habitats. It prefers still or slow-moving freshwater bodies such as ponds, lakes, canals, and ditches. It can also tolerate a wide range of temperatures, from mild to relatively high ones.
Regarding water composition, the plant can survive in both nutrient-rich and nutrient-poor waters; however, it tends to produce more flowers in nutrient-rich conditions. Seasonally, the Yellow Floating Heart is a summer bloomer, with the most vigorous growth observed during warmer months.
Anatomy of Yellow Floating Heart
The leaves of the Yellow Floating Heart are broad and heart-shaped, a trait that gives the plant its name. These leaves, which have a waxy texture, float on the water surface with their stems attached in the center.
The flowers of the Yellow Floating Heart are a striking yellow colour with five fringed petals each. They bloom above the water surface, catching the eye with their vibrant hue.
As for the root structure, the Yellow Floating Heart has a creeping root system composed of rhizomes. These string-like roots provide the plant with the prowess to grow across the water surface rapidly.

Propagation and Growth
The Yellow Floating Heart reproduces through various methods. It can generate new plants from fragments of its leaves and stems, drops seeds into the water that later germinate, and spreads through its creeping roots system.
The growth rate of the Yellow Floating Heart varies, but the plant is generally recognized for its vigorous growth. Under optimal conditions, it can spread rapidly to cover large water surfaces. However, it may encounter growth challenges in environments with less favourable conditions, such as nutrient-poor water bodies or extreme temperatures.
Ecological Role and Importance
The Yellow Floating Heart contributes to its ecosystem in multiple ways. It provides shelter and food for various forms of aquatic life and helps oxygenate the water. However, its dense growth may lead to algal blooms by limiting light penetration, thereby lowering water quality.
The plant’s interactions with other species are complex. While it may offer beneficial habitats to some species, its invasive qualities can outcompete native plants and substantially alter local ecosystems.
Cultivation and Care
Growing Yellow Floating Heart in garden ponds or water gardens can add aesthetic value, thanks to its attractive foliage and flowers. However, the plant requires mindful care to prevent excessive growth. Regular trimming may be necessary, particularly during warmer months when growth is most vigorous.
Excessive growth, which can lead to the domination of the water surface and disrupt the balance of life beneath, must be held under control. Many gardeners regularly remove floating leaves and flowers to keep the population in check.
Potential Uses and Benefits
Aside from its ornamental uses, the Yellow Floating Heart holds potential for various scientific and medical research. The plant’s compounds may possess therapeutic properties for treating certain conditions.
In several Asian countries, the roots, leaves, and stems of the Yellow Floating Heart have a role in traditional medicine, often used to treat inflammation, nausea, fever, and more. Moreover, they also incorporate the plant into various culinary dishes.
Hazards and Concerns
Primarily, the invasive nature of the Yellow Floating Heart poses a significant threat to local biodiversity. It can choke water bodies and outcompete native species, leading to imbalanced ecosystems. Furthermore, its dense mats disrupt water circulation and light availability, which impacts fish and other wildlife populations.
Legislative and Conservation Status
Due to its invasive nature, the Yellow Floating Heart is included in various regions’ invasive species regulations. There are controls and restrictions on its trade, especially in countries where the plant is not native.
Despite these restrictions, management and conservation efforts to keep the Yellow Floating Heart population under control continue, incurring substantial costs and environmental labour.
Future Outlook and Research
Presently, there’s significant research focused on understanding the Yellow Floating Heart’s biology, growth patterns, and ecological impacts, bringing valuable insights about its management. However, there is room for further studies, particularly concerning its impacts on various ecosystems.
Given the potential impacts of climate change on aquatic ecosystems, understanding how species like the Yellow Floating Heart might respond to changing conditions is crucial. As such, it is expected that this plant will continue to be a significant focus in aquatic plant research in the coming years.