Facing the prospects of analyzing the peculiarities of aquatic life, one encounters the Western Water Milfoil, a fascinating marine plant. This article embodies a comprehensive exploration of this water-loving flora, scrutinizing its attributes, ecological significance, and the role it plays in its aquatic environment. By engaging in this educational venture, you would cultivate a deeper understanding of aquatic ecosystems and this particular component’s role, especially Western Water Milfoil, contributing to their balance and vitality.
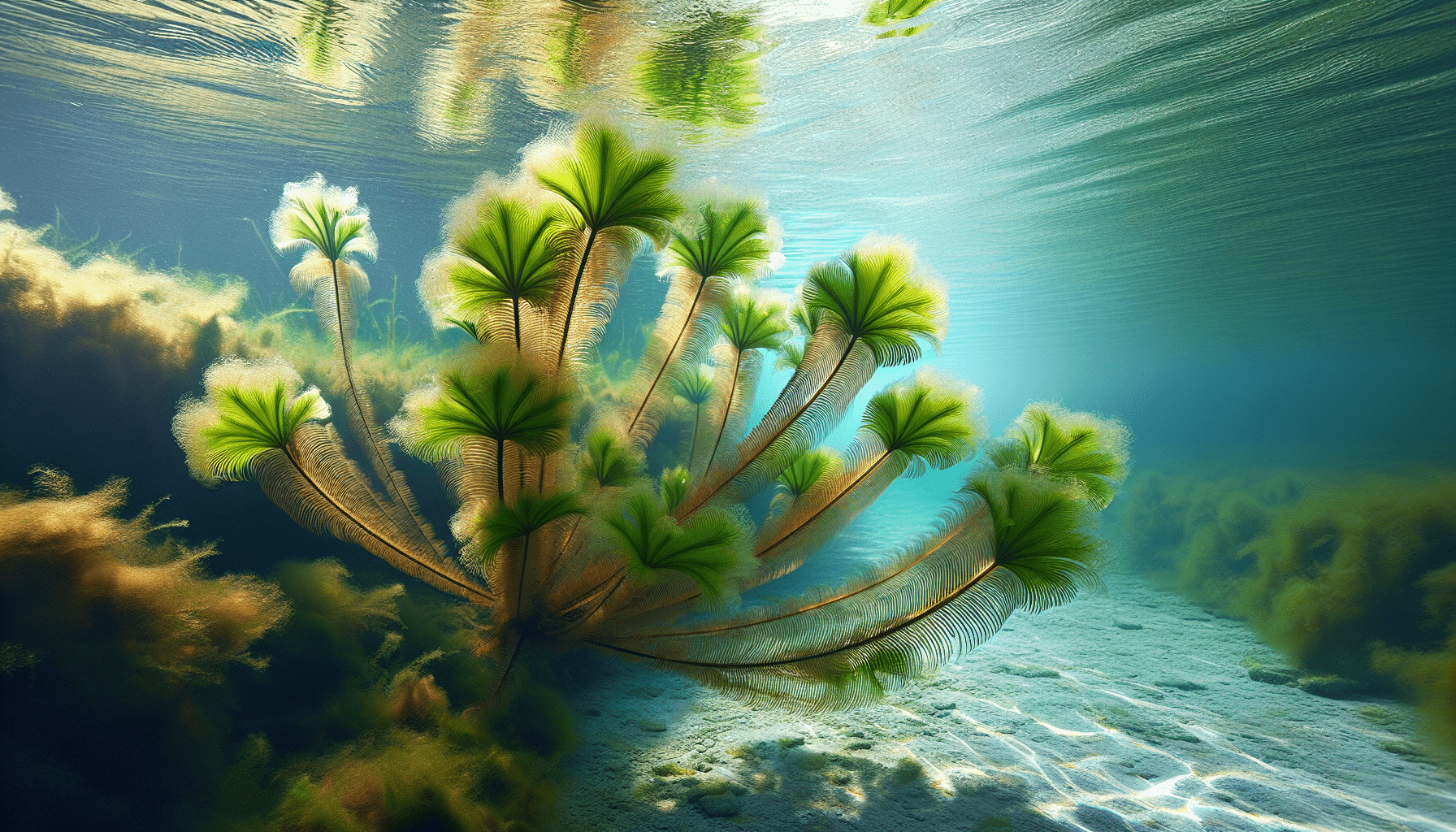
Overview of Western Water Milfoil
In the comprehensive study of aquatic plants, Western Water Milfoil is an intriguing species. This article provides you with insightful details about this aquatic plant, helping you understand its characteristics, life cycle, role in the ecosystem, and impact on water quality.
Definition of Western Water Milfoil
Western Water Milfoil, scientifically known as Myriophyllum hippuroides, is a submersed perennial herb and a member of the watermilfoil family. As an aquatic plant, this species flourishes in water, producing tufts of soft, feathery leaves around its stem.
Scientific Classification
Scientifically, Western Water Milfoil falls under the Plantae kingdom, more specifically within the Angiosperms class, Eudicots clade and Rosids order. Its family is Haloragaceae, and it is part of the genus Myriophyllum.
Habitats
As a water-dwelling plant, Western Water Milfoil prefers shallow and calm water bodies. It typically flourishes in lakes and ponds, not exceeding eight meters depth. The species is adaptive to a range of light conditions, demonstrating resilience in low light environments.
Global Distribution
Western Water Milfoil is a native plant to a vast range of areas across North America — from southern Alaska extending to parts of California, and eastwards to Quebec and New England.
Description of Western Water Milfoil
Understanding Western Water Milfoil involves exploring its physical attributes, comparisons with other species, and brilliance in growth patterns.
Physical Characteristics
Western Water Milfoil, standing up to 6 meters high, exhibits an emersed flowering spike. The leaves are submerged, pinnately divided, and occur in whorls. Its bright green leaves grow in dense clusters giving an overall feathery appearance.
Comparative Descriptions with Other Species
In comparison to the Eurasian Watermilfoil, another species within the same family, Western Water Milfoil exhibits larger leaves clustered more closely along the stems. Its flowers are larger and arrayed in a semi whorl fashion.
Growth Patterns
Western Water Milfoil displays a quick growth pattern. When conditions are propitious, the plants form dense underwater mats that may extend across the water’s surface, impeding water activities.
Life Cycle of Western Water Milfoil
In order to thrive, grow, and reproduce, Western Water Milfoil follows a particular life cycle involving both sexual and asexual reproduction.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction in Western Water Milfoil involves the production of flowers, which grow just above the water line. The pollination is predominantly through wind transfer of pollen. After pollination, the plant produces fruits which house the seeds.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a survival strategy developed by the plant in less favorable conditions. Increasing its spatial spread, Western Water Milfoil can reproduce asexually through its stem fragments that can root and grow into a new plant.
Growth and Development Stages
The growth stages of Western Water Milfoil include growth from seed or stem fragments, sprouting of leaves, development of flowers, and spreading through fragmentation.
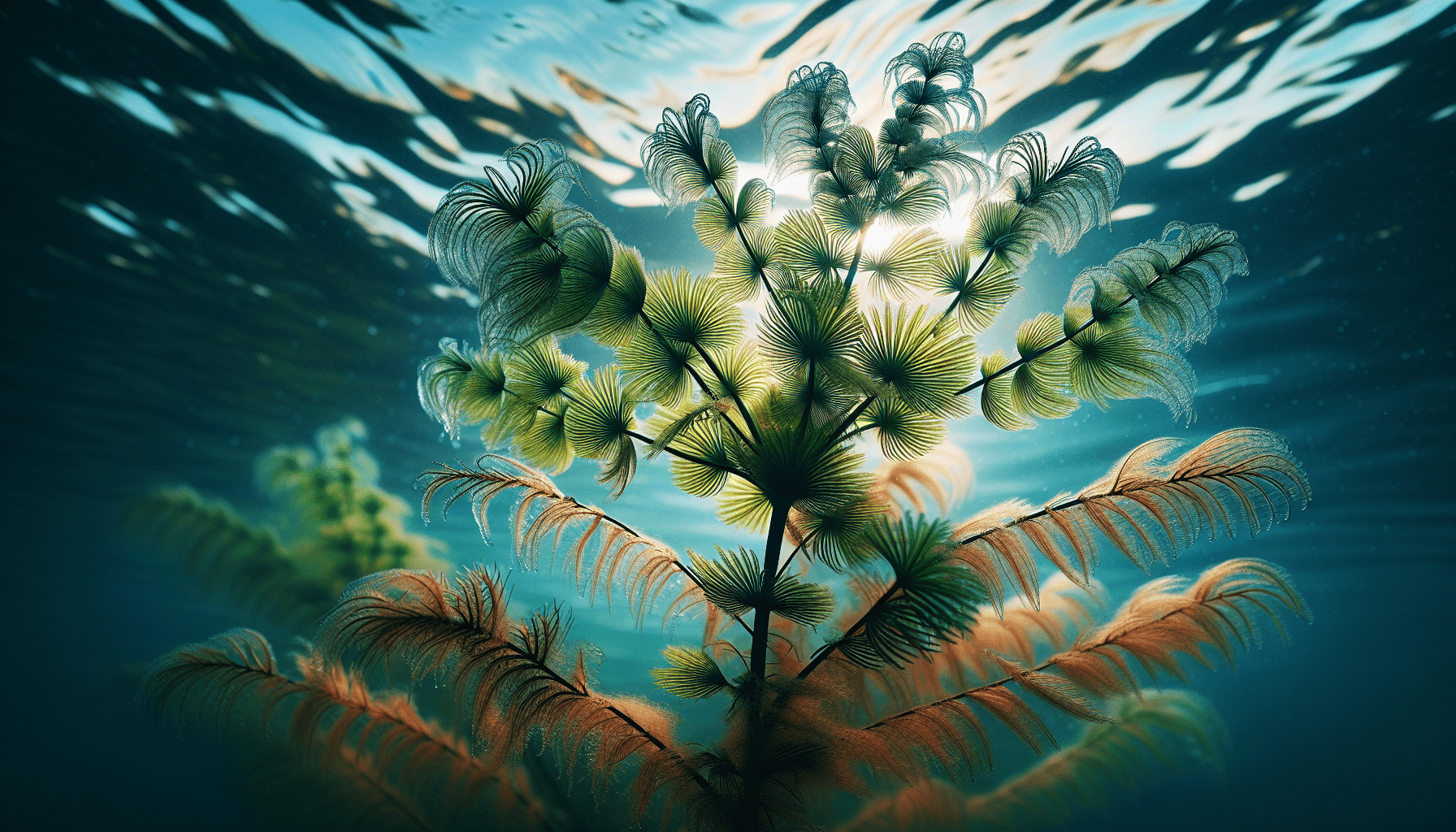
Ecology of Western Water Milfoil
Western Water Milfoil’s interactions with its surroundings and the effects of its invasive characteristics present an interesting ecological dynamic.
Interactions with Other Aquatic Organisms
The dense canopy formed by Western Water Milfoil provides habitat for many invertebrates, insects, and fishes, but it also affects the availability of sunlight to other aquatic plants and can compete for resources with native plant communities.
Roles in Ecosystems
As an ecological player, Western Water Milfoil contributes to biodiversity by providing fish and invertebrate habitat, while also aiding in nutrient cycling within the ecosystem.
Invasive Characteristics
Though beneficial in natural contexts, when Western Water Milfoil becomes too invasive, it presents numerous ecological concerns. Dense surface mats can impede recreational activities and potentially alter the ecology of water bodies.
Western Water Milfoil and Water Quality
The impacts of Western Water Milfoil are directly linked to water quality, including aspects such as water clarity, oxygen levels and nutrient cycling.
Impacts on Water Clarity
The plant’s rapid growth and density can cause a decrease in water clarity. This can directly alter the underwater light climate, affecting other aquatic species.
Impacts on Oxygen Levels
Through its photosynthetic process, Western Water Milfoil increases dissolved oxygen levels in the water during the day. However, this oxygen can be depleted at night through respiration, potentially leading to large diel fluctuations in oxygen levels.
Impacts on Nutrient Cycling
Western Water Milfoil plays a role in nutrient cycling within the aquatic systems. As it absorbs nutrients from the water column, it alters nutrient dynamics within the ecosystem.
Control and Management of Western Water Milfoil
Though beneficial, Western Water Milfoil requires effective management strategies should it become a disruptive presence. These can take physical, chemical or biological forms.
Physical Control Methods
Physical control methods to manage Western Water Milfoil include hand harvesting, raking, dredging and the use of benthic barriers to inhibit growth. These can be labor intensive but offer a direct means of control.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control through the application of herbicides is another management strategy. It is essential to follow all guidelines to ensure minimal ecological impact.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control aims to use natural enemies of the plant to manage its populations. The milfoil weevil is a promising yet still experimental method of biological control for Western Water Milfoil.
Western Water Milfoil in Landscaping and Aquascaping
This plant is not only found in the wild, it’s used in landscaping and aquascaping, particularly for those aiming to achieve natural designs.
Uses in Aquatic Gardens
Western Water Milfoil is a popular addition to aquatic gardens. With its lush green and attractive feathered appearance, it adds a natural aesthetic to water-based settings.
Suitable Environmental Conditions
For successful cultivation in an artificial context, Western Water Milfoil requires a stable water temperature, adequate lighting, and pH.
Maintenance and Care
Considered a hardy plant, Western Water Milfoil requires low maintenance. Occasional trimming to manage its growth and prevent it from becoming overly invasive in its artificial context is recommended.
Current Research on Western Water Milfoil
Research efforts on Western Water Milfoil are a thriving field aimed at understanding more about its growth, reproduction and invasive traits, and developing effective control methods.
Studies on Growth and Reproduction
Major research inquiries on Western Water Milfoil relate to its growth and reproduction. An understanding of how this species continues to thrive is essential for continued management strategies.
Research on Invasive Characteristics
Ongoing investigations also focus on the potential invasive characteristics of Western Water Milfoil. The ability of the species to rapidly colonize new areas is of particular interest.
Development of Control Methods
EffORTS are underway in the development of effective and sustainable control methods, including the exploration of more environmentally-friendly and target-specific biocontrol agents.
Economic Impacts of Western Water Milfoil
Western Water Milfoil holds significant implications for both the economy and society. These range from control costs to the impact on property values and recreational activities.
Cost of Control and Management
Due to its rapid growth and invasive nature, significant funding and resources are often needed to control and manage Western Water Milfoil populations.
Impact on Recreational Water Activities
Dense mats of Western Water Milfoil can disrupt recreational water activities such as swimming, boating, and fishing. This has significant socio-economic implications for communities that rely on these activities.
Impact on Property Values Near Infested Waters
Infestations can cause a decline in property values, particularly for waterfront properties. This is due to the decreased aesthetic value and potential impact on recreational use.
Case Studies of Western Water Milfoil Infestations
Western Water Milfoil infestations have occurred across various locales, offering valuable case studies for understanding its impacts and management efforts.
Documented Infestations
Reported infestations of Western Water Milfoil have occurred in the majority of the United States and parts of Canada. These infestations provide valuable insights into the species’ adaptability and resilience.
Impact Assessments
Impact assessments highlight how Western Water Milfoil infestations impact local environments and economies. This yields knowledge not only on the species itself, but also on the importance of early detection and management.
Management and Control Efforts
These case studies also elucidate the various management and control efforts undertaken. They offer a closer look at strategies that are working and where modifications may be needed.
Western Water Milfoil is undeniably a remarkable aquatic plant, with its ability to transform both aquatic and artificial landscapes. At the same time, it underscores the importance of effective aquatic plant management for ensuring balanced ecosystems. Through the ongoing research efforts and insights from case studies, the conversation around Western Water Milfoil continues to evolve, contributing valuable knowledge to the broader realm of aquatic ecology and management.