You are about to explore the theological, taxonomic domain of the aquatic plant known as Water Speedwell. As we journey into the realms of botany, we will discuss this distinct plant’s vital characteristics, understand its evolutionary adaptations, comprehend its habitat preference, and embark on grasping its significant role in the broader ecosystem. This water-loving perennial will offer you insights into aquatic botany in regions where it predominantly thrives, reiterating the profound, symbiotic relationships between each life form and its tune to nature’s rhythm. Considered an epitome of adaptive success in wet environments, Water Speedwell creates an exciting string of learning moments that expand your understanding of life beneath water surfaces.
Overview of Water Speedwell
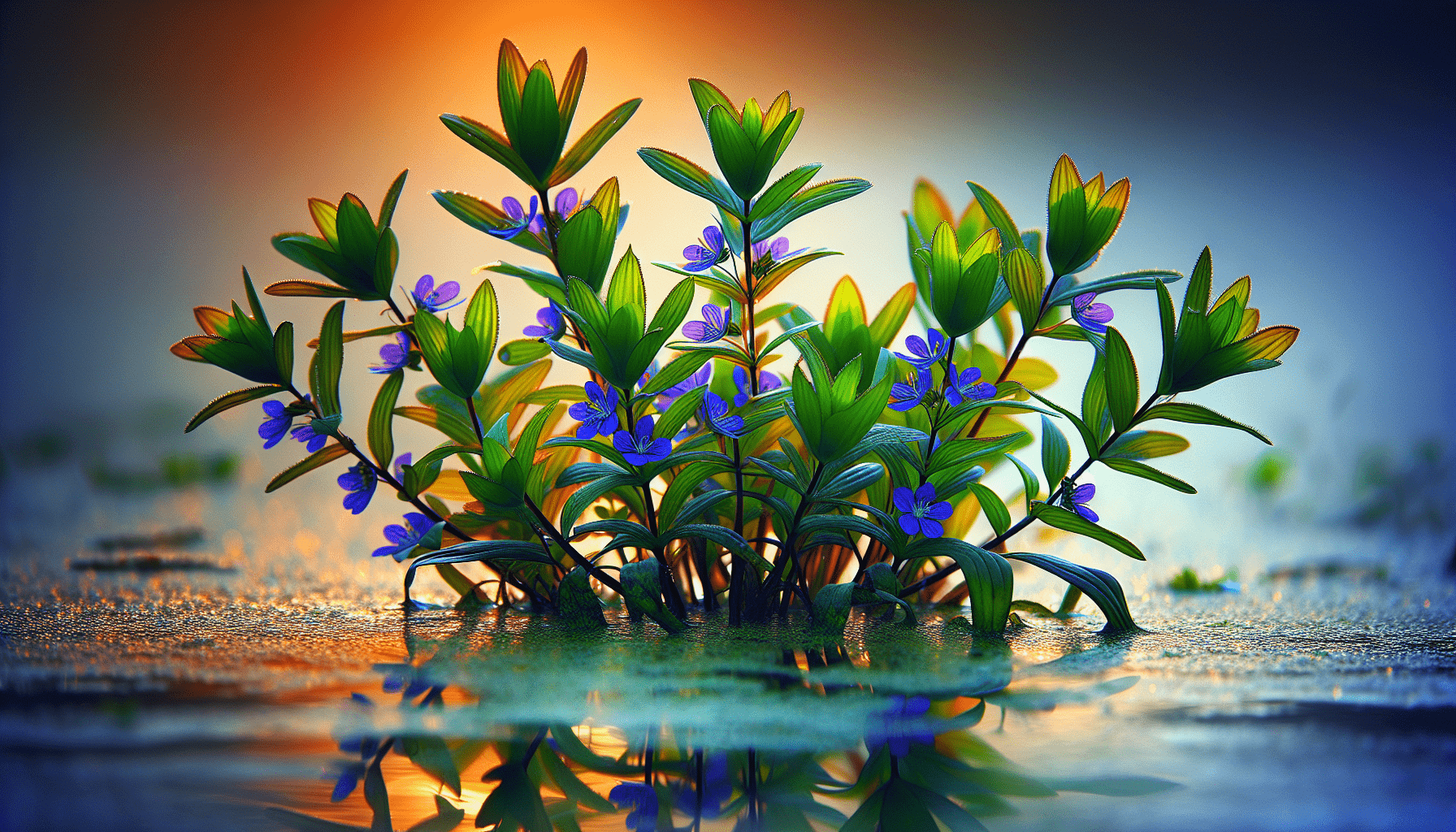
The Water Speedwell, scientifically known as Veronica anagallis-aquatica, is a unique aquatic or semi-aquatic perennial, distinguished by its delicate blue-to-violet flowers and lance-shaped leaves. Though often assumed as a weed, it holds notable significance in various traditional cultures, medicinal applications, and ecological roles.
Known scientific name: Veronica anagallis-aquatica
Veronica anagallis-aquatica is the scientific name for the plant commonly known as the Water Speedwell. Its classification within the species ‘Veronica’ stems from its resemblance to other similar species, while ‘anagallis-aquatica’ connotes its capability to grow in the presence of water.
Common names and synonyms
The plant is also frequently recognized by a variety of alternative titles such as ‘Blue Water-Speedwell,’ ‘Brook Pimpernel,’ and ‘European Speedwell’ due to its vivid floristic features and extensive geographical reach. Other synonyms include ‘Anagallis aquatica,’ reflecting its original scientific nomenclature.
Family and place in plant taxonomy
Water Speedwell belongs to the Plantaginaceae family, which comprises a diverse assortment of flowering plants. Structurally, its placement in the plant taxonomy acknowledges its distinct morphological characteristics and its predilection towards aquatic habitats.
Habitat and Distribution
Water Speedwell exhibits a high degree of adaptability which is reflected in its extensive global distribution.
Global distribution patterns
You may encounter the Water Speedwell in almost every corner of the globe. Although native to Europe, it has spread to North America, Asia, Australia, and parts of Africa. This broad distribution illustrates the plant’s ability to thrive in a wide range of climatic conditions from temperate to subtropical regions.
Preferred aquatic environments
Water Speedwell’s habitat preference leans towards aquatic settings. It largely thrives in slow-moving or stagnant water bodies such as ponds, ditches, and stream margins. The soil of these environments tends to be moist, loamy, and mildly acidic to neutral.
Role in ecosystem diversity
By using its unique ability to adapt in the various aquatic settings, Water Speedwell plays a crucial part in sustaining ecosystem diversity. It provides food and shelter to many freshwater organisms, and its dense growth can help stabilize waterway banks, preventing soil erosion and promoting ecosystem stability.
Morphological Characteristics
The prime identifiers of Water Speedwell are its morphological characteristics that prominently include its leaves, flowers, stem, and roots.
Description of leaves: shape, size, and color
The leaves of Water Speedwell are typically lance-shaped, radiating an inviting shade of green. They are oppositely arranged on the stems, with their sizes averaging around 4-8 cm long and 0.5-2 cm broad.
Flower characteristics: Blooming period, color, and structure
The vibrant flowers of Water Speedwell usually manifest a blue-to-violet aura and bloom in large clusters. Their blooming season stretches from late spring to early autumn. Each flower bears four petals and two green sepals behind it, which lends it a dynamic visual appeal.
Stem and root properties
Water speedwell possesses a sturdy yet flexible stem that frequently branches out and can grow up to 50 cm long. Its root system, relatively shallow, predominantly thrives at the margin of the water body.

Reproduction and Growth
Water Speedwell has a fascinating life cycle, and its reproduction and growth mechanisms are critical for its survival and propagation.
Life cycle stages
Water Speedwell’s life cycle kicks off when the seeds germinate, usually in spring or early summer. As the seedlings mature, they produce flower-bearing stems. Post budding and pollination, the flowers mature and produce seeds that mark the final stage of the plant’s life cycle.
Mechanisms of propagation
Water Speedwell adopts two routes for propagation: vegetative propagation through the spread of its roots and sexual reproduction via seeds. The plant’s seed production is prolific, enabling it to colonize extensive areas over a short span of time.
Speed and conditions for germination
The seeds of Water Speedwell are quite resilient and can germinate under a variety of conditions. The ideal circumstance requires stagnant or slow-moving water bodies with moist, loamy soil. Germination is relatively swift only taking around a week post proper environmental exposure.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Water Speedwell’s cultural symbolism and historical relevance extol its multifaceted role.
Cultural symbolism and uses
In many cultures, Water Speedwell is treasured as a symbol of serenity and tranquility due to its delicate blue blossoms and peaceful aquatic preference. Additionally, several societies harness its medicinal and culinary properties to address various health and dietary preferences.
Historical relevance in folklore and tradition
Historically, Water Speedwell is featured in multiple folklore and traditions due to its eye-catching appearance and perceived mystical properties. In medieval Europe, it was believed to ward off evil spirits.
Artistic depictions in literature and visual arts
Water Speedwell has made fleeting appearances in the realms of literature and visual arts. Its delicate, jewel-toned flowers and lush leaves often inspire artistic renditions, while poems and prose occasionally sprinkle references to this tranquil plant.
Medicinal and Culinary Uses
Water Speedwell’s medicinal properties merit attention, as do its intriguing culinary potentials.
Traditional and Modern medicinal applications
Traditionally, Water Speedwell has been used as an herbal remedy across many cultures. It has been employed as a treatment for coughs, ulcers, skin disorders, and gastrointestinal problems. Modern science is currently exploring these potentials further.
Edible components and nutritional value
While not often a first choice for dietary consumption, Water Speedwell’s leaves, stem, and even flowers carry some nutritional value, primarily in vitamins and minerals. They can be prepared as infusions, salads, or even garnishes.
Usage in culinary dishes and recipes
Water Speedwell can be incorporated into several culinary dishes. Native cultures have used it to add flavor to stews and soups. It can also be employed as a green supplement to salads or as a vibrant decorative element for plating.
Cultivation and Maintenance
Cultivating and maintaining Water Speedwell requires particular steps and optimal conditions.
Cultivation procedures
Cultivating Water Speedwell primarily involves the planting of seeds or root divisions in a suitably damp and sun-exposed area. The soil should ideally be loamy and acidic to neutral for optimal development.
Ideal conditions for growth
Water Speedwell’s ideal growth conditions encompass full sunlight with ample access to stagnant or slow-moving water. It can endure seasonal variations of temperature, though it grows astoundingly well in temperate settings.
Pruning and maintenance needs
Pruning needs of Water Speedwell are minimal and mostly include the removal of dried or wilting leaves. Regular surveillance for pests and diseases and ensuring its preferred environmental conditions remain consistent are part of its maintenance routine.
Dealing with Pests and Diseases
Managing pests and diseases affecting Water Speedwell is paramount even though the plant has substantial natural resilience.
Common pests affecting Water Speedwell
A few common pests that pose a threat to Water Speedwell include aphids and snails. These can often be controlled by manual removal or with organic deterrents.
Typical diseases: symptoms and treatments
Water Speedwell is notably resistant to most diseases but is susceptible to fungal infections during damp seasons. Symptoms include mold formation and curling leaves. Treatment usually involves anti-fungal treatments or removal of the infected portions to prevent further spread.
Prevention and control measures
Prevention and control measures for Water Speedwell often involve vigilant monitoring, healthy growing conditions, and prompt response to any signs of disease or infestation. Using organic deterrents for pests and ensuring clean, debris-free environment can also aide in prevention.
Environmental Impact and Conservation
Water Speedwell’s environmental footprint is comprehensive and often beneficial.
Role in water purification
Water Speedwell adsorbs harmful substances in water, acting as a natural purifier. Its roots and dense foliage also diminish water turbidity by trapping sediments.
Impact on biodiversity
The plant provides refuge and sustenance to a variety of aquatic organisms, therefore enhancing local biodiversity. It also mitigates soil erosion, thereby preserving the health of aquatic environments.
Conservation needs and strategies
While Water Speedwell is not a threatened species, maintaining its habitats and preventing its over-exploitation are practical conservation steps. Its use in freshwater habitat restoration projects could also certainly benefit biodiversity conservation efforts.
Potential Hazards
Despite its many benefits, Water Speedwell may pose certain threats.
Possible allergenic reactions
Some individuals might experience allergic reactions when exposed to Water Speedwell. These reactions commonly manifest as dermatitis or respiratory complications.
Toxicity in pets and livestock
Although not typically toxic to pets or livestock, excessive consumption may lead to stomach upset. Owners should monitor pets or livestock to prevent overconsumption.
Invasive properties and environmental dangers
Despite its ecological benefits, Water Speedwell can become invasive under suitable conditions. Its capacity for rapid proliferation could lead to domination over native plant species in certain habitats. As such, careful management becomes necessary to maintain the balance of various ecosystems.