In your exploration of diverse aquatic plant species, you may have undoubtedly come across the intriguing term “Water Hyacinth.” Considered one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth, the Water Hyacinth, scientifically known as Eichhornia Crassipes, is an aquatic perennial native to the Amazon basin and has an interconnected global presence. Your understanding of its characteristic features, remarkable growth rate, applications and its role within its ecosystem will be profoundly enhanced as you read through this comprehensive article.
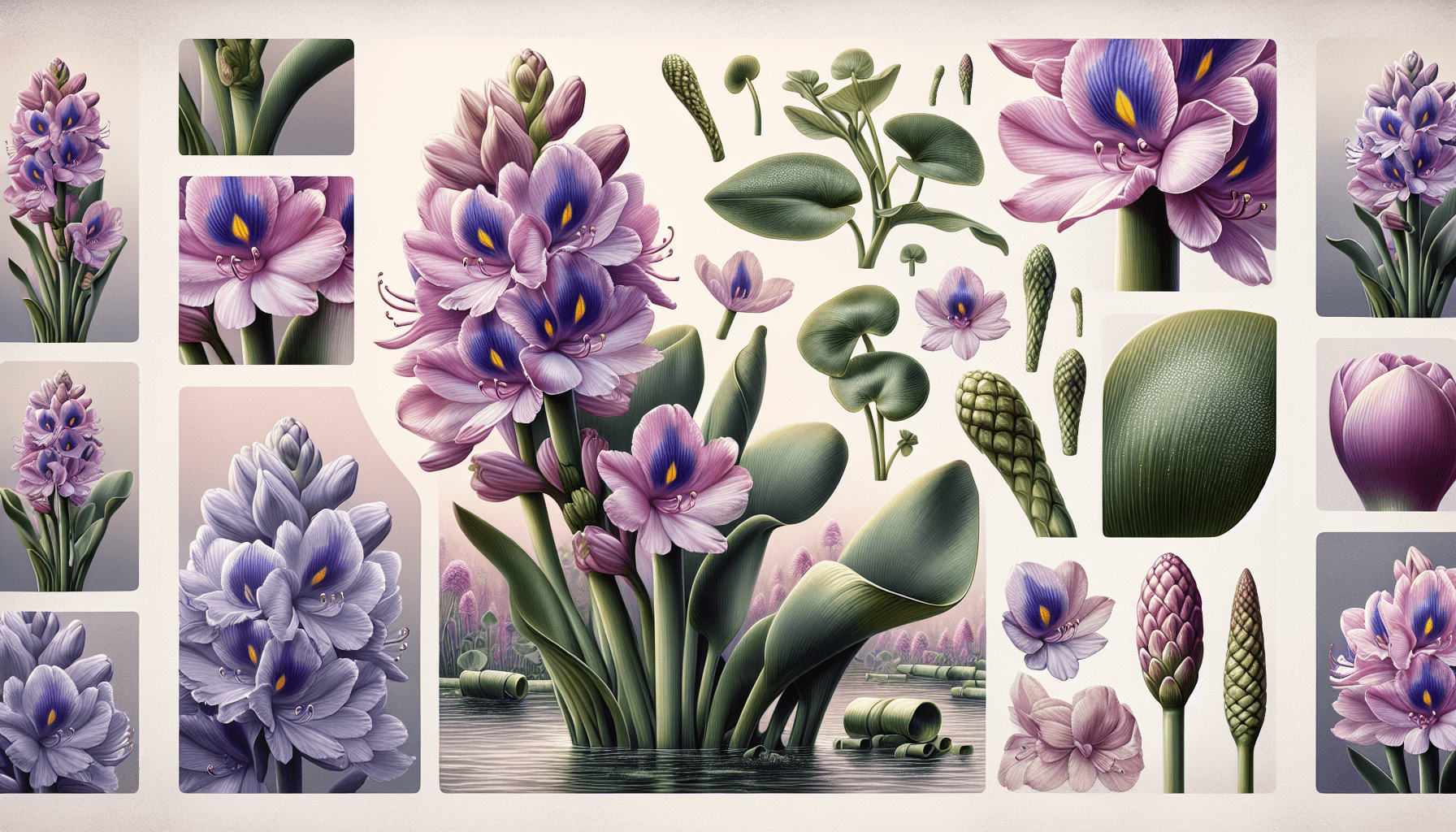
Identification of Water Hyacinth
Water Hyacinth is a floating aquatic plant belonging to the family Pontederiaceae. Recognizing this plant may be a task you are keen on, considering its drastic ecological and economical implications.
Physical Characteristics
As you might expect, the Water Hyacinth possesses distinct physical characteristics identifiable from afar. It stands with dark green tint broad and glossy leaves to catch your eye. A notable feature, its swollen leaf stalks, gives buoyancy to the plant, allowing it to float elegantly on the water surfaces.
Size and Growth Patterns
Water Hyacinth isn’t impressive in size; you might notice mature plants averagely ranging from 1 to 1.5 feet height. However, plant growth in water hyacinthest can be substantial: under optimal conditions, a single plant can cover an area of 600 m2 within a year due to its capability of exponential growth and high reproductive fertility.
Distinct Bloom
Come summer season, and Water Hyacinth brings forth a spectacular lavender bloom. They produce a beautiful, orchid-like flower, with six petals and a yellow spot in the center. Such distinguished blooming patterns of water hyacinth make it easily recognizable.
Origins and Natural Habitat
Identifying the origins and natural habitat of Water Hyacinth can provide new insights into its ecological characteristics and preferences.
History and Introduction
This tropical plant first made its appearance in an 1884 World Fair in New Orleans, imported from its native regions in the Brazilian Amazon Basin. You would later find it introduced globally due to its spectacular blooms and easy-propagation nature.
Native Regions
Since the Water Hyacinth originates from South America, it is inherently well-adapted to tropical and subtropical regions. In fact, Brazil and nearby Amazon basin areas are counted as its native regions.
Preferred Environment
Ever noticed the liking of Water Hyacinths to static or slow-moving water bodies? They show a preference for thriving in still freshwater habitats, including ponds, lakes, and marshes. Warm climate and nutrient-rich water further enhance their growth and distribution.
Propagation and Spread
Understanding how Water Hyacinths multiply can give insights into their invasive nature and how to control it.
Reproduction Process
Water Hyacinth reproduces both sexually, by producing viable seeds, and asexually, by creating offshoots or ‘daughter’ plants. Both these characteristics cause the water hyacinth to proliferate unusually.
Growth Rate
You can deem Water Hyacinth as a fast-growing plant. Its doubling time ranges from 6 to 18 days under optimal conditions, making it one of the world’s fastest-growing plants. This rapid growth rate is partly why water hyacinths can become invasive in certain environments.
Factors Affecting Spread
Various factors affect the spread of Water Hyacinths. Its growth usually soars with high nutrient conditions, particularly in waters with excessive nitrogen and phosphorous. Besides, atmospheric factors like light intensity, temperature, pH of the water, and carbon dioxide concentration can also influence its proliferation.
Water Hyacinth as Invasive Species
Deeming Water Hyacinth as an invasive species seems justified considering its growth rate and adaptability—evident from its vast distribution range across the globe.
Impact on Ecosystems
The primary reason for considering water hyacinth as an environmental hazard is its impact on aquatic ecosystems. The plant’s rapid growth and spread lead to a dense mat covering the water body. Consequently, this hampers sunlight penetration, disrupting underwater photosynthesis, and altering habitat conditions, impacting local flora and fauna.
Strategies for Controlling Spread
Besides physical methods like mechanical removal, chemical methods like using effective herbicides are developed to control water hyacinth’s spread. Biological control through introduction of the plant’s natural predators, such as weevils and moths, is another eco-friendly control strategy.
Global Impact
On the global scale, water hyacinth demonstrates a wide range of impacts – from clogging irrigation channels and hydroelectric plants to impacting fishing and navigation. It presents a massive problem for water utilities and disrupts economic activities dependent on open water.
Ecological Role of Water Hyacinth
Despite being notorious for being an invasive species, water hyacinth plays an essential ecological role.
Role in Aquatic Ecosystems
Water hyacinth serves as a habitat for a range of aquatic organisms, including insects, microbes, and fish, thus ensuring biological diversity. It also contributes to nutrient recycling in the water body it inhibits.
Biodiversity
Dense mats of water hyacinths create rich habitats for different species. The underside of the leaves houses a variety of insects and larvae, assisting in maintaining aquatic biodiversity. Additionally, it becomes food for certain bird species, contributing to their survival.
Potential Environmental Benefits
Interesting as it may sound, water hyacinth also has certain environmental benefits. It serves as a natural water purifier, sucking up heavy metals and toxins from water bodies. Thus, its growth can signify water pollution and trigger necessary interventions.
Water Hyacinth in Commercial Use
You might be surprised knowing about various commercial uses of Water Hyacinth.
Biofuel Potential
Due to its high growth rate, water hyacinth potentially serves as an abundant source of biomass for biofuel production. Its use as a bio energy crop is being researched extensively.
Use in Handicrafts
The fibrous stems of water hyacinth are also used to make ropes, mats, and other craft materials. To some artisans, these plants are a source of livelihood contributing towards sustainable development.
Agricultural Use
Interestingly, water hyacinth is also used as a green manure in agriculture. It’s a rich source of nutrients and organic matter. When integrated with soil, it enhances fertility and eliminates the need for chemical fertilizers.
Water Hyacinth in Human Culture
Even in human culture, the presence of water hyacinth is felt.
Symbolism and Aesthetics
Water hyacinths are often used to enhance the aesthetics of ornamental ponds due to their attractive blooms. In certain cultures, their abundant growth is seen a symbol of fertility and spiritual purity despite the overwhelming negative impacts.
Cultural Events
In parts of Eastern India, the Water hyacinth plant plays a role in the ‘Kati Bihu’ festival where people float it in rivers as an offering.
Medicinal Usage
In traditional medicine, water hyacinth has many uses, most part of the plant are used as remedy for ailments like jaundice, diarrhea, and skin diseases.
Cultivation and Care for Water Hyacinth
Despite its invasive nature, if you desire to cultivate water hyacinth for its blooms or other uses, consider these factors.
Water and Soil Requirements
Water hyacinth doesn’t require any soil and grows directly in fresh water bodies. These water bodies should be rich in nutrients for the plant to thrive.
Temperature and Light Needs
As Water Hyacinth is a tropical plant, it favors warm temperatures. Light exposure is also essential for its growth as it is a photosynthetic organism.
Dealing with Pests
You won’t find many pests feeding on water hyacinths except for a few species of weevils and moths, which you could control using suitable insecticides.
Harvesting and Disposal of Water Hyacinths
Knowing how to responsibly manage Water Hyacinths is crucial.
Gathering Techniques
Mechanical harvesting is a common technique used to remove water hyacinths. This involves manually or machine-assisted collection of plants from the water body.
Composting
Composting water hyacinths is a common practice. As they are organic in nature, these plants decompose and contribute to nutrient-rich compost.
Responsible Disposal Methods
Proper disposal of water hyacinths involves drying them under the sun and later incinerating or composting them. Care is necessary to avoid dispersing the seeds that could lead to re-infestation.
Controversies and Challenges involving Water Hyacinths
The management of Water Hyacinths is entangled in certain debates and difficulties.
Environmental Concerns
The major environmental concern regarding water hyacinth is its adverse impact on aquatic ecosystems. The dense foliage obstructs light and airflow leading to anoxic conditions detrimental to aquatic life.
Regulation and Control Challenges
Regulating the growth and spread of water hyacinth is challenging due to its rapid reproduction and adaptation to varied environments. Ensuring it doesn’t turn invasive while exploiting its ecological and economical value is a major challenge.
Economic Implications
On one hand, where water hyacinth poses costs due to environmental damage and control measures, it also presents prospects in the bio-energy sector, handicraft industry, and agriculture. So, managing this resource wisely can yield significant economical benefits.