In the extensive and diverse world of aquatic plant life, the Ulva-like Aponogeton holds a unique position. This intriguing species, part of the Aponogetonaceae family and characterized by its resemblance to the Ulva genus, is an integral component of aquatic ecosystems. Perusing this article will engender an understanding of the plant’s make up, its role within its environment, and the noteworthy features that make it such a compelling research subject.
Understanding the Genus Aponogeton
Aponogeton is a distinct genus consisting of approximately 50 species of aquatic plants. These species are native to the fresh waters of the Old World, predominantly found in tropical climates. They belong to the family Aponogetonaceae and are characterized by their tuberous rhizomes and an exceptional rate of growth.
General characteristics of Aponogeton
Generally, Aponogeton species are recognized by their erect, floating leaves, often appearing delicate and translucent. They exhibit flowering habit, often producing inflorescences that rise above the water. Moreover, they might grow extremely fast, probably due to their ability for tuberous reproduction, a feature distinctive in aquatic biomes.
Unique features of the genus
One of the unique features of the Aponogeton genus is the remarkable variety of leaf types present within the species. These may range from large, broad leaves in some species to slender, virtually translucent leaves in others. Some species have undulating or crisped margins on their leaves, contributing to a visually arresting display.
Distribution and habitat of Aponogeton species
Aponogeton species are widely distributed in the tropical belt, primarily found in Asia, Australia, and Africa. They particularly thrive in freshwater habitats, including rivers, ponds, lakes, and occasionally in marshes. These plants have a preference for slow-moving or stagnant water and require ample light for growth.
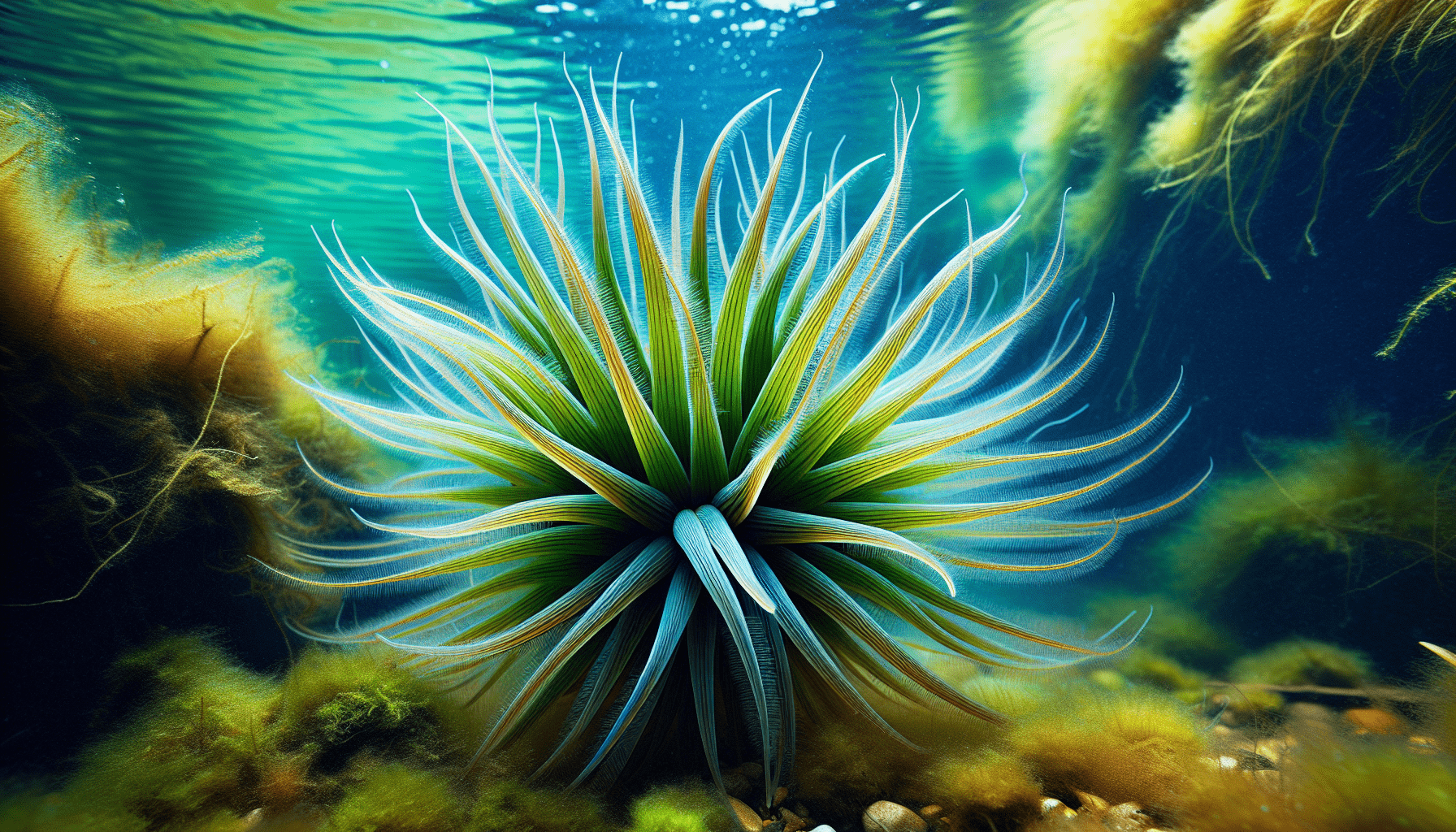
Ulva-like Aponogeton: The Unique Specimen
Among the Aponogeton genus, Ulva-like Aponogeton is one of the distinctive species with several unique features that set it apart.
Distinguishing features of Ulva-like Aponogeton
Ulva-like Aponogeton, as the name suggests, possesses characteristics akin to Ulva, a genus of ubiquitous sea lettuce. Its leaves, in particular, are ultra-thin, flat, broad, and resemble leafy green algae in appearance.
Why is it called ‘Ulva-like’?
The moniker ‘Ulva-like’ comes from the visual similarity between the leaves of this plant and the green seaweed, Ulva, also known as sea lettuce. It is a metaphorical descriptor that paints a vivid image of the plant’s structure and appearance.
Typical appearance and size
Ulva-like Aponogeton grows to a moderate size, with leaf lengths reaching up to 30 centimeters on maturity. The translucent green leaves are remarkably thin and delicate. From a distance, the plant may also exhibit an appealing, fluffy appearance owing to its dense, leafy growth.
Habitat and Distribution of Ulva-like Aponogeton
Understanding the ecological distribution and preferred habitats of Ulva-like Aponogeton give an insight into its survival and growth mechanism.
Where is the Ulva-like Aponogeton found?
Ulva-like Aponogeton is native to certain regions in Asia and Africa. Specifically, these plants can be found in abundance in the freshwater bodies in these regions, including rivers, streams, lakes, and even flooded rice fields.
Preferred habitat type
Much like other species in the Aponogeton family, Ulva-like Aponogeton prefers slowly moving or stationary freshwater bodies with abundant light. It is typically a submerged plant, although it may occasionally emerge partially during the flowering season.
Factors influencing its distribution
The distribution of Ulva-like Aponogeton is primarily driven by water conditions and light availability. It ideally thrives in water bodies with moderate to high light, low current, and considerably soft, silty substrates.

Life Cycle and Growth of Ulva-like Aponogeton
A deeper understanding of the life cycle and growth patterns of Ulva-like Aponogeton can provide insights into optimizing its propagation and conservation.
Understanding the growth stages
Ulva-like Aponogeton undergoes a fascinating growth cycle, starting as dormant tubers which sprout leaves on emergence. With time, it matures into a leafy plant, eventually forming flowers and seeds. Post reproduction, the plant progressively enters a dormant stage, only to revitalize and start the cycle anew.
Seasonal variations in growth
Growth of Ulva-like Aponogeton usually subside during the colder months, as the plant enters dormancy. With the arrival of warmer seasons, the plant revitalizes, exhibiting accelerated leafy growth.
Longevity of the plant
Barring any adverse environmental conditions, Ulva-like Aponogeton can exhibit amazing longevity. As a perennial, its life cycle extends over several years, often continuing to thrive and reproduce year after year.
Environmental Requirements for Ulva-like Aponogeton
For optimum growth, Ulva-like Aponogeton requires specific environmental conditions.
Water temperature and quality
The plant typically prefers moderate to slightly warm temperatures, with a range of 22 to 28 degrees Celsius being ideal. It thrives in soft, neutral to slightly acidic waters.
Light requirements
Ulva-like Aponogeton is a light-loving plant and requires moderate to high light conditions for optimum growth. However, excessive light may cause damage to the delicate leaves.
Preferred type of substrate
This species usually prefers a soft silty substrate, rich in organic matter, which allows easy anchorage and nutrition absorption.
Reproduction of Ulva-like Aponogeton
A closer look at the reproduction mechanisms can provide vital insights into the species’ perpetuity and genetic diversity.
Understanding its reproduction system
Ulva-like Aponogeton follows a fascinating reproductive approach. It is primarily an angiosperm, meaning it produces seeds inside a protective fruit.
Frequency and timing of reproduction
Reproduction often coincides with the warmer months, triggering when the plant is at its peak growth. This frequency may vary based on specific environmental conditions.
Seed dispersal mechanisms
The plant employs water-mediated dispersal as a primary method of distributing its seeds. Post maturation, these seeds escape the parent plant, being carried away by the water currents to establish in a new location.
Threats and Conservation Status of Ulva-like Aponogeton
Conservation status and recognising potential threats are key to ensuring the survival of Ulva-like Aponogeton.
Current conservation status according to IUCN
It’s not uncommon for lower plant groups such as aquatic plants to remain poorly represented in conservation databases such as the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. This appears to be the case with Ulva-like Aponogeton as there seems to be a lack of specific conservation status for this species.
Key threats to Ulva-like Aponogeton
Potential threats to Ulva-like Aponogeton include habitat destruction due to urbanization, water pollution, and invasive species competing for similar resources.
Efforts made to protect the species
While specific conservation actions for Ulva-like Aponogeton are currently scarce, there are broader initiatives aimed at conserving freshwater biomes where such plants often thrive.
Ulva-like Aponogeton in Aquascaping
Given its aesthetic appeal, Ulva-like Aponogeton is a popular choice for aquascaping and aquarium design.
Why is it popular among aquascapers?
Aquascapers particularly favour Ulva-like Aponogeton for its delicate, flowing leaves, vivid green color, and the significant size it can achieve, providing a striking focal point in the aquatic scene.
How it contributes to the overall aesthetics
When correctly cared for, Ulva-like Aponogeton can transform any aquatic setting into a lush underwater forest, adding both depth and visual interest to the aquarium.
Care and maintenance in an aquarium setting
Regular maintenance, including the removal of dead or wilted leaves, along with the provision of adequate light, nutrients, and a suitable substrate, will encourage the best growth and health of the plant.
Benefits of Including Ulva-like Aponogeton in Aquatic Ecosystem
Including Ulva-like Aponogeton in the aquatic ecosystem offers several advantages, beyond its aesthetic value.
Role in providing shelter and food
Ulva-like Aponogeton can provide shelter for smaller aquatic organisms and act as a source of food for some species, thereby contributing to the overall health and diversity of the ecosystem.
Contribution to water quality
Like other aquatic plants, this species helps to improve water quality by absorbing excess nutrients and releasing oxygen in the water.
Enhance biodiversity
Ulva-like Aponogeton addition helps to improve ecological diversity by providing habitats and resources to a range of freshwater species, promoting robust biodiversity within the aquatic community.
Studies and Research on Ulva-like Aponogeton
Scientific understanding of Ulva-like Aponogeton, while not extensive, is gradually progressing. This section explores the current state of knowledge, key findings, and potential areas of future research.
Current state of scientific understanding
While there is a wealth of knowledge on the Aponogeton genus as a whole, specific scientific studies and understanding of Ulva-like Aponogeton remain relatively limited.
Key findings from research studies
Preliminary studies have highlighted the interesting growth mimicking Ulva, and the unique ecological role it plays in supporting freshwater biodiversity.
Potential areas of future research
Future research on Ulva-like Aponogeton could focus on areas such as detailed habitat preferences, propagation mechanisms, specific genetic characteristics, and its potential applications in aquaculture or water treatment. Comprehensive studies on threats and conservation measures for this species remain highly warranted.
In conclusion, the Ulva-like Aponogeton, with its unique characteristics, significant ecological roles, and potential applications, warrant further exploration and continued conservation efforts. Through increased understanding and efforts to protect this remarkable species, we can ensure it remains a thriving part of our world’s aquatic biodiversity.