As you venture through the expansive realm of aquatic plant species, you may encounter the distinct Typha Austro-orientalis. This article is tailored for those who seek to enrich their understanding of this fascinating species. Through the course of this study, you will explore the biological attributes of Typha Austro-orientalis, its ecological role within aquatic environments, and its relevance to human cultures across the globe. Engaging with this carefully researched exploration will undoubtedly enrich your knowledge on an intriguing aspect of aquatic biodiversity.
Overview of Typha Austro-orientalis
The aquatic world is diverse and home to a plethora of plant species. One such fascinating group includes the genus Typha. Specifically, Typha Austro-orientalis, also known as the Asian cattail, is an emblematic cattail species native to East Asia. This perennial herbaceous plant often associates with wetland habitats, offering an environment for wildlife while also serving ecological and economic purposes.
Definition of Typha Austro-orientalis
Typha Austro-orientalis refers to a species of monocotyledonous flowering plants that belongs to the Typha genus within the Typhaceae family. Despite its simplified terminology as an ‘Asian cattail’, it is important to distinguish this species from other members of the Typha genus which also hold the ‘cattail’ common name.
Distribution of Typha Austro-orientalis
The distribution of Typha Austro-orientalis predominantly spans across East Asia. From China to Japan and until the Russian far east, its presence is quite palpable in these regions. With its preference for wetland habitats, the plant is often found growing alongside lakes, marshes, and slow-moving streams.
Aquatic plant classification
Typha Austro-orientalis falls under the category of emergent aquatic plants, those that root under the water surface but have a majority of their vegetative growth visible above water. This aspect contributes to its characteristic appearance and the various ecological roles it fulfills.
Morphology of Typha Austro-orientalis
The physical appearance of Typha Austro-orientalis comprises a harmonized combination of roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Each of these components has its own function, contributing collectively to the plant’s survival and reproduction.
Root system
The root system of Typha Austro-orientalis is composed of extensive rhizomes. These horizontal, underground plant stems not only anchor the plant firmly within the soil substrate but also enable vegetative propagation, facilitating the plant’s spread within the habitat.
Stem description
The stem of the Typha Austro-orientalis is erect and unbranched, providing a strong and sturdy framework for the plant’s growth. It commonly reaches heights of up to 2 meters, emerging out of the water in a visually striking manner.
Leaf structure
The leaves of the Typha Austro-orientalis appear as long, narrow, and flat structures that sheath around the stem at its base. Their vertical growth resembles the bearing of a sword, hence the epithet of sword-shaped leaves often associated with this plant.
Flower and fruit description
The flowers of the Typha Austro-orientalis are dioecious, meaning that male and female reproductive organs are borne on separate inflorescences. These inflorescences provide the definitive ‘cattail’ appearance with the male flowers located higher up the stem, whereas the female flowers sit lower. Post-pollination, these female flower spikes transform into fruiting spikes composed of dry achenes that contain the plant’s seeds.
Growth conditions for Typha Austro-orientalis
Typha Austro-orientalis is a resilient plant species, capable of withstanding various environmental conditions, yet it exhibits a clear preference for certain growth parameters.
Preferred climate
Typha Austro-orientalis is known to thrive best in temperate climates that experience well-defined seasons. Its presence in East Asia, a region known for its temperate climate zones, validates this preference.
Water requirements
Given its status as an emergent aquatic plant, Typha Austro-orientalis demonstrates an affinity for abundant water supplies. It can survive in both freshwater and mildly brackish water environments, primarily suit the habitats of marshes, freshwater, and slow-moving streams.
Light requirements
Typha Austro-orientalis has a high light demand. The plant typically grows best in full sunlight and can struggle in areas of minimal light exposure, such as under heavy tree canopies or in the shadows of larger structures.
Soil or substrate conditions
The soil substrate in which Typha Austro-orientalis grows usually tends to be wet or even waterlogged. Despite this, Typha Austro-orientalis exhibits a broad tolerance for varying soil types, be it clay, loam, or sandy soils. However, it is essential for the soil to be nutrient-rich to support its growth.
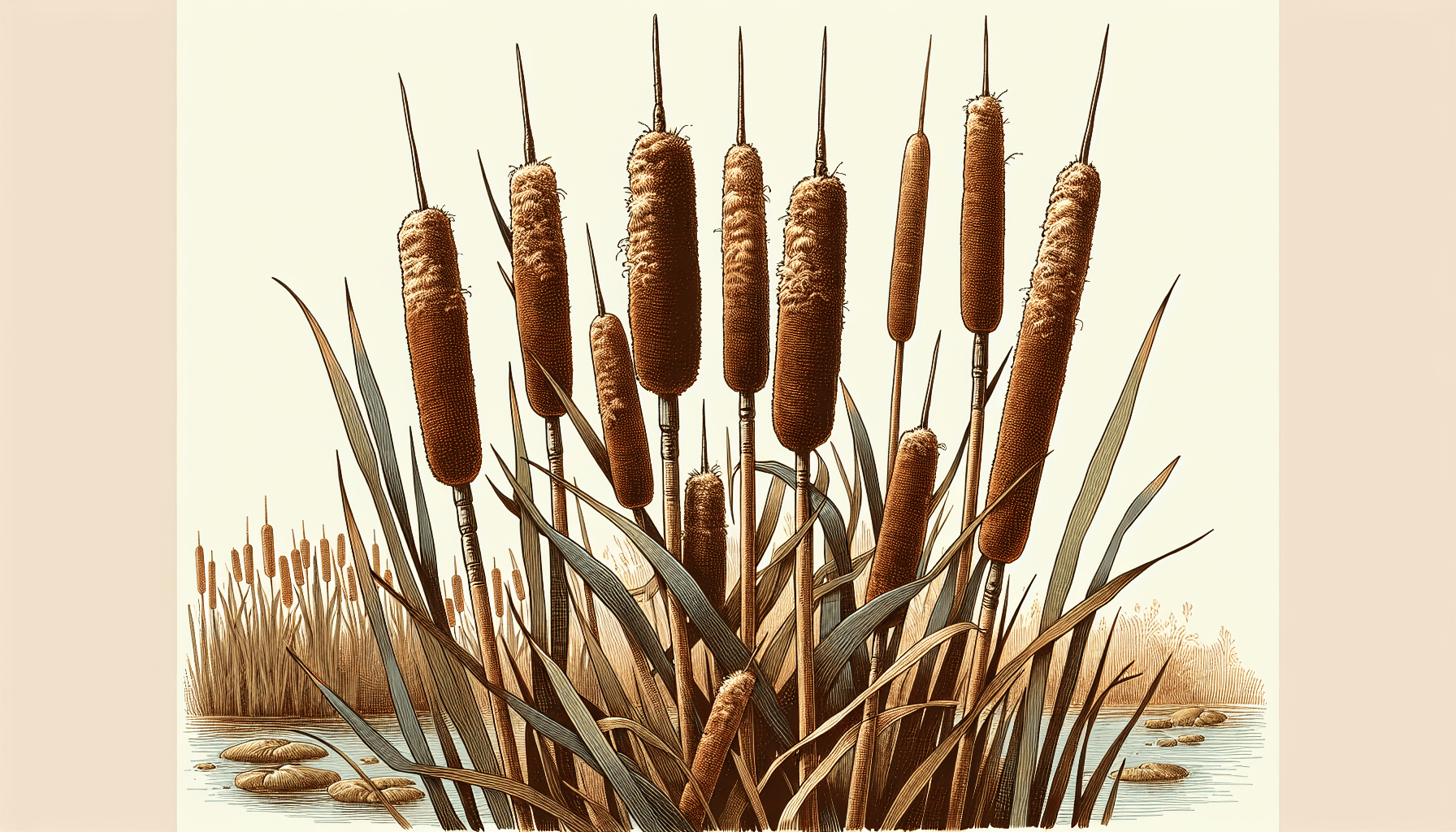

Blooming and growth cycle of Typha Austro-orientalis
The life cycle of Typha Austro-orientalis encompasses several critical stages.
First growth stage
This initial stage involves the emergence of shoots from the underground rhizomes and the growing of leaves and stems. These structures provide the requisite framework for the plant’s growth and prepare for the blooming phase.
Blooming period
The blooming period typically occurs in late spring or early summer and is marked by the emergence of distinct male and female flower spikes. Post-pollination, these female flower spikes transform into fruiting spikes composed of dry achenes that contain the plant’s seeds.
Fruiting and seed production stage
Following pollination, the female inflorescences eventually transform into seed-bearing fruits. These fruiting spikes ultimately disintegrate, releasing seeds into the surrounding environment, thus closing the growth cycle and preparing for the forthcoming one.
Adaptive mechanisms of Typha Austro-orientalis
Typha Austro-orientalis has developed sophisticated adaptive mechanisms over its evolutionary journey, enabling it to survive and reproduce in different environmental conditions.
Response to underwater stress
Typha Austro-orientalis employs aerenchyma, a specialized tissue consisting of air-conducting channels, enabling oxygen transportation to its submerged roots. This adaptation allows it to survive underwater stress and thrive in wet or waterlogged habitats.
Response to changes in light and temperature
Being a high light-demanding plant, Typha Austro-orientalis tends to grow taller or broader leaves as an adaptation to low light conditions. This measure increases its light interception potential, enhancing photosynthetic capability. The plant also adjusts to varied temperature conditions by modifying its growth rate.
Seed dormancy and germination mechanisms
Typha Austro-orientalis seeds are mature by late summer or early autumn and can remain dormant in the soil for several years before germinating. Germination typically occurs when conditions are optimal – generally when exposed to light, oxygen, and a suitable temperature range.
Ecological importance of Typha Austro-orientalis
Typha Austro-orientalis performs diverse ecological roles, evidenced by its interaction with the surrounding environment and various other species.
Habitat for aquatic wildlife
Typha Austro-orientalis provides a crucial habitat and breeding ground for a range of wildlife species. Aquatic invertebrates, birds, and mammals are known to rely on these stands for shelter, nesting sites, or as a food source.
Maintenance of water quality
By absorbing excess nutrients within its aquatic habitat, Typha Austro-orientalis aids in preserving water quality. Its filtration capability can capture sediments and pollutants, thus minimizing the potential impact of eutrophication.
Role in nutrient cycling
The decomposing plant material from Typha Austro-orientalis contributes to the nutrient cycle of the ecosystem. These released nutrients support the growth of phytoplankton and other vegetation, benefitting the entire aquatic community.
Economic uses of Typha Austro-orientalis
Apart from its ecological role, Typha Austro-orientalis also possesses numerous economic uses.
Use in wastewater treatment
Given its ability to absorb excess nutrients and filter sediments, Typha Austro-orientalis is being increasingly utilized in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment.
Culinary uses
Some parts of Typha Austro-orientalis, such as the young shoots and pollen, are edible and have been traditionally used across various cultures as a food source.
Use in horticulture
Owing to its robust growth and striking appearance, Typha Austro-orientalis also finds a place in horticulture, particularly in water gardens.
Potential threats to Typha Austro-orientalis
As resilient as Typha Austro-orientalis may be, it still confronts several threats that may impact its survival.
Impact of pollution
Water pollution, particularly due to industrial discharges or agricultural runoff, may pose a threat to Typha Austro-orientalis. Excess pollutants can interfere with the plant’s growth and reproduction.
Threats from invasive species
Invasive species can competitively exclude Typha Austro-orientalis from its habitat, threatening its survival. The impact is particularly significant if the invasive species have similar ecological niches.
Effects of climate change
Global climate change could potentially alter the distribution and growth of Typha Austro-orientalis, representing a looming threat. Changes in temperature, rainfall patterns, or severity of extreme weather events could directly or indirectly pose challenges for the plant’s survival.
Conservation effort and regulations for Typha Austro-orientalis
To safeguard Typha Austro-orientalis against these threats, conservation efforts and protective regulations have been employed, some of which include:
Conservation strategies
Popular strategies often encompass habitat protection, control of invasive species, and environmental pollution mitigation. These measures aim to maintain healthy populations of Typha Austro-orientalis within their natural environment.
Legal protection and regulations
In certain regions, legal steps have been taken to protect critical habitats of Typha Austro-orientalis from destruction or disturbance. These regulations usually include restrictions on development activities in identified areas, ensuring the conservation of its habitats.
Community-based conservation initiatives
Local communities often participate in conservation initiatives, like clean-up drives, awareness campaigns, and citizen science projects, thereby contributing to the conservation of Typha Austro-orientalis indirectly.
Research and studies on Typha Austro-orientalis
Interested in tapping into its ecological potential and economic values, researchers have been studying Typha Austro-orientalis extensively.
Recent scientific studies
Recent studies focus largely on the species’ potential for wastewater treatment and bioenergy production. Its ability to sequester carbon and maintain water quality has drawn interest from ecologists and environmental scientists around the globe.
Future research directions
Many research directions lay open for Typha Austro-orientalis—its potential in remediation of contaminated soils, as a biofuel source, or in pharmaceutical applications, are all promising fields worth further exploration.
Potential for pharmaceutical and medicinal uses
Given that Typha Austro-orientalis possesses antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties, pharmaceutical and medicinal applications represent a promising research domain. Traditional systems of medicine have often utilized various parts of the plant for treating different ailments.
Therefore, Typha Austro-orientalis is not merely an Asian cattail but an essential part of our natural heritage that merits understanding and protection. Its role in the ecosystem, coupled with the economic and medicinal potential it promises, underlines the importance of the continued conservation of this unique species.