You are about to embark on a journey of discovery about a rather unique aquatic phenomenon – the Twinflower Nymphoides. This intriguing aquatic plant, hailing from the Nymphoides genus, is far removed from mundane pondweeds. Within this article, you’ll explore the Twinflower Nymphoides’ captivating biology, its diverse geographical distribution, and its fascinating ecological role. Prepare to encounter an exceptional creation of nature in detail that you might not have anticipated.
Definition of Twinflower Nymphoides
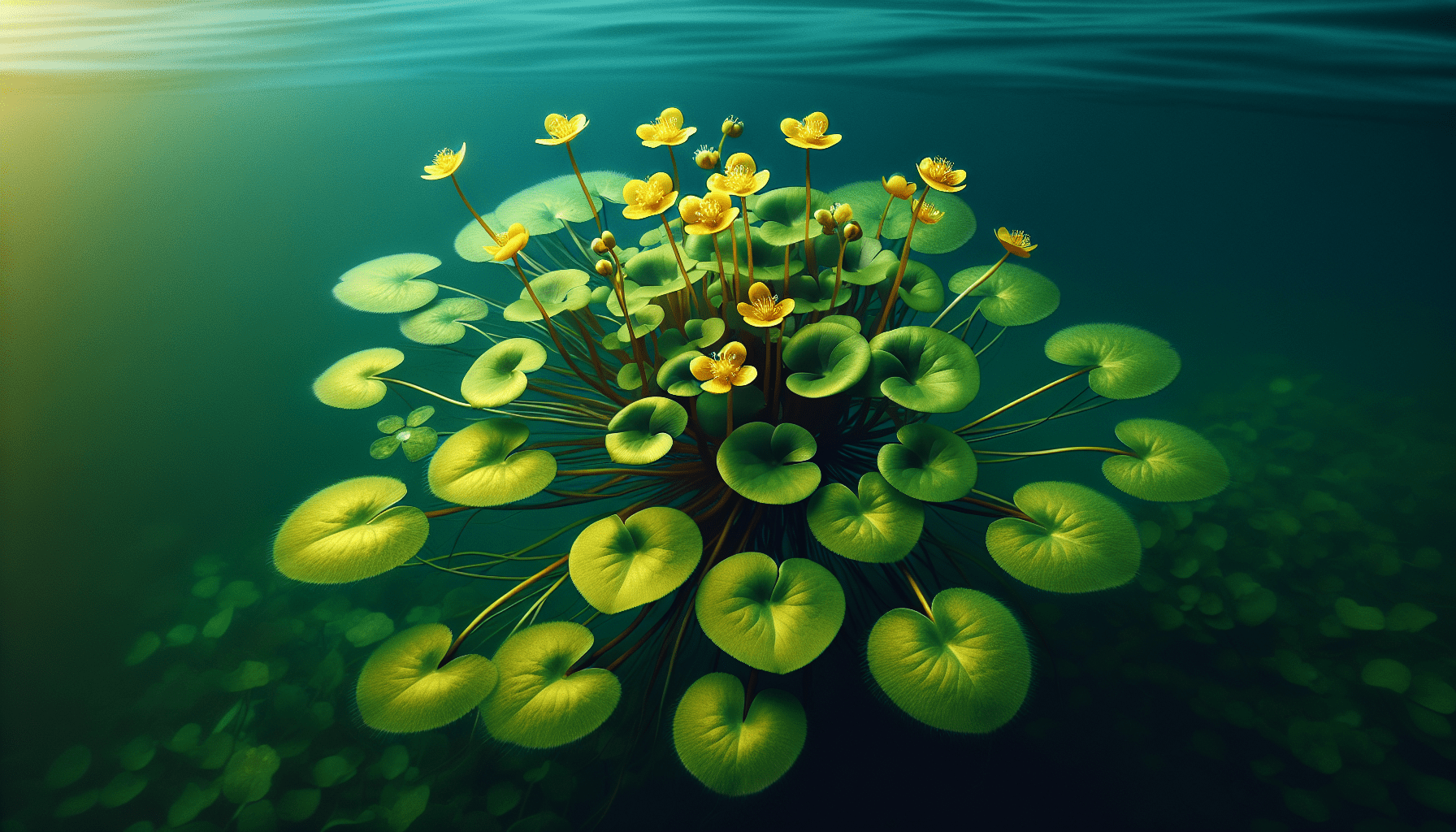
The Twinflower Nymphoides is a maritime aquatic plant that holds a place of significance in the genus Nymphoides. This genus belongs to the rich family of Gentianaceae, bearing distinct commonalities with its siblings, yet standing out due to certain unique traits.
Meaning of the Nymphoides species
The Nymphoides species refers to a collection of plants commonly known as floatingheart or water snowflake. The genus lives predominantly in freshwater environments and presents a wide diversity within its ranks, consisting of about 50 different species. These plants are largely recognized for their crested, orbiculate foliage and the beautiful, delicate flowers they produce.
Specific traits of the Twinflower species
The Twinflower Nymphoides, also known as Nymphoides crenata, is a special subsect of this family, set apart by its peculiar qualities. It is particularly known for the two small white flowers that arise on each peduncle, lending to its name ‘Twinflower.’ While it shares the characteristic orbicular leaves with its kin, the Twinflower presents these leaves in a finely crenate pattern, adding to its unique charm and differentiating it from other members.
Physical Characteristics
The distinctive physical traits of the Twinflower Nymphoides make this species easy to identify.
Leaf structure and size
The leaves of this plant are rounded, measuring about 4-6 cm in diameter. The leaf margin is finely crenate, giving the leaf a slightly serrated appearance. The leaves are known to float on the water surface, providing a lily pad-like aesthetic.
Flower features
The Twinflower Nymphoides has small white bilaterally symmetrical flowers with a yellow center. As the name suggests, two flowers emerge from each peduncle, adding to its uniqueness.
Height and spread of the plant
Depending on the growing conditions, Twinflower Nymphoides can reach a height of 15-20 cm, measured from the bottom of the water body to the apex of the flowering stem. It spreads horizontally, presenting a sizable vegetative mass across the water surface.
Origins and Natural Habitat
The Twinflower Nymphoides doesn’t just offer a visual treat; its roots and origin story provide interesting insights as well.
Geographic origin of Twinflower Nymphoides
The Twinflower Nymphoides is said to have originated from the lands of Australia and New Zealand.
Typical environments where it is found
Typically, you will find this lovely species gracing freshwater bodies like lakes, ponds, streams, and rivers. In its native lands, it is frequently seen flowering amidst other aquatic and semi-aquatic vegetation.

Life Cycle of Twinflower Nymphoides
Understanding the life cycle of Twinflower Nymphoides can help in its proper cultivation and maintenance.
Stages in growth cycle
The Twinflower Nymphoides initiates its growth cycle through seed germination, sprouting from a small mound of peaty soil. Once established, the plant spreads laterally through stolons, producing additional leafy rosettes on the water surface. It flowers in the warmer months, giving rise to the characteristic pair of white flowers. It reproduces both vegetatively and through self-fertilization to produce seeds.
Lifespan of the plant
Life expectancy can significantly vary depending on the environmental conditions and care provided. In optimum conditions, these plants are known to thrive and spread profusely across the water body.
Common Uses for Twinflower Nymphoides
The Twinflower Nymphoides, owing to its charm and minimal maintenance, has found varied applications.
Role in aquariums, ponds, and water gardens
Using this plant in aquariums, ponds, and water gardens can add a touch of nature’s brilliance. With its floating leaves and exquisite white flowers, it offers a beautiful aesthetic appeal. Additionally, it serves as a hideout and spawning ground for fish, enhancing the underwater fauna.
Use in decor and design
The Twinflower Nymphoides is also a popular choice in decor and design, especially for water-centric themes. With their pale green floating leaves and delicate white flowers, they can lend an air of tranquility and elegance to any setting.
Cultivation Process
While the Twinflower Nymphoides is relatively low-maintenance, there are certain factors to consider for its successful cultivation.
Propagation methods
The plant propagates mainly through seeds and vegetative fragments. Seed-based propagation can be a longer process as compared to cultivation through vegetative fragments.
Preferred soil and water conditions
For proper growth, Twinflower Nymphoides prefers a relatively acidic soil rich in organic matter. It thrives in stagnant or low-flow fresh water bodies and is tolerant of a wide range of pH levels and salinity.
Light and temperature requirements
This plant prefers full sunlight but can also tolerate partial shade. It has a broad temperature tolerance, though the ideal range lies between 15°C and 28°C.
Common Diseases and Pests
Despite its resilience, Twinflower Nymphoides is not immune to plant diseases and pests.
Types of diseases that affect Twinflower Nymphoides
The Twinflower Nymphoides, like many aquatic plants, is susceptible to a range of fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases, which can be manifested as leaf spots, rot, and blight.
Insects and other pests that commonly attack the plant
Insect pests include aphids and whiteflies, which feed on the plant sap, weakening the plant and potentially transmitting diseases.
How to Care for Twinflower Nymphoides
The care for Twinflower Nymphoides is relatively simple, given its low-maintenance nature.
Optimal feeding and watering schedule
This plant grows best in well-hydrated soils rich in nutrients. Given its aquatic nature, overwatering is not a concern. Feeding with a lightly balanced, slow-release fertilizer could contribute to its buoyant growth.
Pruning and maintenance tips
Regular pruning can help maintain an attractive shape and prevent overgrowth. Removal of diseased or infested sections can preserve the overall health of the plant.
Environmental Impact
Twinflower Nymphoides isn’t just visually pleasing; it plays a significant role in the ecosystem.
Role in ecosystem
This plant provides food and habitat for several species of insects and freshwater mollusks. Its floating leaves offer shelter to small fish and invertebrates, promoting a dense, diverse underwater habitat.
Impact on biodiversity
By offering food and habitat, the Twinflower Nymphoides helps maintain biodiversity in fresh water ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions about Twinflower Nymphoides
Among the several queries about Twinflower Nymphoides, three are often asked.
How large do Twinflower Nymphoides grow?
Twinflower Nymphoides can reach a height of 15-20 cm from the bottom of a water body. Horizontally, it tends to spread across the water surface, providing a sizable display of greenery.
Can it be grown in home aquariums?
Yes, it is a popular choice for home aquariums and planted tanks due to its visual appeal and low maintenance.
What animals does it attract or repel?
Twinflower Nymphoides is known to attract a variety of insects and provides shelter for small fish and freshwater invertebrates. There aren’t any specific reports of it repelling any particular species.