In the realm of aquatic botany, a little-known gem of considerable importance exists, the Threadleaf Arrowhead. Slipped away in water bodies worldwide, yet often unnoticed, this article seeks to shed light on its peculiarities and characteristics. As you read on, you’ll find yourself engrossed in the wondrous world of this little known plant species, gaining enlightened knowledge of its distribution, morphology, ecological impact, cultivation methods, and potential uses. Indeed, each sentence enriches your understanding of this hidden treasure tucked away in the watery crevices of our planet, the Threadleaf Arrowhead.
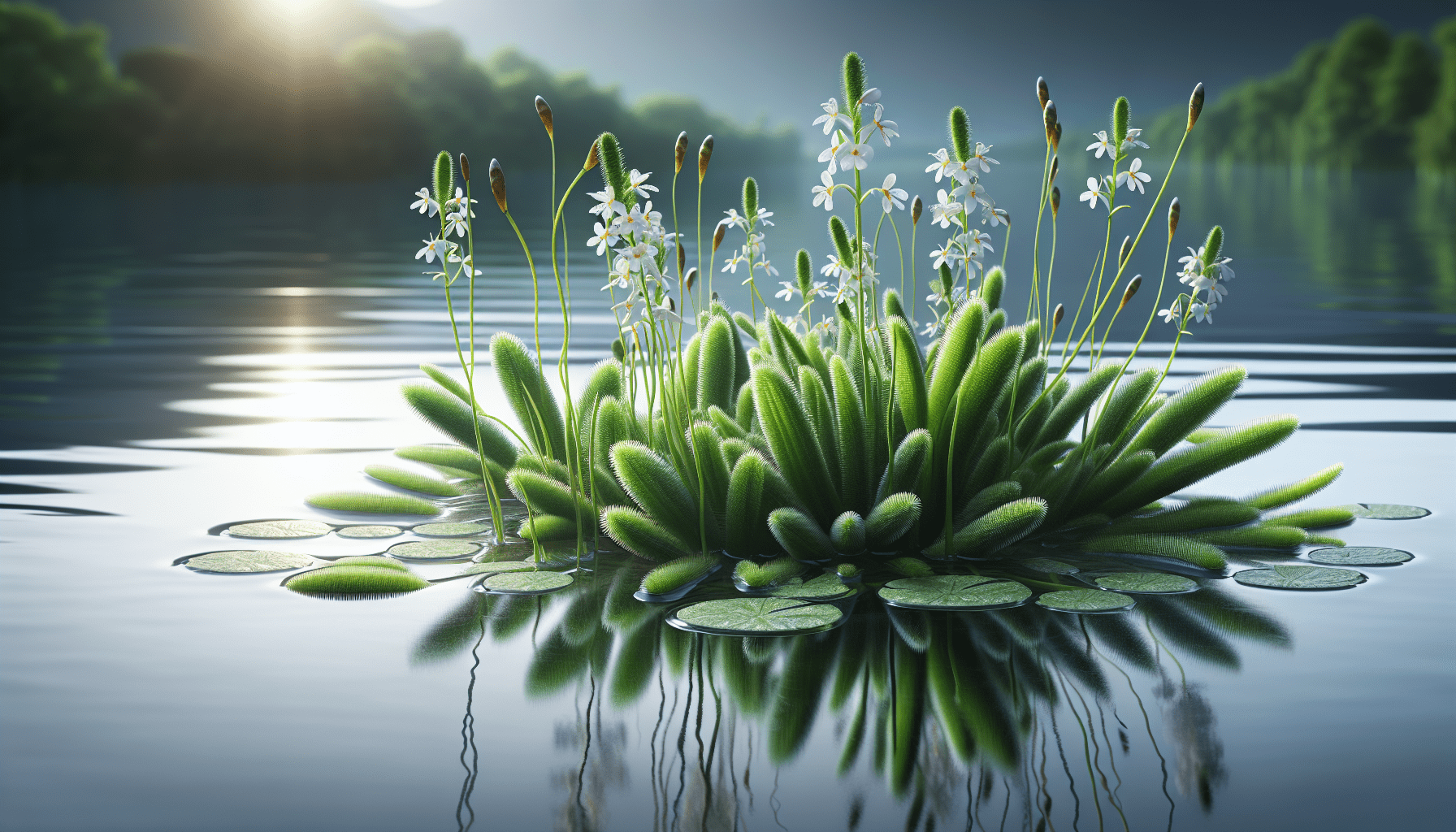

Basic Characteristics of the Threadleaf Arrowhead
Threadleaf Arrowhead, scientifically known as Sagittaria lancifolia, belongs to the Alismataceae family. It is an aquatic plant native to the eastern regions of North America and is particularly prominent in wetlands or other similar water bodies, including marshes, swamps, and ponds.
Scientific Classification
As a member of the Sagittaria genus, the threadleaf arrowhead is in the plant Kingdom, within the Tracheophyta division, and belongs to the order called Alismatales. Beyond the scientific classification of Sagittaria lancifolia, the common names that you may encounter for this plant include lance-leaved arrowhead or duck potato.
Physical Description
Physically, threadleaf arrowhead plants are characterized by their long, slender leaves appearing as arrowhead-shaped, hence their name. The leaves often reach lengths of between 15 and 30 cm and are typically a bright, lush green. Threadleaf arrowhead plants also produce flowers, typically a brilliant shade of white, with their blooming period being the summer months.
Root Structure
Threadleaf arrowhead is characterized by its robust root system, which allows the plant to anchor firmly in the submerged soil of aquatic habitats.
Presence of Rhizomes
A distinguishing characteristic of this plant is the development of starchy, edible tubers or “rhizomes” at the ends of its roots, akin to potatoes—hence, one of its common names, “duck potato.”
Aquatic Nature of the Threadleaf Arrowhead
Threadleaf arrowhead is prevalent in aquatic environments, with characteristics distinctly adapted for survival in water.
Adaptation to Water Environments
This plant is endowed with adaptations that help it survive and even flourish in aquatic environments. These include a strong root system, lanceolate leaves to break water surface tension, and rhizomes that store food for both plant and aquatic creatures.
Water Quality Preferences
Threadleaf arrowhead is highly tolerant of different water qualities and can thrive in varied water pH levels. However, it does prefer somewhat neutral to slightly acidic water.
Temperature Tolerance
Threadleaf arrowhead displays a broad temperature tolerance, being able to withstand colder climates while thriving in relatively warm regions.
General Growth Pattern
Threadleaf arrowhead’s growth pattern is largely dictated by the temperature and light conditions of its environment. It typically displays a seasonal growth pattern, flourishing mostly in the warm summer months.
Propagation and Reproduction of the Threadleaf Arrowhead
The propagation and reproduction of the threadleaf arrowhead can be both sexual and asexual.
Sexual Reproduction Mechanisms
Sexual reproduction typically takes place through pollination of the plant’s flowers, which subsequently develop into seed pods.
Asexual Reproduction Mechanisms
Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, occurs through the plant’s rhizomes. These nut-like tubers can detach from the parent plant and create new plants when conditions are favorable.
Season of Reproduction
The reproduction season of the threadleaf arrowhead typically coincides with its flowering period, which is typically during the summer months.
Germination Period
Following successful pollination, the germination period for threadleaf arrowhead seeds typically spans a few weeks to a month, depending on the conditions of its environment.
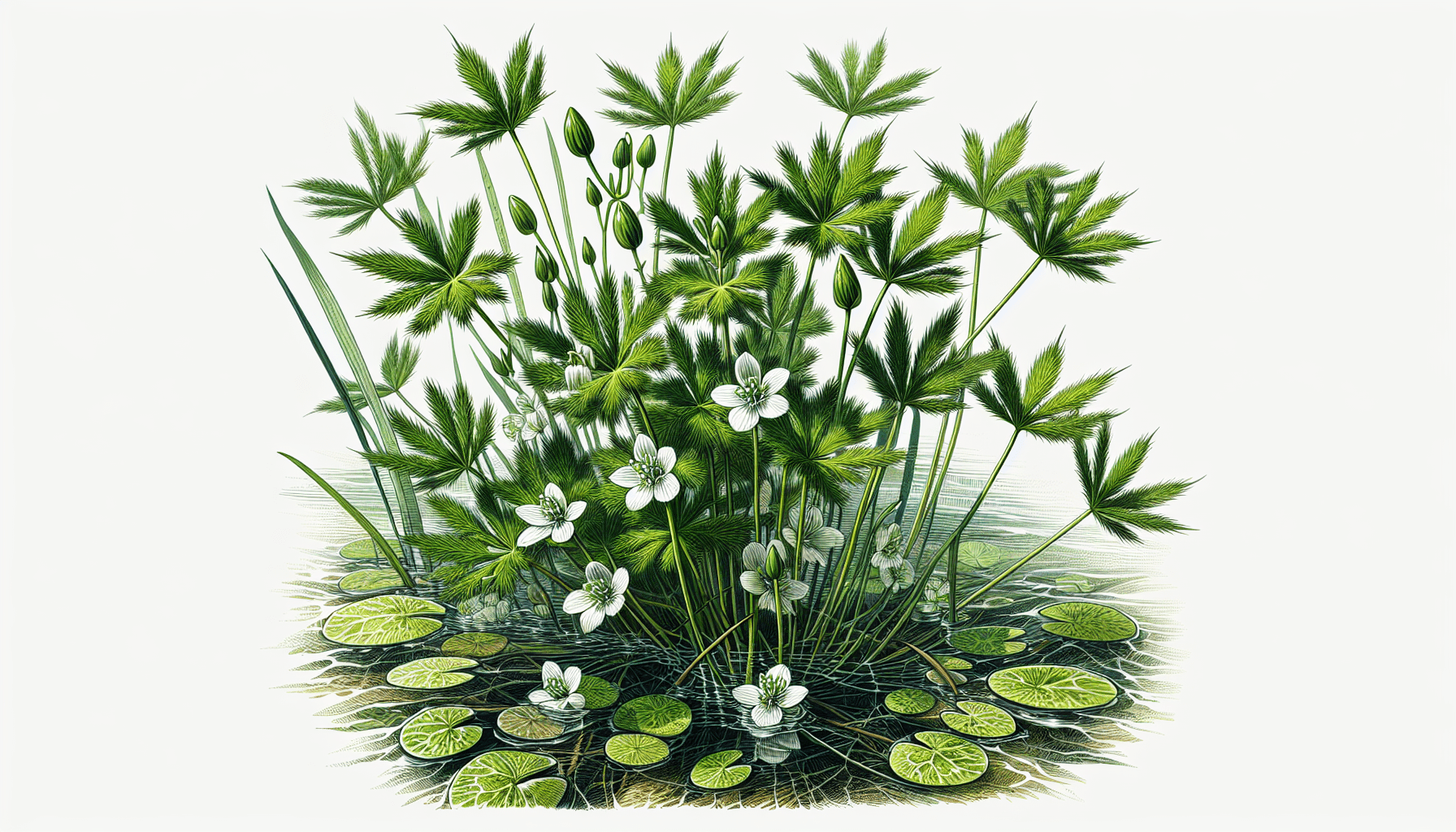
Ecological Importance of the Threadleaf Arrowhead
Threadleaf arrowhead plays significant roles in the ecosystems in which it resides.
Habitat Creation for Aquatic Species
These plants provide shelter and habitat for a wide variety of aquatic creatures, from small invertebrates to larger animals like ducks and other waterfowl.
Improvement of Water Quality
By absorbing nutrients and contaminants from water, threadleaf arrowhead plants can help improve water quality.
Erosion Control Abilities
Their extensive root systems help reduce erosion by stabilizing soil and preventing it from washing away in water currents.
Cultivation and Management of Threadleaf Arrowhead
Cultivation of the threadleaf arrowhead requires attention to several specific conditions.
Preferred Soil Conditions
Threadleaf arrowhead prefers rich, loamy soil that is regularly damp or flooded.
Watering Requirements
Given its aquatic nature, arrowhead requires consistent water supply. However, the plant is resilient and can withstand temporary periods of drought.
Sunlight Requirements
Threadleaf arrowhead can thrive in full sunlight or partially shaded environments.
Pest and Disease Management
Pests and diseases are generally not significant concerns for threadleaf arrowhead. However, some specific insect species may become a problem if left unchecked.
Harvesting and Usage of Threadleaf Arrowhead
Once established, threadleaf arrowhead yields both consumable and aesthetic values.
When Are They Harvested
Harvesting typically occurs in the late summer and early fall, when the tubers or “rhizomes” have adequately developed.
Common Uses
Threadleaf arrowhead tubers, often referred to as “duck potatoes”, are gathered for human consumption and are used similarly to regular potatoes. The plants also add decorative value to ponds and other water features.
Medicinal Uses
While research is limited, there is some historical evidence that threadleaf arrowhead have been used medicinally by indigenous communities.
Culinary Uses
The starchy tubers of threadleaf arrowhead have been utilized in similar ways as potatoes in various traditional and modern culinary applications.
Common Diseases and Natural Pests of Threadleaf Arrowhead
Threadleaf arrowhead is generally a robust plant, but there are certain challenges to look out for.
Recognition of Pest Infestations
Certain insects, especially those attracted to aquatic environments, can create problems for Threadleaf arrowhead plants.
Common Disease Identification
Diseases are uncommon but can include root rot when conditions are excessively damp or stagnant. The presence of yellowing leaves may signal the onset of disease.
Methods to Combat Diseases and Pests
Maintaining healthy growing conditions and vigilance for early disease and pest signs can assist in mitigating damage.
Impact of Threadleaf Arrowhead on Biodiversity
The threadleaf arrowhead has notable impacts on biodiversity within its habitats.
Role in Aquatic Food Chains
As a source of food, shade, and breeding grounds, Threadleaf arrowhead forms an integral part of the food chain in its environment.
Influence on Reliant Species Diversity
By providing diverse resources, Threadleaf arrowhead plays a key role in supporting and increasing the species diversity in its environment.
Impact on Nearby Environments
Threadleaf arrowhead’s role in filtering water and holding soil together can have beneficial effects on surrounding ecosystems as well.
Threats and Conservation Status of Threadleaf Arrowhead
While not critically endangered, the threadleaf arrowhead does face several threats.
Current Conservation Status
Currently, the conservation status of threadleaf arrowhead is not of significant concern. However, regional variances can occur due to local environmental conditions and disruptions.
Human-Induced Threats
Pollution, development encroachment, and disruptive recreational activities can threaten threadleaf arrowhead populations.
Environmental Threats
Unusually harsh climates, high levels of water contamination, or steep changes in water levels can also pose threats.
Efforts to Conserve Threadleaf Arrowhead
Maintaining and creating more wetland habitats and enforcing regulations to preserve existing populations are primary conservation efforts.
Interesting Facts about Threadleaf Arrowhead
Threadleaf arrowhead has a fascinating natural history and several unique features.
Historical Use and Cultural Significance
Historically, threadleaf arrowhead was a significant food crop for native peoples of North America, who harvested its rhizomes for consumption.
Unusual Traits or Adaptations
One of the unique adaptations of the threadleaf arrowhead is its rhizomes, which are starchy tubers similar to potatoes.
Famous Locations to Find Threadleaf Arrowhead
While threadleaf arrowhead can be found throughout eastern North America, it is particularly abundant in places like Florida’s wetlands and the wetland habitats of the Midwest.
For practitioners of ecology, botany, or simply nature enthusiasts, the diverse characteristics and ecological significance of the threadleaf arrowhead capture a fascinating aspect of aquatic life. Beyond its inherent beauty, this sturdy plant serves fundamental roles in maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems, making it a valuable component of our natural world.