Commencing the exploration into the realm of aquatic vegetation, this article specifically focuses on the intriguing plant known as the Shining Flatsedge. As your guide, this piece will equip you with details encapsulating the botanical characteristics, habitat and ecological importance of this species. Illuminating the path of knowledge, you are invited to join this exploration of the Shining Flatsedge’s uniqueness in the diverse world of aquatic flora.
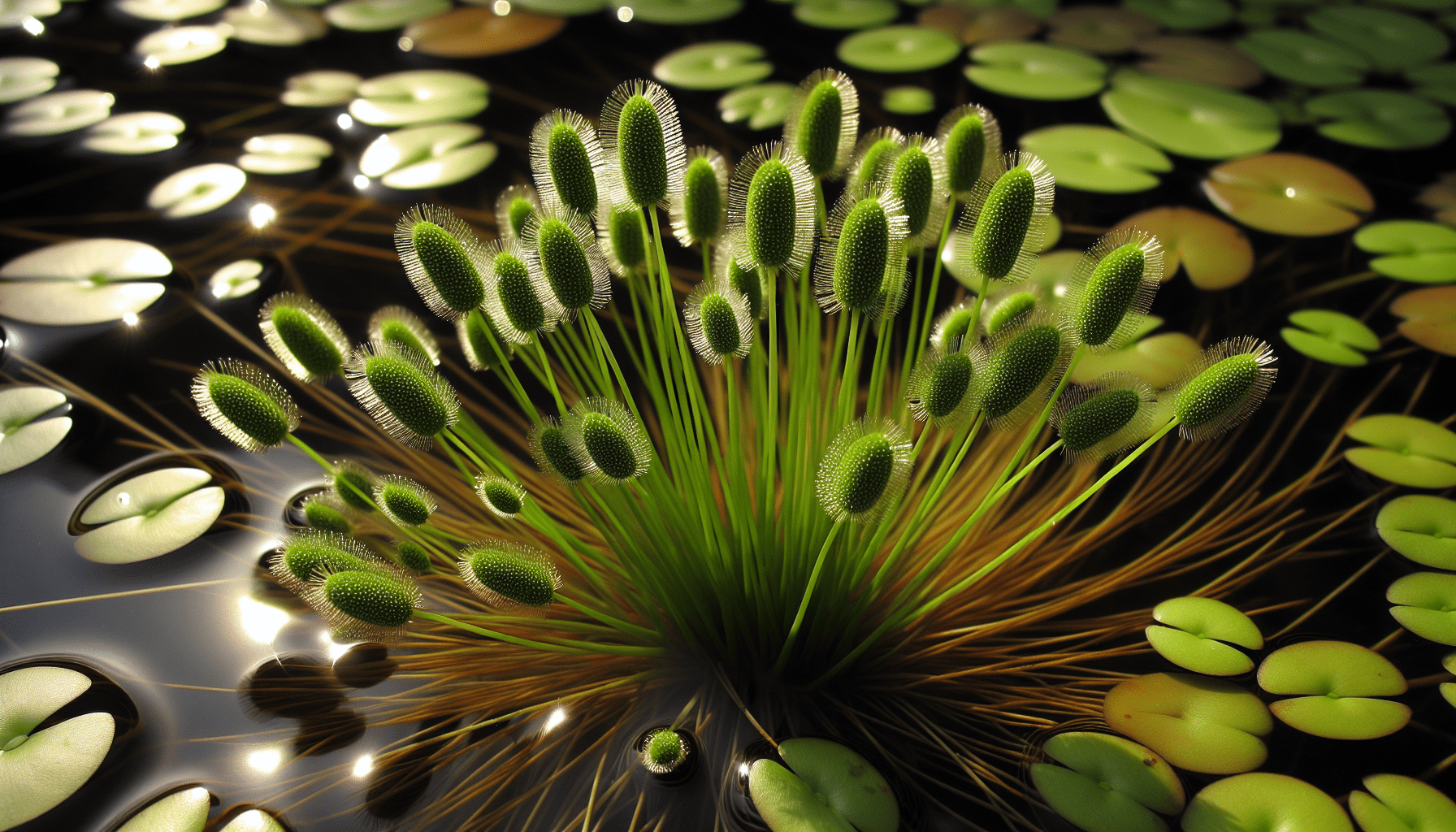

Brief Overview of Shining Flatsedge
Shining flatsedge, scientifically designated as Cyperus eragrostis, belongs to the family Cyperaceae, also known as the sedge family. The sedge family is predominantly known for their grass-like plants that inhabit a vast array of environments across the globe. Shining flatsedge is one such diverse plant that has notably adapted itself to thrive largely in semi-aquatic environments.
Description and Identification
Shining flatsedge bears a keen resemblance to grass, thanks to its long, slender, and bright green leaves. The stem is triangular, erect, and stiff, while the flowers form a dense cluster at the top of the stems. It can grow up to a height of around 80 centimeters, with the leaves spanning up to 10 millimeters in width.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Shining flatsedge is primarily an aquatic or semi-aquatic plant that predominantly thrives along the edges of water bodies like ponds, lakes, and streams. It also adapts well to wetlands and marshy areas. Geographically, Shining flatsedge has a wide distribution and can be found around the globe in North and South America, Africa, Asia, Australia, and parts of Europe.
Common Names
Shining flatsedge is also commonly referred to as umbrella sedge, tall flatsedge, or nutgrass. These names are largely attributed to the plant’s appearance and growth characteristics.
Taxonomy of Shining Flatsedge
The taxonomical classification of Shining flatsedge allows us to explore its botanical characteristics in great detail.
Botanical Name and Family
The botanical name of Shining flatsedge is Cyperus eragrostis, and it belongs to the Cyperaceae family. This family is known for the diversity of its members, many of which are strictly aquatic or marsh plants.
Similar Species
Shining flatsedge has multiple relatives within the Cyperaceae family, known for their similar growth forms and aquatic or semi-aquatic habitats. These include species like the yellow nut sedge (Cyperus esculentus) and the pale galingale (Cyperus eragrostis).
Genus and Species Description
The genus Cyperus is varied and widespread, with over 500 species worldwide. The species eragrostis is uniquely characterized by its preference for wetter environments and its shining, bright green leaves.
Morphology of Shining Flatsedge
The physical structure and characteristics of Shining flatsedge are distinct and complex, contributing to its adaptability and survival.
Roots
Shining flatsedge possesses a rhizomatous root system, allowing it to effectively absorb moisture from the water-logged soils it prefers. The rhizomes, or horizontal stems, both anchor the plant in place and also allow for vegetative propagation.
Stem and Leaves
The stem of shining flatsedge is solid, erect, and triangular, offering it stability against water currents. The leaves are linear, arranged in an alternating fashion along the stem, and distinctly bright green in color.
Flowers and Fruits
The flowers of shining flatsedge are grouped into clusters, appearing at the end of the stems. The fruits take the form of small nuts.
Reproductive Strategies
Shining flatsedge primarily reproduces through its rhizomatous root system, but it can also reproduce sexually via its seeds.
Adaptation to Aquatic Environment
Shining flatsedge displays very specific adaptations that help it to survive in water-logged environments.
Surviving in Waterlogged Environment
Its rhizomatous roots not only provide stability on the unstable soils but also help it to absorb oxygen despite water logging. The color and texture of the leaves suggest the adaption to the lower light conditions found under the water.
Adaptation to Changing Water Levels
The height of shining flatsedge helps it to survive fluctuations in water levels. Its stems have air spaces known as aerenchyma that provide buoyancy and allow it to stay afloat during periods of inundation.
Ecological Role of Shining Flatsedge
Shining flatsedge plays a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance of its habitat.
Role in Aquatic Food Chain
It provides shelter and food for myriad small aquatic creatures and insects, which in turn serve as sustenance for larger animals, thus assisting in structuring the aquatic food chain.
Contribution to Habitat Formation
Its clustering growth pattern helps to stabilize the banks of water bodies, thus preventing soil erosion and maintaining the overall terrain of the wetland habitat.
Impact on Water Quality
Shining flatsedge filters pollutants from the water, improving water quality and, thereby, the overall health of the aquatic ecosystem.
Shining Flatsedge and Biodiversity
Shining flatsedge is instrumental in enhancing biodiversity in its habitat.
Support for Aquatic Fauna
The plants provide refuge and a breeding ground for a variety of aquatic fauna including small fishes and amphibians.
Role in Supporting Insect Biodiversity
Shining flatsedge produces a substantial pollen source attracting various insect pollinators, thereby supporting insect biodiversity.
Cultivation of Shining Flatsedge
Cultivation of Shining flatsedge is easy due to its robust and adaptable nature.
Soil and Water Requirements
Although it prefers water-logged soil, it can also survive on moist soil types. Therefore, it can be used for landscaping in areas with poor drainage.
Light and Temperature Requirements
Shining flatsedge tends to do well in full sun exposure. However, it can also tolerate part shade. As for temperature, it has a broad range, able to survive in both warm and cool climates.
Propagation Methods
Propagation of Shining flatsedge is primarily carried out by dividing its rhizomes and replanting them.
Benefits and Uses of Shining Flatsedge
Shining flatsedge holds a variety of applications, spanning from traditional medicine to landscaping.
Uses in Traditional Medicine
Traditionally, parts of the plant have been used to treat ailments like diarrhea, dysentery, and hemorrhoids.
Culinary Uses
In some cultures, parts of the plant, particularly the tubers, are consumed as nourishing food.
Importance in Landscaping and Gardening
Due to its ability to thrive in water-logged soil and its pleasing appearance, Shining flatsedge is often used in landscape design, particularly in water gardens and pond margins.
Conservation Status of Shining Flatsedge
The conservation status of Shining flatsedge is not currently of major concern.
Threats and Conservation Measures
While there are no immediate threats to the species, habitat destruction and pollution can have negative impacts. Conservation measures include the protection of wetlands and the establishment of conservation areas.
Invasive Status and Impact on Native Flora
In certain areas, the Shining flatsedge can become invasive and displace native flora. So, it is essential to manage and control its growth.
Research and Studies on Shining Flatsedge
Scientific research on Shining flatsedge is paving the way for new discoveries about its ecological impact and potential uses.
Key Scientific Studies
Various studies have been undertaken on Shining flatsedge that further our understanding of its role in biodiversity, as well as its medical and culinary potential.
Emerging Areas of Research
New areas of research are being explored regarding its role in water filtration and pollution control, as well as its potential use as a biofuel.
Impact on Environmental Science
By observing the adaptive strategies and ecological impacts of Shining flatsedge, scientists are developing a deeper understanding of aquatic plant environments. This has significant implications for both environmental conservation and the broader field of environmental science.