In this scholarly exploration, you will unearth the nuanced attributes and ecology of the aquatic plant commonly termed as Sanford’s Arrowhead. An understanding of this obscure, yet fascinating flora is indispensable for botanical enthusiasts seeking to broaden their knowledge within the realm of aquatic biology. Within this context, you are acquainted with the intricate life cycle, significant habitat nuances, and unique biological necessities that govern the existence of this aquatic marvel. The information finds grounding in meticulous research and evidence-based science, offering you a rich, comprehensive interpretation of the Sanford’s Arrowhead in all its amphibious glory.
Overview of Sanford’s Arrowhead
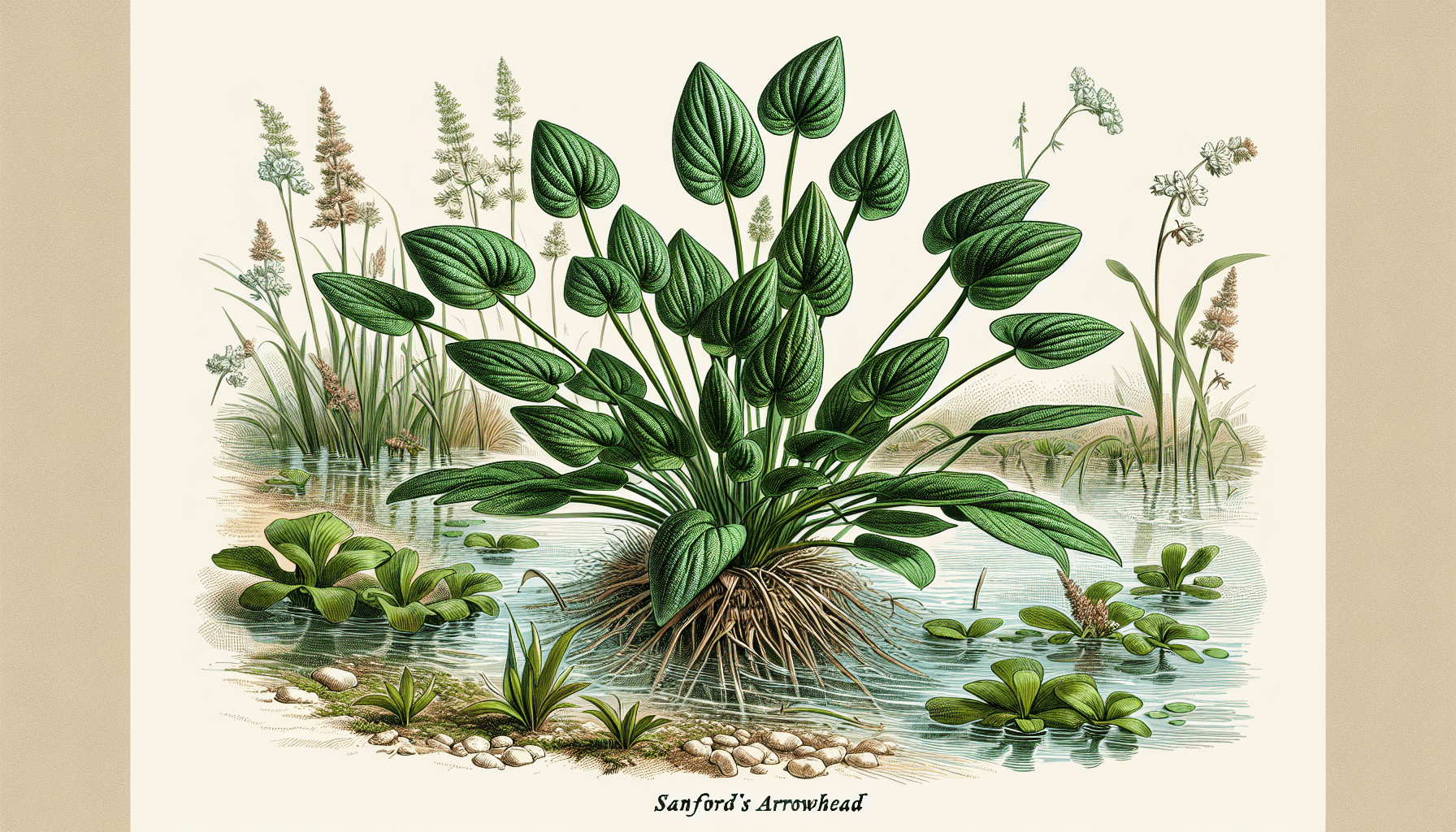
Sanford’s Arrowhead is an aquatic perennial plant species. Known for its distinctive arrowhead-shaped leaves and beautiful white flowers, this plant occupies a unique niche in the ecosystem, providing food and habitat for various forms of aquatic life.
Defining Sanford’s Arrowhead
Sanford’s Arrowhead, Sagittaria sanfordii, belongs to the water plantain family, Alismataceae. It is identified by its rosette growth pattern, arrowhead-shaped foliage, and white three-petaled flowers. This plant species is native to certain geographies in North America.
Scientific Classification
The scientific classification of Sanford’s Arrowhead reveals its position in the biological hierarchy. From a broader view, it is a part of the Plantae kingdom and Alismatales order, falling under the Alismataceae family. The genus Sagittaria includes arrowhead species such as the Sagittaria sanfordii.
Description of Sanford’s Arrowhead
Characteristically, Sanford’s Arrowhead presents distinctly-shaped leaves suggestive of an arrowhead, lending to its common name.
Appearance of Sanford’s Arrowhead
From a distance, the Sanford’s Arrowhead is easily distinguishable by its arrowhead-shaped leaves. The leaves are attached to long petioles submerged in water or mud. During its blooming season, the plant displays clusters of white, showy, three-petaled flowers.
Size and Growth Pattern
Sanford’s Arrowhead typically grows to a height of 1 to 3 feet, depending on the growing conditions. It follows a rosette growth style, where leaves grow in circular-shaped clusters at the base of the plant.
Flowering and Fruiting
Sanford’s Arrowhead flowers between July and September. The flowers are usually grouped in whorls of three on the top of a stout, leafless stalk. Post-pollination, these flowers give way to small, beaked fruits that contain several seeds.
Habitat and Distribution
Sanford’s Arrowhead has developed survival mechanisms that allow it to thrive in both stagnant and flowing bodies of water.
Natural Habitat
Sanford’s Arrowhead typically inhabits shallow freshwater environments, including the edges of ponds, swamps, and streams where the water is slow-moving. It’s also found in marshy ditches and canals.
Geographical Spread
This aquatic plant is found throughout the western and southwestern United States in regions like California, Nevada, and Oregon. It has also been reported in parts of British Columbia in Canada.
Cultivation Requirements
The propagation of Sanford’s Arrowhead can be achieved with relative ease under monitored conditions.
Soil Condition
This plant prefers slightly acidic to neutral pH conditions. It thrives in muddy or sandy soil that is flooded with shallow, slow-moving water.
Water Requirements
Sanford’s Arrowhead is an aquatic plant and, as such, it requires a significant amount of water. The roots are usually partly submerged in water, and the soil around the plant must be consistently moist.
Exposure to Sunlight
Sanford’s Arrowhead prefers full sunlight conditions; therefore, it should be planted in an area that receives unobstructed sunlight for most of the day.
Life Cycle of Sanford’s Arrowhead
Understanding the life cycle of the Sanford’s Arrowhead helps humans manipulate its growth for cultivation or control.
Growth
Sanford’s Arrowhead emerges in the spring, producing its distinctive arrowhead-shaped leaves. By midsummer, it begins to produce flowers, which eventually result in fruits by the end of the summer or the onset of fall.
Reproduction
The plant typically reproduces sexually through its flowering and fruiting period. However, it can also reproduce vegetatively from its rhizomatous roots.
Longevity
Sanford’s Arrowhead is a perennial plant, meaning it has a lifespan of more than two years. Under optimal conditions, it can continually produce leaves, flowers, and fruits throughout its lifespan.
Ecological Importance
The ecological significance of Sanford’s Arrowhead is underscored by its role in the ecosystem and inter-species interactions.
Role in the Ecosystem
The Sanford’s Arrowhead provides essential habitat and food for a wide range of creatures in the ecosystem. Its dense growth offers refuge for small invertebrates, and its seeds serve as a food source for ducks and other waterfowl.
Specific Interactions with Fauna
In particular, Sanford’s Arrowhead is a prized food source for the American Widgeon, a species of migratory duck. Some insects, like dragonfly nymphs, use the plant stalks for climbing before emerging as adults.
Threats and Conservation
Despite its ecological importance, the Sanford’s Arrowhead faces the threat of habitat loss due to human activities.
Threats
Major threats to Sanford’s Arrowhead include habitat destruction due to urbanization and agricultural activities. Additionally, water pollution and the invasion of non-native plant species also pose grave threats to its natural populations.
Conservation Efforts and Status
Although not listed as endangered or threatened, the conservation status of Sanford’s Arrowhead is of concern due to its declining populations. Conservation efforts for this species often involve habitat preservation and restoration.
Uses of Sanford’s Arrowhead
Apart from its ecological significance, the Sanford’s Arrowhead is valued for its ornamental appeal, medicinal uses, and culinary potential.
In Ornamental Landscaping
Sanford’s Arrowhead is a popular choice for water gardens and pond edges due to its showy flowers and unique leaf structure. Its dense growth also provides visual interest and adds texture to landscapes.
In Traditional Medicine
In some cultures, the plant has been used traditionally to treat digestive issues and stomach ailments. However, these medicinal uses have not been scientifically validated.
Culinary Uses
Although not mainstream, some parts of the Sanford’s Arrowhead, such as its tubers, are edible and have been consumed by indigenous cultures in the past.
Dealing with Problems
Like all plants, Sanford’s Arrowhead is susceptible to certain diseases and pests that can affect its health.
Common Diseases and Pests
Common issues include leaf spot diseases and rot. Various types of insects such as aphids, leaf beetles, and spider mites may also infest the plant causing substantial damage.
Preventive Measures and Treatment
Preventive strategies include monitoring the plant’s health regularly, removing any infested parts immediately, and maintaining optimal growing conditions. Treatment often involves applying organic or chemical insecticides and fungicides as needed.
Interesting Facts
Beyond its natural and cultivated use, Sanford’s Arrowhead brings with it a rich botanical history and some unique features.
Various Common Names
Sanford’s Arrowhead is known by several common names including Sanford’s Duck Potato, Sanford’s Sagittaria, and Arrowhead-Sanford.
Botanical History
The plant is named after Dr. Daniel Sanford, a prominent 19th-century American botanist who first described the species.
Unusual Features
A unique feature of Sanford’s Arrowhead is its ability to tolerate moderate levels of salinity, a characteristic not common among freshwater plants.