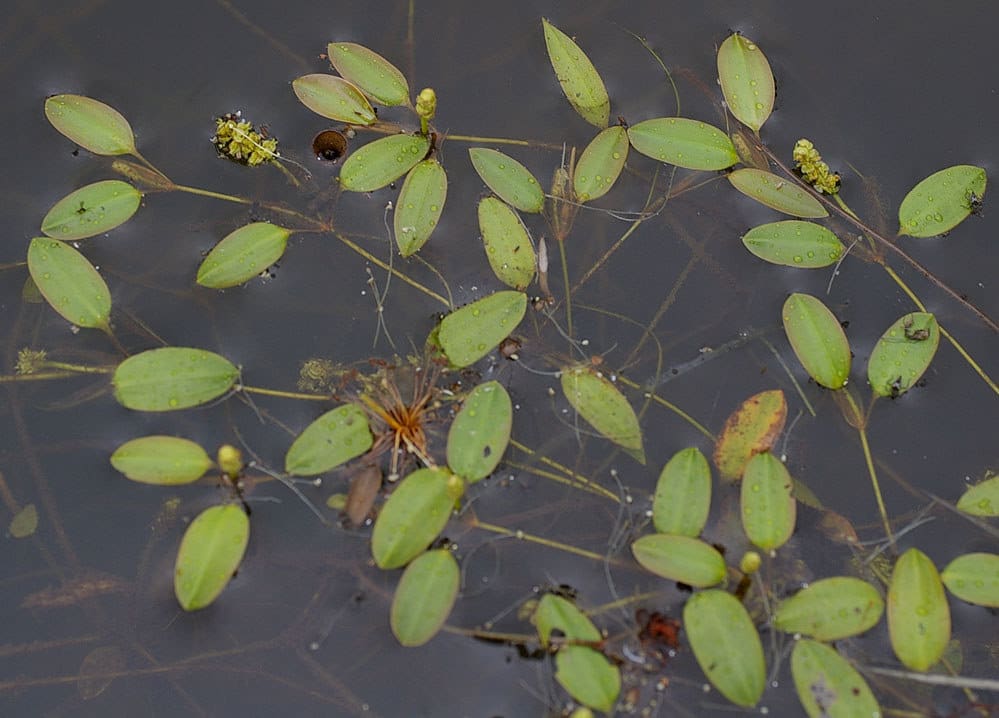
As you embark upon the exploration of the diverse world of underwater botany, your attention may inevitably be drawn to the aquatic plant known as Potamogeton Octandrus. A species belonging to the robust Potamogetonaceae family, this unique organism has sparked intrigue and interest among biologists and environmental scientists alike. As you proceed with this text, you will be provided with veritable and comprehensive details about Potamogeton Octandrus; its origins, physical characteristics, its role in the ecosystem and its overall significance in the realm of aquatic botany are illuminated upon.
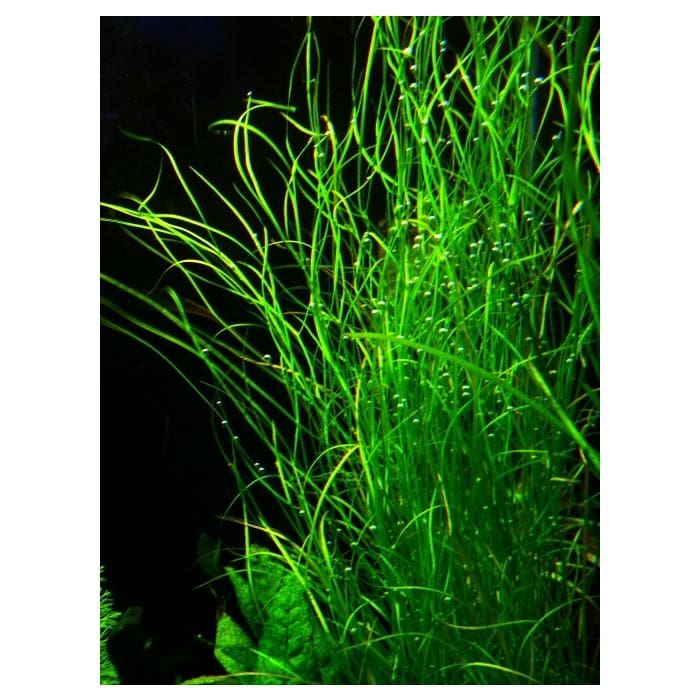

Overview of Potamogeton Octandrus
Definition of Potamogeton Octandrus
Potamogeton octandrus is a species of aquatic plant that belongs to the family Potamogetonaceae. It is a submerged perennial species that is primarily found in freshwater bodies such as ponds, lakes, and slow flowing rivers.
Origins and Natural Habitats
This particular species originated in Australia, but has since spread to other parts of the globe. It is frequently found in temperate regions and in diverse types of water basins, showcasing its adaptability. This includes streams, canals, and other aquatic environments.
Features and Characteristics
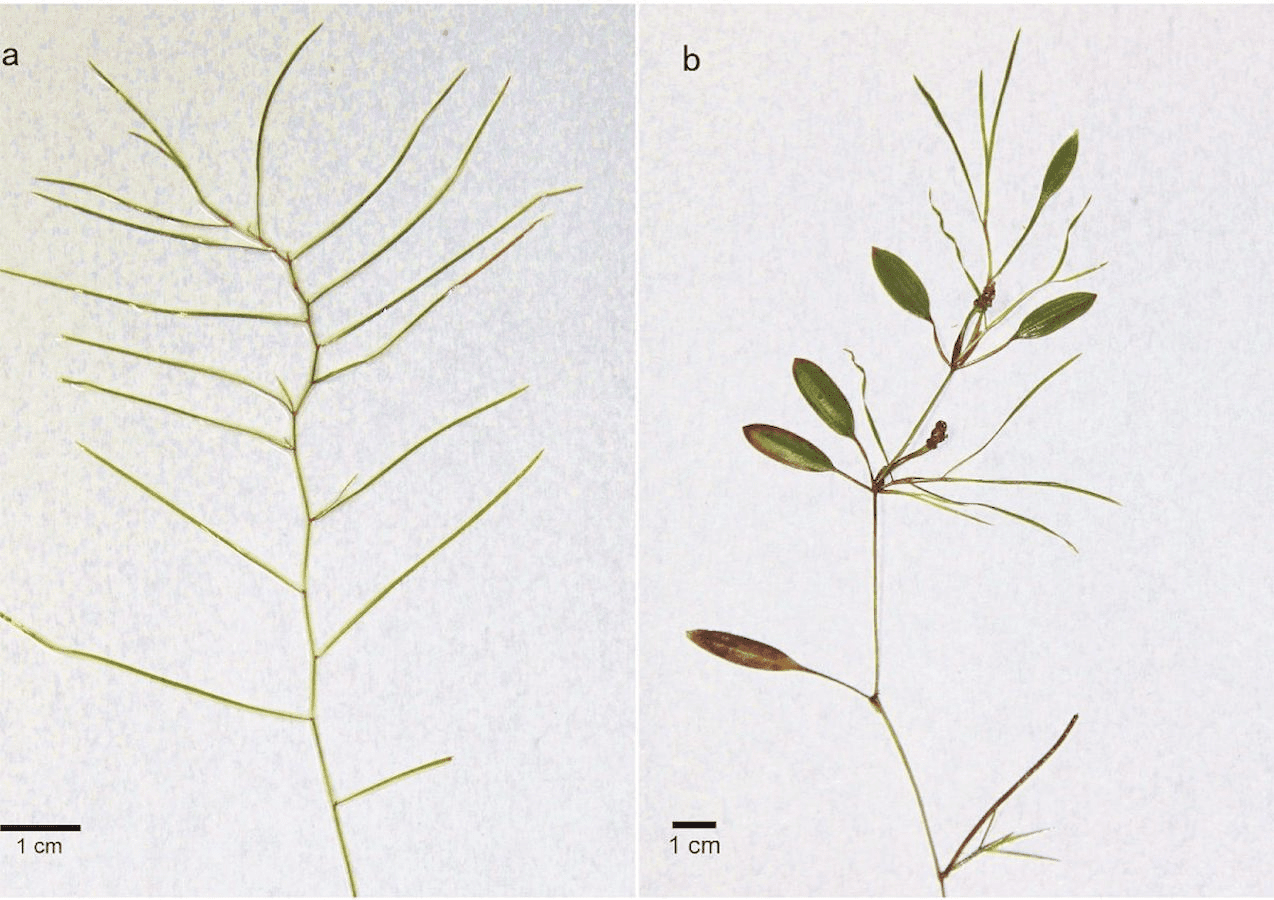
Potamogeton octandrus is notable for its slender leaves and branches, which beautifully adorn the underwater landscapes. The leaves are relatively translucent. It is characterized by its unique submerged leaves and floating foliage, which adapts to the variances in its aquatic habitat.
Botanical Description of Potamogeton Octandrus
Plant Structure
The plant structure of Potamogeton octandrus is extremely flexible, enabling it to live completely underwater. The plant is characterized by its elongated stems, which can grow up to 1-2 meters in length.
Leaf Structure and Features
The leaves of this plant are opposing and linear. They are pale green to sometimes almost translucent in color, and are usually over 7cm but less than 12cm in length. The length allows efficient photosynthesis underwater while the color helps absorb light better.
Stem and Root system
The plant possesses a robust stem and root system, which helps anchor it to the water bed. The stem is largely submerged and is characterized by its notable elongation whereas the roots are a mass of fine, hair-like structures.
Floral Structure
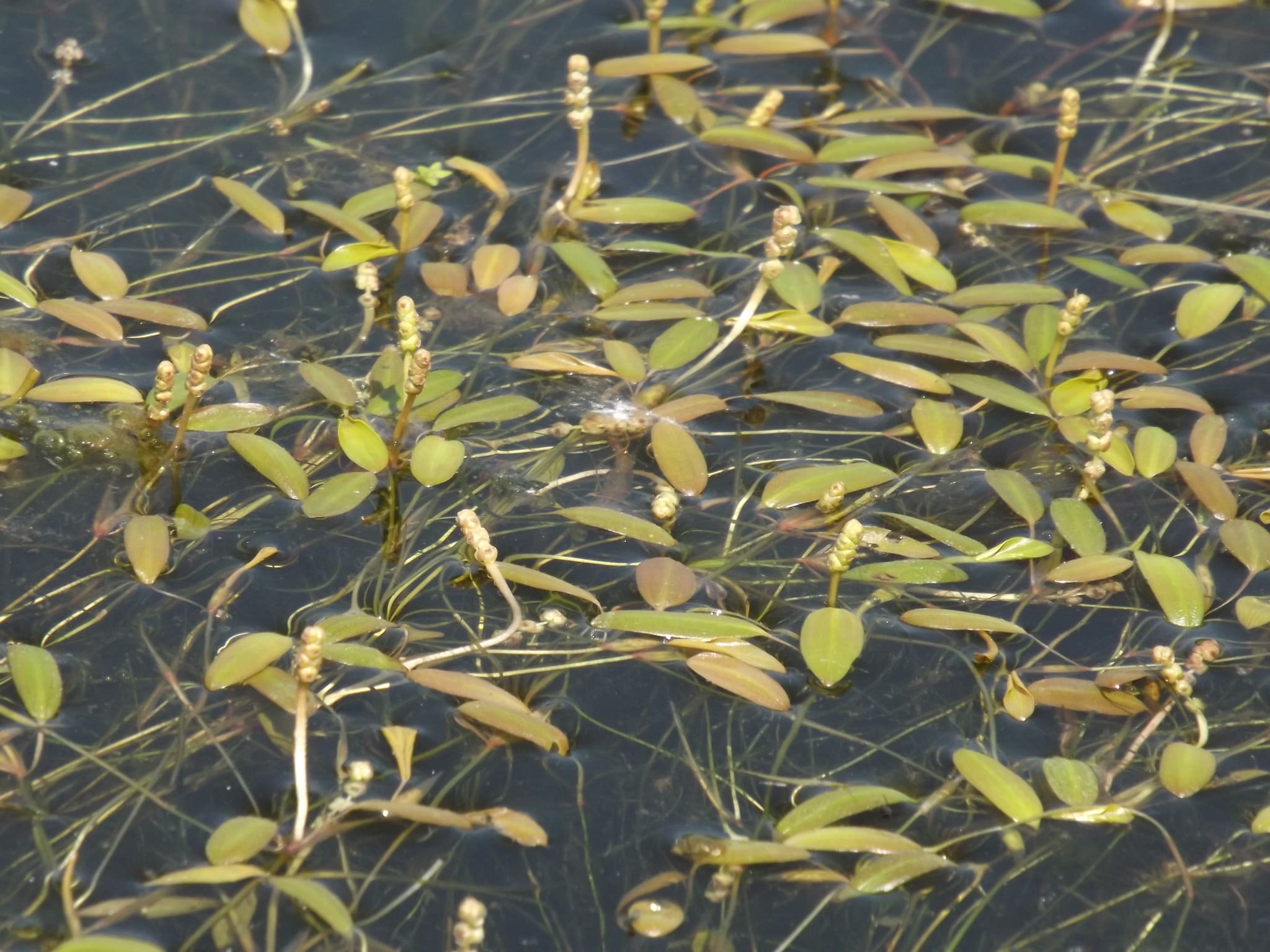
Potamogeton octandrus produces small, inconspicuous flowers that emerge just above the water surface. These little, 4-petaled flowers are arranged in a clustered spike, and are pollinated by either wind or water.
Fruit and Seed Characteristics
Each flower produces a small, egg-shaped fruit that contains a single seed. The green or brownish fruits are often dispersed by water currents.
Ecological Role of Potamogeton Octandrus
Role in Aquatic Ecosystems
The species plays an essential role in its ecosystem, offering habitat and food to diverse species. Many types of fish and aquatic insects find refuge in its dense foliage. Its submerged leaves provide a significant food source for waterfowl and an ideal breeding habitat for several aquatic animals.
Role in Biodiversity
This plant contributes significantly to biodiversity, as its presence helps maintain a balanced aquatic ecosystem. Its abundance provides refuge for smaller organisms, while its organic matter decomposition contributes to nutrient cycling.
Impact on Water Quality and Clarity
Potamogeton octandrus has the capacity to improve water quality and clarity. It can assimilate pollutants from the water, thus helping to purify the ecosystem. Its root system is also efficient at consolidating sediment, preventing cloudiness in the surrounding water.
Distribution and Habitat of Potamogeton Octandrus
Global Distribution
Although originating in Australia, Potamogeton octandrus is now found worldwide, particularly in temperate regions.
Preferred Habitats and Conditions
This species prefers clear and moderately flowing waters, as well as shallow ponds and lakes with muddy bottoms. It thrives particularly well in full light conditions, although it can adapt to slightly shaded environments.
Adaptations to Aquatic Environments
To thrive in aquatic environments, the plant has developed several physiological adaptations. These include flexible leaves and stems that resist water currents, and translucent leaves that facilitate underwater photosynthesis.
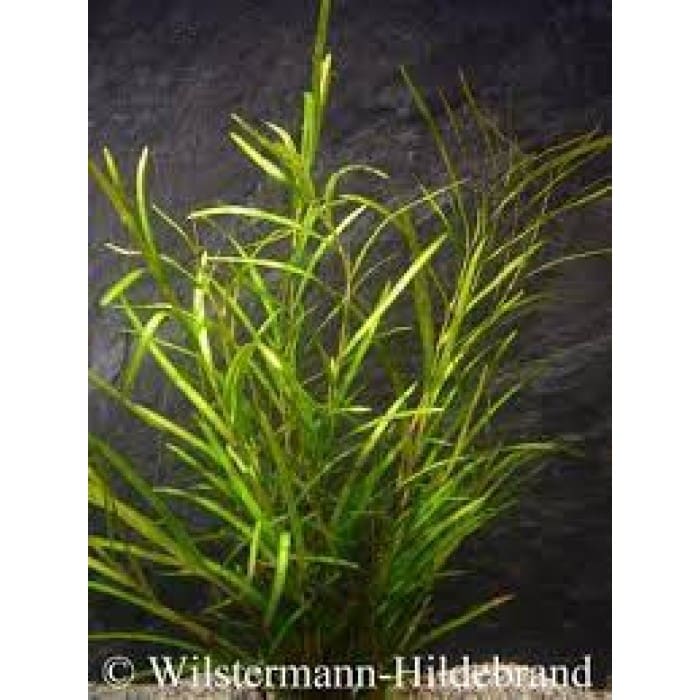

Reproduction and Propagation of Potamogeton Octandrus
Flowering and Pollination
The small flowers of Potamogeton octandrus generally bloom from spring to summer, showing up above the water surface. These flowers are usually pollinated by wind and sometimes by water movement.
Seed Production and Dispersal
Seed production ensues upon the fertilization of the flowers. The water disperses the small fruits of the plant, allowing for the propagation of new individuals in different locations.
Asexual Reproduction Mechanisms
While the plant sexaully reproduces through seed dispersal, asexual reproduction is also common. The plant can propagate through fragmentation, where broken stem pieces develop into new individuals.
Environmental Threats to Potamogeton Octandrus
Human Impacts
Human activities pose a considerable threat to Potamogeton octandrus. Urbanisation, pollution and other activities disrupting its environment, such as construction near water bodies, can lead to habitat loss.
Invasive Species Interactions
Invasive species are another significant threat, as they can outcompete the native plant for resources, eventually leading to its decline in the affected area.
Impacts of Climate Change
Climate change, with its associated alteration to temperature and precipitation patterns, can destabilize the aquatic ecosystems where Potamogeton octandrus grows, potentially hindering its survival.

Conservation Efforts for Potamogeton Octandrus
Current Conservation Strategies
Conservation strategies currently in place include habitat preservation and the creation of laws against the disruption of ecosystems. In some places, restoration projects are also undertaken to re-establish the plant in its native habitats.
Recommended Management Techniques
Habitat restoration and the control of invasive species are two highly recommended management techniques. Also, encouraging the cultivation of the plant, especially in ponds, can supplement wild populations.
Role of Regulation and Policy
Environmental policies and regulations play a vital role in ensuring the conservation of Potamogeton octandrus. A legal framework is crucial in managing human activities that could potentially destroy its habitat.
Uses of Potamogeton Octandrus
Culinary Uses
While not commonly consumed by humans, some cultures do include Potamogeton octandrus in their cuisines. The young shoots and leaves can be used in salads.
Medicinal Uses
There is not much documentation about the medicinal uses of this plant. Nevertheless, in certain indigenous cultures, it has been reportedly used for various herbal remedies.
Aquarium and Ornamental Uses
Potamogeton octandrus makes for an excellent aquarium plant due to its aesthetic appeal. It can also be used in ornamental water gardens, contributing to both the beauty and biodiversity of the setup.
Future Research Directions for Potamogeton Octandrus
Potential Applications and Uses
More research is needed to unlock the full potential of Potamogeton octandrus. Its potential medicinal properties or ability to improve water quality are areas that warrant further investigation.
Ecological and Evolutionary Research
Understanding the plant’s ecological role and contribution to biodiversity could enhance ecosystem management and conservation efforts. Additionally, evolutionary studies might shed light on its adaptability to different habitats.
Impacts of Environmental Change
Research on how Potamogeton octandrus responds to changes in environmental variables such as temperature, light and pollutant levels would be beneficial, given the current global context of climate change.
Interesting Facts about Potamogeton Octandrus
Historical and Cultural Significance
Historically, various cultures have used Potamogeton octandrus for food and medicine. It also holds cultural significance in certain communities for its role in mythologies and folklore.
Unique Adaptations
One of the most intriguing aspects of Potamogeton octandrus is its underwater survivability. From its flexible stems and leaves, which can withstand water currents, to its ability to complete the process of photosynthesis sub-aquatically, the plant’s adaptations are truly remarkable.
Fascinating Trivia
Interestingly, the name ‘Potamogeton’ is derived from Greek and roughly translates to ‘river neighbor’, which aptly describes its preferred habitats. Despite its global distribution, the plant is still relatively less-known compared to other aquatic species. This adds to the allure of Potamogeton octandrus, inspiring ongoing research and discovery with this unique plant.
