As an individual with an interest in aquatic plant life, it is essential that you gain a clear understanding of the Pond Water Starwort. This article will provide an insightful exploration of this fascinating aquatic plant, from its physical characteristics to its ecological significance. You will come to appreciate the integral role that the Pond Water Starwort plays in aquatic environments, enhancing your grasp of botany and ecology. Prepare to enhance your knowledge as we embark on this enlightening journey through the world of the Pond Water Starwort.
Overview of Pond Water Starwort
Scientific name and classification
Pond Water Starwort, botanical name “Callitriche stagnalis”, belongs to the family Plantaginaceae, the extensive plantain family. Renowned for its underwater proliferation and floating rosettes, this aquatic plant holds significant relevance in wetland ecosystems and human utility.
General description
You might typically find Pond Water Starwort as a conspicuous inhabitant of still, calm waters, thriving in ponds, ditches, and marshes. Its distinct morphology, characterized by copious, thin, and somewhat translucent leaves, extends a pleasing sight in aquatic environments. Its submerged form displays a dichotomous branching pattern, while it exhibits a different appearance above water by forming humble floating rosettes.
Physical characteristics
Pond Water Starwort is unique in its physical form. Its submerged leaves are opposite, filamentous, and notched at the tips. On the contrary, its emersed leaves are ovate, succulent, and with a shallow basal notch. The plant is known for its diminutive flowers, which are inconspicuous yet add to the overall aquatic charm.
Habitat and distribution
Pond Water Starwort thrives in a wide range of geographical areas across the globe, showing preference for temperate regions and tropical highlands. It has made its mark from the plains and valleys of the US to the wet grasslands in Europe and landscapes surrounding Asian rivers.
Physical Characteristics of Pond Water Starwort
Leaf structure and color
The leaves of Pond Water Starwort are of two distinct types: submerged and floating. The submerged leaves are typically long, thread-like, and pale green. In contrast, the floating leaves, forming a rosette on the water’s surface, are thicker, oval, and yellower green. Both leaf types contribute to the plant’s mesmerizing aquatic appearance.
Flower and fruit description
The flowers of Pond Water Starwort, unlike many aquatic plants, are not of a commanding presence. They are minute, inconspicuous, unisexual, and typically without petals. The flowering period extends from May to September. The fruit is a tiny, dry nut comprising of two joined carpels.
Size and shape
When submerged, Pond Water Starwort generally grows to about 30 cm in length, but may occasionally extend up to 100 cm. The floating form has no leaf stalks and takes on a rosette-like appearance. The plant undergoes an alteration in morphology above and below water, impressing with its adaptive capabilities.
Special features
The Pond Water Starwort demonstrates a unique dichotomous branching habit underwater, creating a feather-like appearance. Its aptitude to adapt to different light conditions by altering leaf morphology is one of the special features contributing to its widespread distribution.
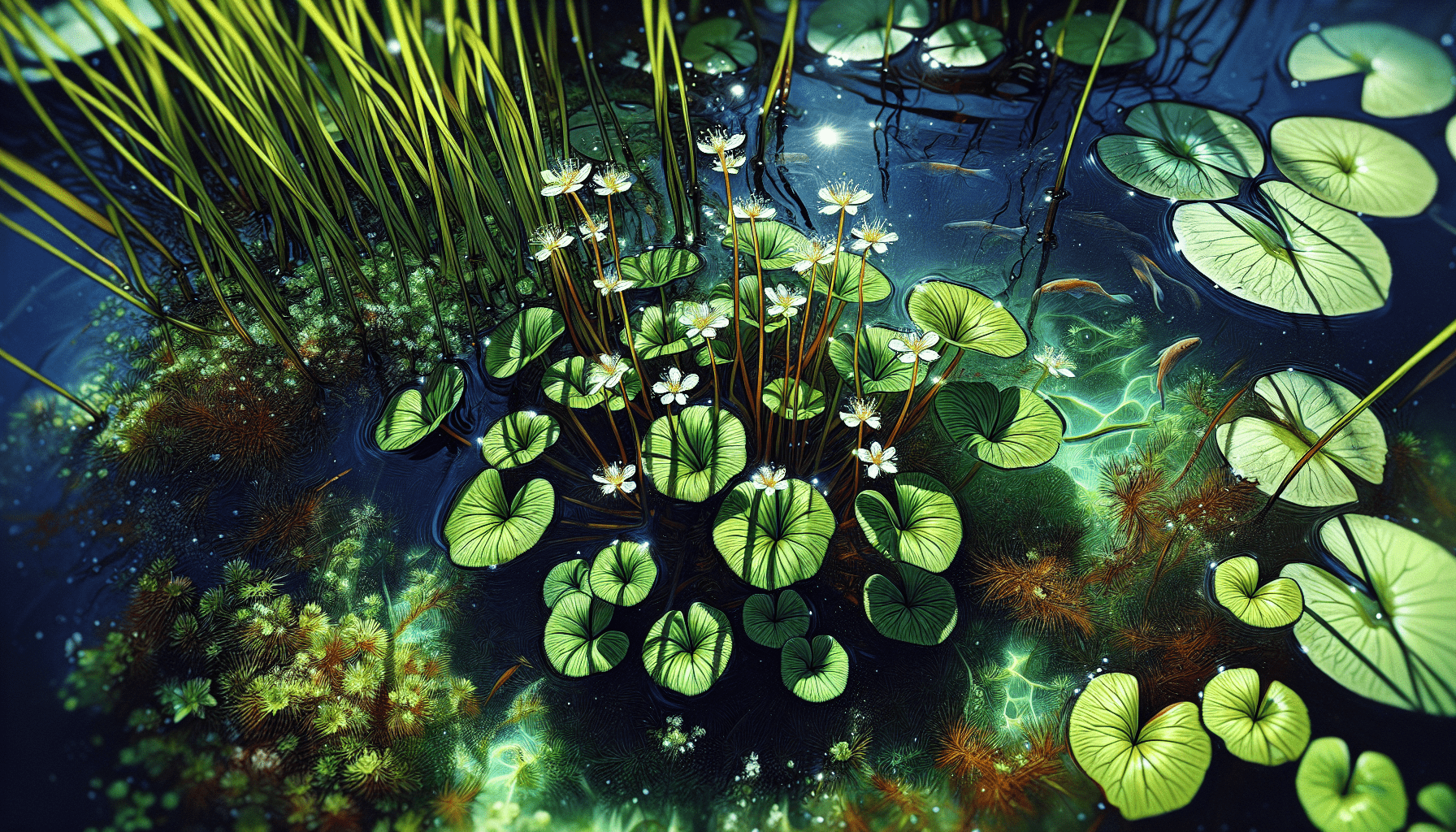

Habitat and Distribution of Pond Water Starwort
Global distribution
Pond Water Starwort enjoys an expansive worldwide distribution, from the temperate regions of North America and Europe to the tropical highlands of South America, Africa, and Asia.
Preferred habitat
Preferring still or slow-flowing freshwaters, you may find Pond Water Starwort in a variety of wet habitats, such as ponds, ditches, marshes, and slow rivers. It can adapt to an array of light conditions and sediment types, demonstrating appreciable ecological flexibility.
Climatic conditions
Pond Water Starwort favors climates ranging from cool temperate to tropical highlands. Its adaptability allows it to sustain under a vast spectrum of water temperatures and water chemistry, making it a common species in many aquatic habitats.
Ecological Role of Pond Water Starwort
Role in the aquatic ecosystem
Pond Water Starwort plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It provides a favorable habitat for invertebrates, offering food and shelter. It aids in water filtration, enhancing water quality by absorbing excess nutrients, thus reducing algal blooms.
Interactions with other organisms
The plant directly influences aquatic life, offering a substrate for the attachment of eggs and larvae of many creatures. Its system of creeping stems and dense submerged mass also provides hiding and breeding places for small fishes and tadpoles.
Importance to wildlife
Pond Water Starwort serves an important role in wildlife sustenance. Aquatic birds and mammals feed on its parts, while invertebrates also consume and utilize it.
Life Cycle of Pond Water Starwort
Stages of life cycle
The life cycle of Pond Water Starwort starts with germination of seeds which often takes place under water. The plant rapidly grows and reproduces in the summer months, while it slows down or even stops growing in the colder months, managing to survive as a small rosette near the base.
Reproduction process
Pond Water Starwort reproduces both sexually and asexually. The tiny flowers are usually pollinated underwater, which produces a fruit containing seeds. The plant also propagates vegetatively, with new plants growing from the fragments of older ones.
Seeds and dispersal
The dispersal of seeds usually happens through water flow, animal transportation or even human intervention. The hardy seeds can be viable for a long time, ensuring its perpetuity.
Uses of Pond Water Starwort
Culinary uses
Though not a significant part of the human diet, Pond Water Starwort has been utilized as an emergency food source. Its leaves are edible when cooked and have been traditionally used in soups or as a green vegetable by some cultures.
Medicinal uses
Historically, Pond Water Starwort was used in folk medicine for treating wounds, ulcers, and other skin conditions. Though these uses are less known today, Pond Water Starwort holds potential for further research.
Other miscellaneous uses
Pond Water Starwort has primarily been used for ornamental purposes in indoor and outdoor ponds due to its aesthetic appeal.
Cultivation of Pond Water Starwort
Ideal conditions for cultivation
The Pond Water Starwort prefers quiet freshwater bodies with a neutral to slight acidic pH. It thrives best in full sun or partially shaded areas with loose, nutrient-rich sediment.
Cultivation methods
Planting Pond Water Starwort is relatively simple. It can be grown through seeds or by using stem cuttings. For optimal growth, it needs to be planted in water bodies with a depth 10 cm to 2 m.
Maintenance and care
Regular trimming encourages dense growth and keeps the plant looking vibrant. To keep the water clean and reduce algae, removing any decaying plant material is advisable.
Threats to Pond Water Starwort and Conservation Status
Common threats
The most common threats include water pollution, habitat destruction, and invasive species that can out-compete the Pond Water Starwort.
Current conservation status
Pond Water Starwort is not currently listed as threatened or endangered in many areas due to its extensive distribution. However, some regional fluctuations in population have been observed, primarily linked to habitat quality and disturbance.
Efforts for conservation
Though not significantly threatened at present, conservation measures like improving water quality, protecting natural wetland habitats, and monitoring invasive species are essential to ensuring the continued survival of Pond Water Starwort.
Pond Water Starwort and Human Interaction
Importance to human populations
Pond Water Starwort serves recreational, ornamental, and to an extent, medicinal and culinary uses to various human populations. It effectively purifies water bodies, thereby indirectly becoming a part of water management systems.
Negative impacts on humans (if any)
Though generally favored for its benefits, Pond Water Starwort sometimes can pose challenges in water bodies where it becomes excessively dominant, hindering water flow and affecting recreational activities like swimming and fishing.
Interesting Facts about Pond Water Starwort
Unique features and abilities
One of the most curious abilities of Pond Water Starwort is its morphological plasticity. It modifies its leaf shape depending on whether it is growing above or under the water. Furthermore, it’s one of the few plants that can pollinate under water.
Historical significance and cultural references
Pond Water Starwort has found a place in the folklore and ethnobotanical practices of many cultures, predominantly for its medicinal uses. Its name, derived from the Greek words ‘beautiful’ and ‘hair’, references its captivating underwater form. Undoubtedly, Pond Water Starwort shapes the narrative of people and places it inhabits.