Opening the gateway to the enchanting world of aquatic flora, you are about to engage with a refined exploration centered around the Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant. As you journey through this greater understanding of such a unique aquatic specimen, you will uncover its significance within aquatic ecosystems, its intriguing characteristics, and its unique methods of propagation. Brace yourself to be enriched with the profound knowledge of one such gem from the plant kingdom, the Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant.
Understanding Aquatic Plants
Definition and Function of Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants, also known as hydrophytes or aquatic macrophytes, are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments be it freshwater, brackish, or saltwater. They generally reside in areas that are submerged or saturated most of the time. Aquatic plants play vital roles in aquatic ecosystems – providing oxygen, food, and shelter to aquatic life, as well as aiding in the reduction of water pollution.
The Role of Aquatic Plants in the Ecosystem
The ecosystem roles of aquatic plants are multifaceted. They function as a primary food source for both directly herbivorous organisms and indirectly, as they break down and contribute to detritus, that serve as a food source for detritivorous creatures. They not only produce oxygen through photosynthesis during the day, but also serve as the primary habitat for a host of organisms, offering refuge and breeding grounds for many species.
Different Types of Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants vary widely in form and ecological functions. Some, like Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant, are rooted in the sediment with portions above the water, while others are wholly submerged or free-floating. Emergent, submerged, floating-leaved, and free-floating are the four main types of aquatic plants, each with their unique anatomies and physiological adaptations to survive in water.
Identification of Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant
Botanical Name and Classification
Botanically named Parnassia palustris, the Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant belongs to the Parnassia family (Parnassiaceae), a small group of five species closely related to the saxifrage family.
Physical Features and Characteristics
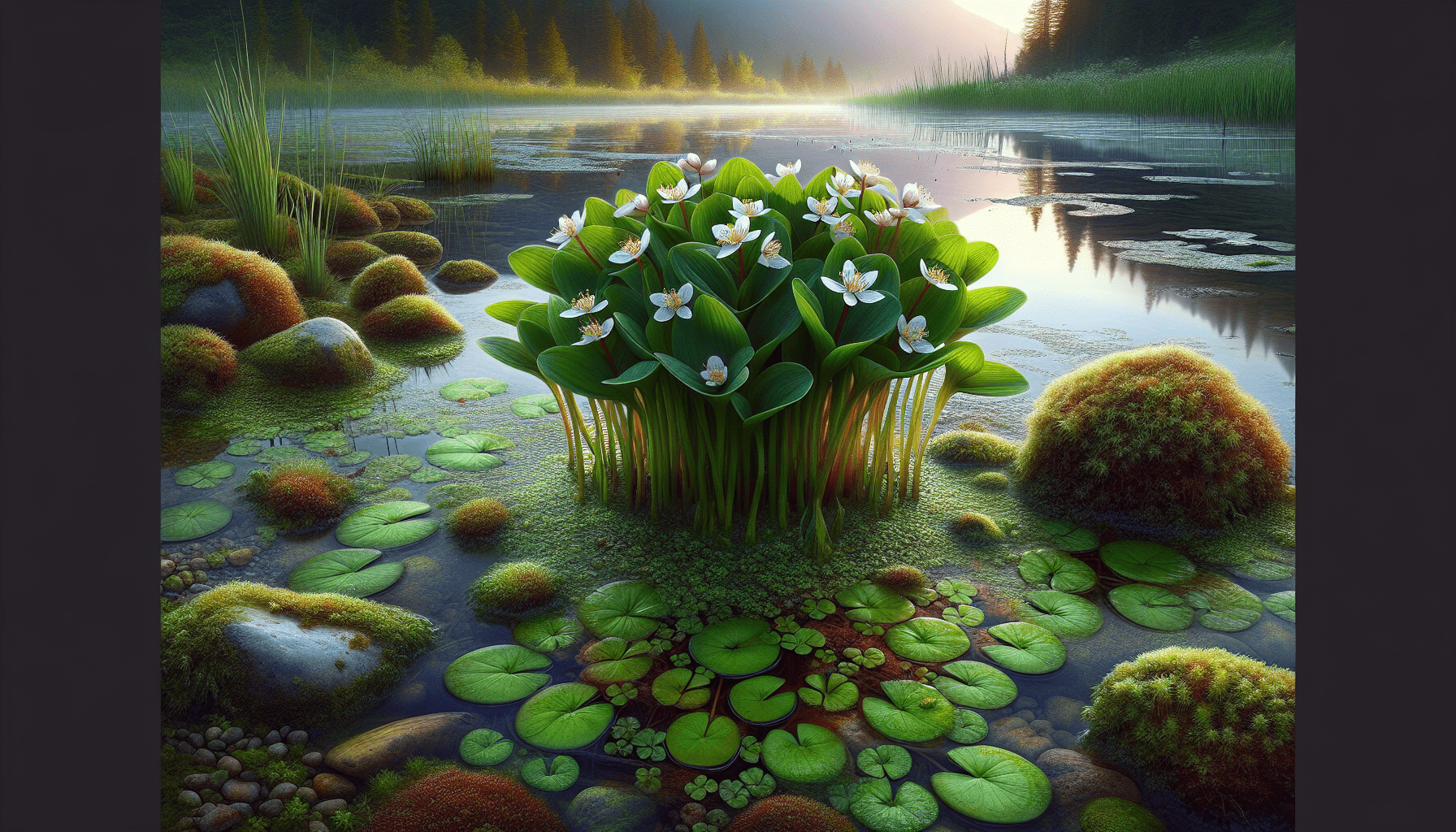
The Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant is a perennial herb that typically grows up to 30 centimeters tall, with broad, basal, spoon-shaped leaves and single, white, star-shaped flowers on long stalks. The flowers, which bloom from July to September, have five petals and five stigma lobes, making them easy to identify.
Geographical Distribution and Native Habitat
Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant has a broad geographical distribution across the Northern Hemisphere. It is native to bogs, fens, and wet meadows in North America, Europe, and Asia. The plant generally thrives in calcareous soils near water bodies, flourishing in areas of sunlight with moderate to high moisture.
Growth and Reproduction
Conditions for Growth
The Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant thrives in standing, medium, to moderately hard, base-rich water, with a pH of 6.0 – 7.5. An optimum light condition of full sun to partial shade is required for proper growth. The plant has a preference for wet, calcareous ground or shallow, standing water.
Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant’s Growth Rate
This perennial herb exhibits a moderate growth rate, and usually blossoms in late summer to early autumn. While it may take several years to reach its full height of about one foot, it can spread easily under suitable environmental conditions.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
The Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant typically reproduces sexually through the process of pollination. It has both male and female organs and is pollinated by insects, particularly bees, and flies, favoring cross-pollination. After successful pollination, the plant produces fruit containing numerous brown seeds which are dispersed through the water.
Ecological Significance
Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant’s Role in the Ecosystem
Parnassia palustris plays a vital role in wetland ecosystems. The plant contributes to oxygen production and is a source of food and shelter for a variety of insects and other small organisms that inhabit wetlands.
Common Species that Interact with Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant
The plant attracts numerous insects including bees and flies, which act as pollinators. It also forms part of the diet of certain types of waterfowl.
The Plant’s Contribution to Biodiversity
Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant enhances biodiversity by providing habitat and food sources for a variety of invertebrate and vertebrate species. In its ecological niche, it helps stabilize soil with its rooting system, thus minimizing erosion.

Cultivation and Care
How to Cultivate Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant
Cultivating Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant requires a moist or wet soil or up to 5cm deep standing water. The plant thrives best in full sun to partial shade. It can be propagated through the division of its clumps in spring or seed sowing in late winter.
Maintenance and Care for Healthy Growth
This plant has low maintenance requirements. It is advisable to keep the soil continuously moist or partially submerged in water to mimic their natural marshy habitat. While the plant can tolerate partial shade, a higher light intensity is preferred.
Common Pests and Diseases
Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant suffers from few pests or diseases. Occasionally, it might be affected by common garden pests such as aphids, but these are usually not a severe threat. Regular monitoring and implementation of basic pest control measures can help keep the plant healthy.
Propagation Techniques
Sexual Reproduction Process
The plant reproduces sexually through pollination followed by the development of fruit containing several seeds. The seeds fall in or nearby the water and grow into new plants the following spring after a period of cold stratification.
Asexual Reproduction Method
Asexual reproduction of Parnassus-leaved Pond Plants can be achieved through division of clumps in spring. This is the easiest and fastest way to propagate these plants.
Recommendations for Successful Propagation
For successful propagation through seed sowing, it’s essential that the seeds are exposed to a cold, moist stratification period of at least 2-3 months to guarantee germination. Division can be done in the spring season, ensuring each divided part includes a shoot for it to grow successfully.
Uses and Benefits
Uses in Traditional Medicine
While not widely documented, Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant has been used in traditional Eastern medicine to treat various conditions including respiratory disorders and hemorrhoids.
Importance in Cultivation and Landscape Design
Because of its ornamental flowers and preference for a wet environment, Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant can be effectively used in decorating gardens, especially in water gardens, ponds, or bog-style patches.
Other Notable Uses and Benefits
Beyond its medicinal and ornamental uses, the plant can play a role in the monitoring of ecological health due to its sensitivity to environmental changes, particularly pH levels.
Conservation Status and Threats
Current Conservation Status
Despite having a wide range, Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant is considered Near Threatened under the IUCN Red List due to its habitat’s vulnerability to human activity.
Threats to the Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant
Threats to this species include habitat destruction mainly due to urbanization, agriculture, and drainage of wetlands. Pollution is another leading factor impacting its survival.
Conservation Efforts and Measures
Conservation measures such as habitat preservation, regulations against illegal harvesting, and reestablishment efforts in depleted areas are being undertaken to secure the plant’s future. Seeds are also stored in seed banks to ensure diversity.
Invasive Potential
Characteristics that Contribute to Invasiveness
While Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant is native to many regions, in areas where it is not native, its characteristics such as its adaptability to varying conditions and effective seed dispersion can contribute to it becoming invasive.
Impacts of the Plant’s Invasive Behavior
In areas where it becomes invasive, this plant can overtake local vegetation, disrupting native plant communities and altering habitats.
Controlling and Managing the Spread
The control of Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant involves maintaining the health of native plant communities and monitoring the population levels regularly. Any notice of invasive behavior should prompt immediate eradication measures such as physical removal.
Fun Facts and Trivia
Interesting Facts about Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant
The Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant was named after Mount Parnassus in Greece, representing its home in wet habitats.
Cultural Significance and History
Some Nordic mythology associates Parnassus-leaved Pond Plant with the goddess Frigg or Freya as they were believed to grow in places she lingered.
Trivia Related to the Plant
The plant’s genus name, Parnassia, is a tribute to the ancient Greek legend of the mountain sacred to the arts and literature, Parnassus. Its species name, palustris, is Latin for “of the marsh” signifying its preferred habitat.