In the field of aquatic botany, you might encounter unique and captivating species, one of which is Parish’s Spike Rush. This remarkable plant embodies the resilience and adaptability inherent to aquatic flora, thriving amidst demanding conditions and contributing significantly to its ecosystem. The exploration of Parish’s Spike Rush not only offers a profound understanding of its physiological properties and ecological roles but also extends to the broader implications this species has on environmental conservation efforts and habitat restoration strategies. It’s the testament to the intriguing complexity nestled within the world of aquatic vegetation, and illuminates the essential interconnectedness of all lifeforms within our biosphere.
Definition of Parish’s Spike Rush
Parish’s Spike Rush, an aquatic plant, is a member of the Cyperaceae family and holds an essential position within the water bodies’ ecosystems. This plant displays a remarkable adaptation to the aquatic environment, fulfilling a significant ecological role while showing potential for various practical applications.
Scientific name and plant classification
The scientific name for the Parish’s Spike Rush is Eleocharis parishii. This plant belongs to the Cyperaceae family, also known as the sedge family. This diverse family comprises over 5000 known species spread over 90 genera, notable for plants that are typically habitants of wet or saturated soils.
Common names
Besides Parish’s Spike Rush, this species also carries several other common names. Some refer to it as Parish’s eleocharis, Parish’s spikerush, or simply Parish’s spike rush sedge.
General description of the plant
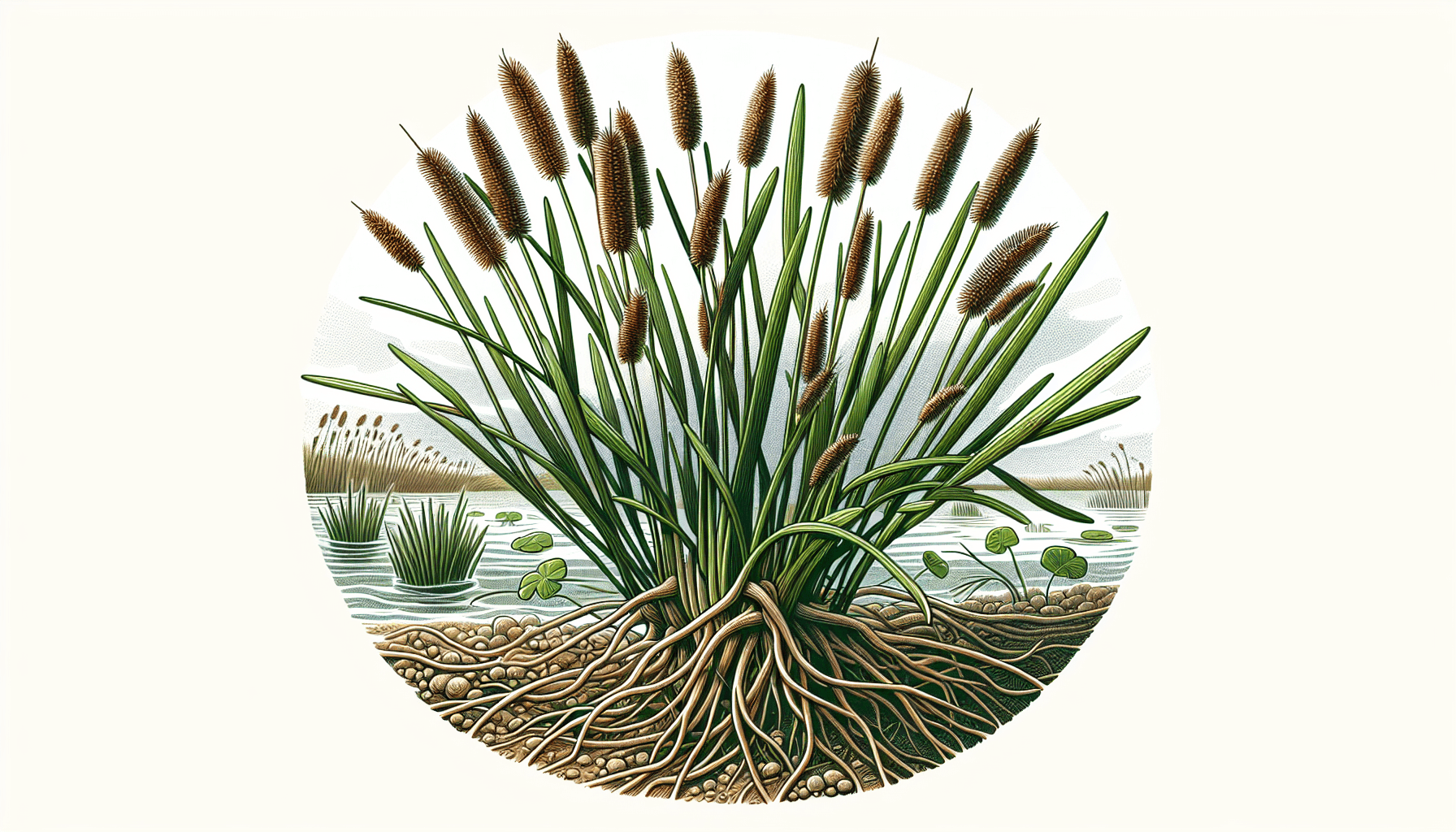
The Parish’s Spike Rush is an elegant and slender perennial aquatic plant characterized by its thin, reed-like green stems and brownish spikelets. It typically grows in shallow, fresh water bodies in a range of ecological settings, contributing significantly to its rich biodiversity.
Physical Characteristics
The sleek green visage of Parish’s Spike Rush adds to a water body’s aesthetic while positively impacting its ecological balance. Understanding its physical characteristics is critical to acknowledging how it exists within its environment.
Plant size and growth form
Parish’s Spike Rush appears as a compact, erect plant ranging from 20 to 80 centimeters in height. The growth form of this plant is characteristically tussocky with long, slender stems.
Leaf and stem description
This plant’s leaves are unique, as they are often inconspicuous or essentially absent. Instead, the more notable feature is the cylindrical, thin, green and hollow stems, which are jointless and offer the plant its reed-like appearance.
Flower and fruit description
The flowers of Parish’s Spike Rush are small and arranged in dense, brown spikelets at the stem’s tip. The fruit, a small achene or nutlet, is brown, egg-shaped with a minute tubercle at the summit.
Root system and propagation
Parish’s Spike Rush has a fibrous root system as adaptation to saturated soils and for absorption. This species propagates both sexually through seeds present in the spikelets and asexually through the formation of rhizomes.
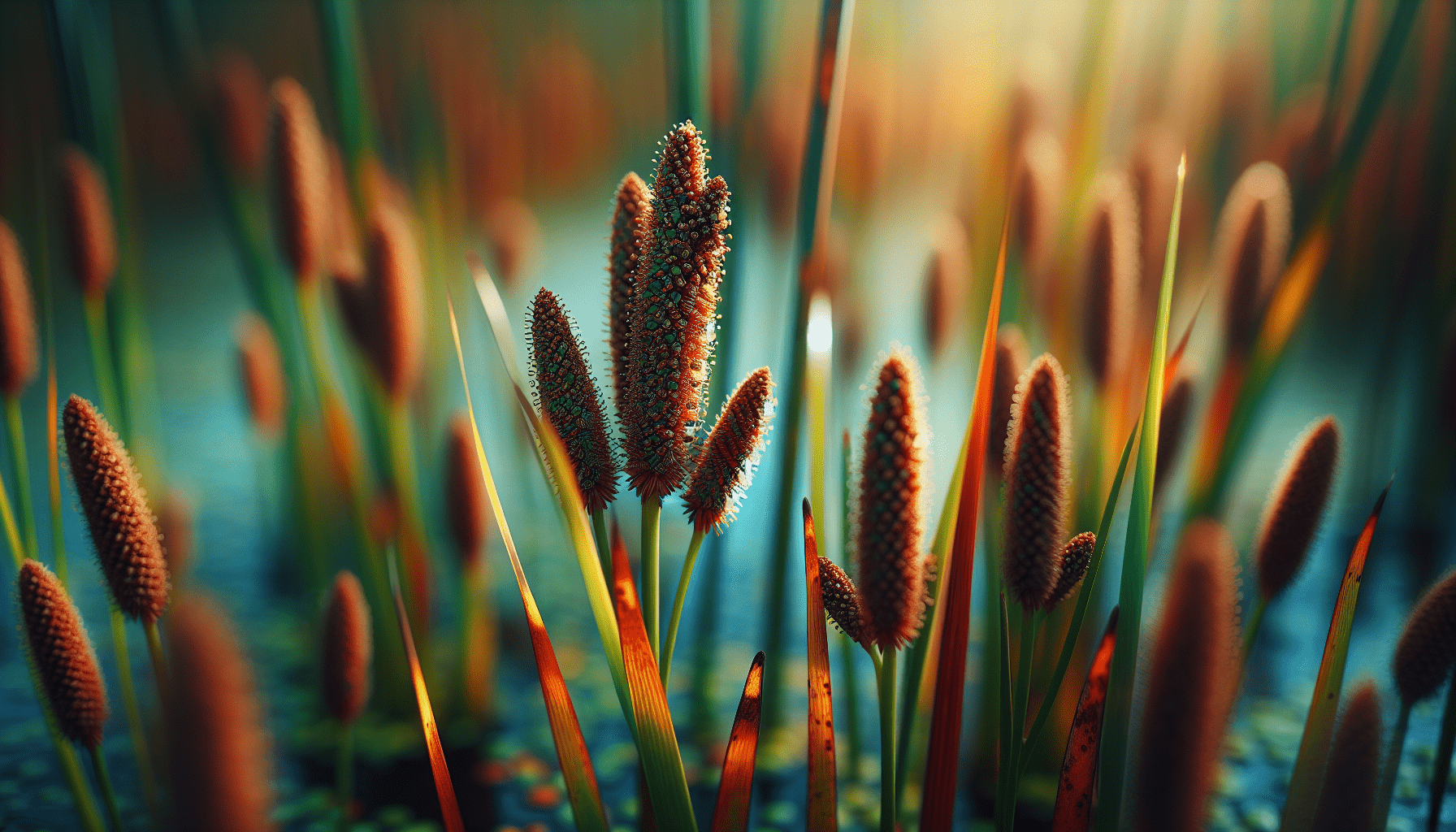

Habitat and Distribution
Worldwide, Parish’s Spike Rush can be found in various locales, mostly favoring wet or damp habitats that suit its ecological requirements.
Geographical areas where it is found
This aquatic plant is native to the western United States and Mexico, from California and Nevada south to Baja California and east to Arizona.
Preferred environmental conditions
Parish’s Spike Rush thrives in freshwater habitats with full sun exposure. It prefers standing or slow-moving water with a water depth ranging from 0 to 50 cm. It can withstand a wide range of soil types but favors those sandy or clayey.
Natural habitat types
Typically, Parish’s Spike Rush can be found in wetlands, swamps, marshes, and streambanks. These areas provide shallow, standing, or slow-moving water necessary for its growth.
Adaptations
Parish’s Spike Rush features a suite of adaptations ensuring its survival, reproduction, and optimal nutrient acquisition.
Adaptations for survival in water
Its adaptation to aquatics includes a fibrous root system for anchorage and nutrients absorption, air spaces within stems for buoyancy, and the ability to grow in both waterlogged soil and submerged conditions.
Adaptations for reproduction
Its flowers and subsequent fruit are adapted to water pollination. Furthermore, asexual reproduction via rhizomes allows the plant to proliferate, even under adverse conditions.
Adaptations for nutrient acquisition
The fibrous root system serves to absorb nutrients efficiently from the waterlogged soils. Intriguingly, Parish’s Spike Rush also exhibits the ability to absorb nutrients directly from the water column.

Lifecycle and Growth
Understanding the life cycle and growth patterns of Parish’s Spike Rush provides insights into its long-term survival and aging process.
Life cycle stages
Parish’s Spike Rush has a perennial life cycle, thus living for more than two years. It reproduces both sexually (by seeds) and asexually (through rhizomes), ensuring continuity.
Seasonal growth patterns
Like most aquatic plants, Parish’s Spike Rush experiences seasonal growth patterns, depending on various environmental factors such as water temperature, day length, and nutrient availability.
Long-term growth and aging processes
Over several years, Parish’s Spike Rush may form extensive colonies via its rhizomes, enhancing its chances of long-term survival. It also potentially resprouts from its base after winters, demonstrating an adaptive aging process.
Cultural Significance
While primarily an ecological asset, Parish’s Spike Rush also carries cultural and symbolic significances.
Uses by indigenous peoples
No direct usage by indigenous people related to Parish’s Spike Rush has been recorded. However, the plant’s large family, Cyperaceae, comprises several members the indigenous peoples used for weaving mats or baskets and medicinal purposes.
Symbolic meanings
Largely, Parish’s Spike Rush has no specific symbolic meaning, although water plants are often associated with adaptability, cleansing, and rebirth in various cultures.
Modern cultural references
Modern cultural references relating directly to Parish’s Spike Rush are sparse. However, in the broader context of biodiversity conservation and wetland restoration, this species regularly features as it forms an integral part of wetland ecosystems.
Ecological Role
Encompassing numerous ecological roles, Parish’s Spike Rush is integral to the ecosystem.
Role in food web
Like many aquatic plants, Parish’s Spike Rush provides a food source for various waterfowl and invertebrates. Its seeds serve as nourishment to various bird species, while its stems provide habitat for multiple aquatic insects.
Interactions with other species
This plant’s presence improves habitat complexity, offering breeding grounds and providing shelter to a range of aquatic creatures, including fish and amphibian species.
Influence on ecosystem processes
By absorbing excess nutrients from the water, Parish’s Spike Rush can prevent eutrophication, thus playing a significant role in maintaining the aquatic ecosystem’s health.
Conservation Status
While Parish’s Spike Rush is not currently listed as endangered, habitat loss presents a potential threat to its conservation status.
Endangered status and threats
Parish’s Spike Rush currently faces no immediate universal threats but is potentially endangered in areas experiencing wetland drainage for urban development and agriculture.
Protection efforts
Efforts to protect Parish’s Spike Rush include conservation of its natural habitats, with special emphasis on preserving marshlands, wetlands, and other water bodies from pollution and destruction.
Conservation needs and challenges
The main conservation challenge for Parish’s Spike Rush lies within the broader context of wetland conservation, primarily hinged on balancing urban development with the preservation of natural habitats.
Research and Scientific Studies
Scientific research serves as an invaluable resource for understanding Parish’s Spike Rush and its ecological contributions.
Key scientific research findings
Research has highlighted the plant’s role in nutrient recycling in freshwater environments and its potential use in bioremediation practices.
Ongoing research projects
Currently, research projects are delving into Parish’s Spike Rush’s genetic makeup, distribution patterns, and its overall ecology and life cycle stages.
Future research directions
Future research should focus on genome sequencing, understanding how Parish’s Spike Rush adapts and reacts to environment change, and potential applications in ecological restoration projects.
Practical Applications
Parish’s Spike Rush has several practical uses, mainly related to its potential role in water purification and aesthetic appeal in aquarium design.
Use in aquaculture
Its ability to absorb excess nutrients makes Parish’s Spike Rush a beneficial inclusion in aquaculture.
Medicinal uses
Currently, no known medicinal uses are associated directly with Parish’s Spike Rush. Still, plants in the Cyperaceae family have been used in traditional medicine, suggesting potential untapped opportunities.
Inclusion in aquarium and pond designs
Thanks to its elegant, reed-like appearance, Parish’s Spike Rush makes a stunning addition to aquariums and ponds, particularly as part of naturalistic or biotope designs.