In pursuit of enhancing your understanding of aquatic plant life, this article embarks on an exploration of Northern Water Plantain, a herbaceous perennial often found in wet habitats. As you navigate through this succinct narrative, you will unravel the botanical characteristics, ecological significance, and widespread applications of this intriguing organism, detailing key aspects that contribute to the uniqueness and relevancy of the Northern Water Plantain within the aquatic ecosystem. This exposure to a seemingly niche aspect of ecology prompts a broader appreciation for biodiversity and the intertwining relationships within nature’s tapestry.
Overview of Northern Water Plantain
Northern Water Plantain, known scientifically as Alisma triviale, is a perennial aquatic plant known for its beauty, medicinal properties and unique growth habits. Transitioning effortlessly from submerged to emergent states, this plant has adapted to a wide range of wet environments, which have greatly influenced its structure and ecological role.
Scientific Classification
Kingdom: Plantae; Order: Alismatales; Family: Alismataceae; Genus: Alisma; Species: Alisma triviale. The Northern Water Plantain is also related to other members in the genus Alisma, a group known for its water dwelling plant species.
Common Names
Aside from Northern Water Plantain, the plant is also occasionally referred to as Western Water Plantain, North American Water Plantain, or simply, Water Plantain.
Physical Description
Northern Water Plantain typically grows to a height of 30 – 100 cm. It shows several erect, slightly wrinkled leaves that can be up to 30 cm long with a heart-shaped or broadly triangular base. The white flowers of the plant are small and displayed in clusters on a tall, erect, and branched inflorescence.
Habitat of Northern Water Plantain
Native Region
Native to North America, the Northern Water Plantain thrives in its aquatic habitat, which extends across Canada and the United States.
Preferred Conditions
This plant prefers wet soils and can thrive in permanently flooded areas or in areas that are periodically dry. It can be found in swamps, marshes, ditches, pond shores, stream edges, and other wetlands. It tolerates a wide range of water conditions from shallow to deep waters.
Habitat Range and Distribution
The Northern Water Plantain can be found across North America in a variety of biomes, from the warm Southern states to colder Northern regions, demonstrating its adaptability.

Growth and Lifecycle of Northern Water Plantain
Seedling Stage
Northern Water Plantain begins its life as a minute seedling under the surface of the water or in very wet soil. The plant will remain in this submerged state until it begins growing leaves.
Juvenile Stage
In the juvenile stage, the plant’s leaves are primarily submerged. As the plant grows, it begins to develop emergent and floating leaves as well.
Mature Plant Stage
In the mature plant stage, the Northern Water Plantain produces an erect stalk with inflorescences of small white flowers. Once fertilized, they develop into fruit and begin the cycle anew.
Flowering and Reproduction
The plant generally flowers between June and August. Each flower blooms for a single day, during which time it is cross-pollinated, setting the seeds for the next generation.
Dormancy and Survival
In winter, the above-water portion of the plant dies off, leaving only the roots and seeds, which can survive below the frost line. The plant will re-emerge in the spring.
Botanical Features of Northern Water Plantain
Leaf Structure
The leaves of Northern Water Plantain have long petioles and broadly triangular to oval blades.
Flower Characteristics
The plant’s flowers are small, white, and clustered. They have three petals and three sepals, and are supported by a tall, branching inflorescence. Each flower only blooms for a single day.
Root System
Northern Water Plantain develops a robust rhizomatous root system, which is critical for its survival during periods of dryness and winter dormancy.
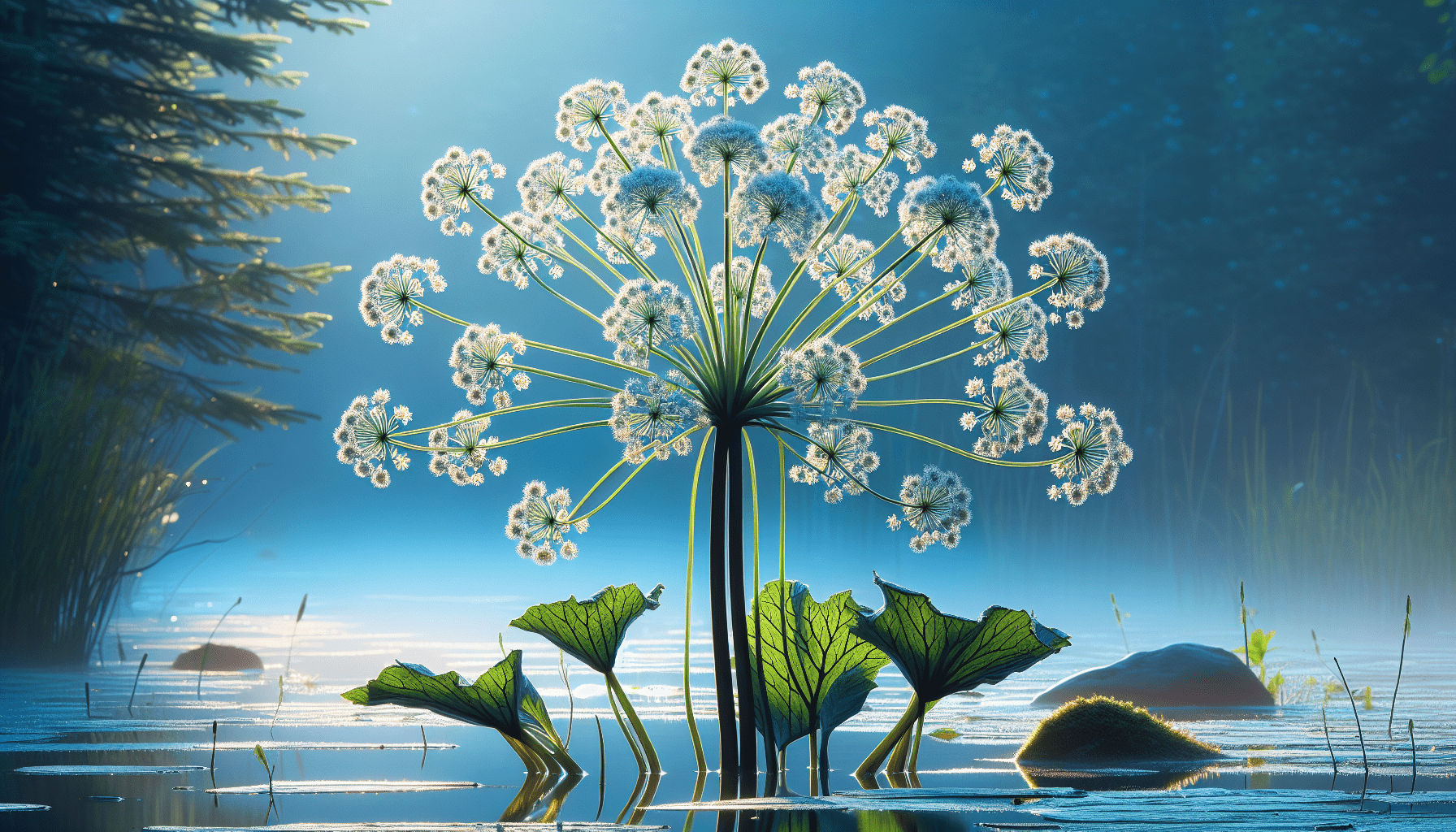
Ecological Role of Northern Water Plantain
In Aquatic Ecosystems
The Northern Water Plantain plays an important role in many wetland ecosystems. Its submerged and floating foliage offers shelter and breeding sites for a variety of aquatic animals, while its leaves and seeds provide a food source.
For Wildlife and Insects
Specifically, waterfowl and other birds are attracted to the seeds, and insects, particularly bees and flies, are attracted to the flowers for pollination.
Interactions with Other Plants
Northern Water Plantain also aids other water plants by helping to stabilize the soil with its extensive root system, thereby reducing erosion and creating more favorable conditions for plant growth.
Uses of Northern Water Plantain
Traditional Medicine
The Northern Water Plantain has been used in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments, such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and digestive disorders.
In Aquatic Gardening
Due to its ornamental appeal, the plant is a popular choice for aquatic and bog gardens.
For Soil Erosion Control
Its strong root system helps prevent soil erosion in areas vulnerable to water movement, making it useful in landscape restoration and erosion control efforts.
Conservation Status and Threats to Northern Water Plantain
Current Conservation Status
While not currently considered threatened or endangered, the Northern Water Plantain’s population is affected by changes in its wetland habitats due to urban development, pollution, and draining of wetlands.
Threats and Challenges
One of the major threats to this species is habitat loss. As wetlands continue to be drained and converted for agricultural and urban uses, the plant’s ability to thrive can be compromised.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to protect wetland habitats can help preserve Northern Water Plantain populations. This includes promoting sustainable land use practices and implementing protective policies and regulations.
Study and Research on Northern Water Plantain
Historical Studies
Historically, the plant has been studied for its medicinal properties and usefulness in preventing soil erosion.
Recent Research Findings
More recent research focuses on the plant’s adaptability to different water conditions, its role in aquatic ecosystems, and potential medicinal applications.
Future Research Directions
Future research on Northern Water Plantain may further explore its ecological role and the potential impacts of climate change on its habitat and distribution.
Cultivation of Northern Water Plantain
Propagation Techniques
Northern Water Plantain can be propagated by seeds, or by dividing the rhizomes.
Maintenance and Care
The plant requires minimal maintenance, as long as it is kept in wet or waterlogged conditions.
Common Diseases and Pests
Despite its aquatic habitat, the plant is surprisingly resilient to most common plant diseases and pests.
Interesting Facts about Northern Water Plantain
Unique Characteristics
The Northern Water Plantain’s ability to transition from submerged to emergent states makes it a formidable presence in aquatic environments.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The plant’s medicinal uses have made it a significant species for traditional healers in indigenous cultures.
Trivia and Unknown Facts
Despite being an aquatic plant, Northern Water Plantain is surprisingly frost-tolerant, allowing it to thrive in a wide range of habitats.