As you navigate the intricate world of aquatic botany, you might be intrigued to discover the narrow-leaved water plantain, a distinctly fascinating species with an intriguing character. Known scientifically as Alisma lanceolatum, this peculiar plant occupies an exceptional niche in the flourished aquatic plant kingdom. In the following scrutiny, you will uncover the elements that devise its unique identity, from its preferred habitat, distinct morphology, to its intricate survival strategies in a bid to bring to light the lesser-known details about this aquatic marvel. Your journey into the depths of botanical exploration continues here.
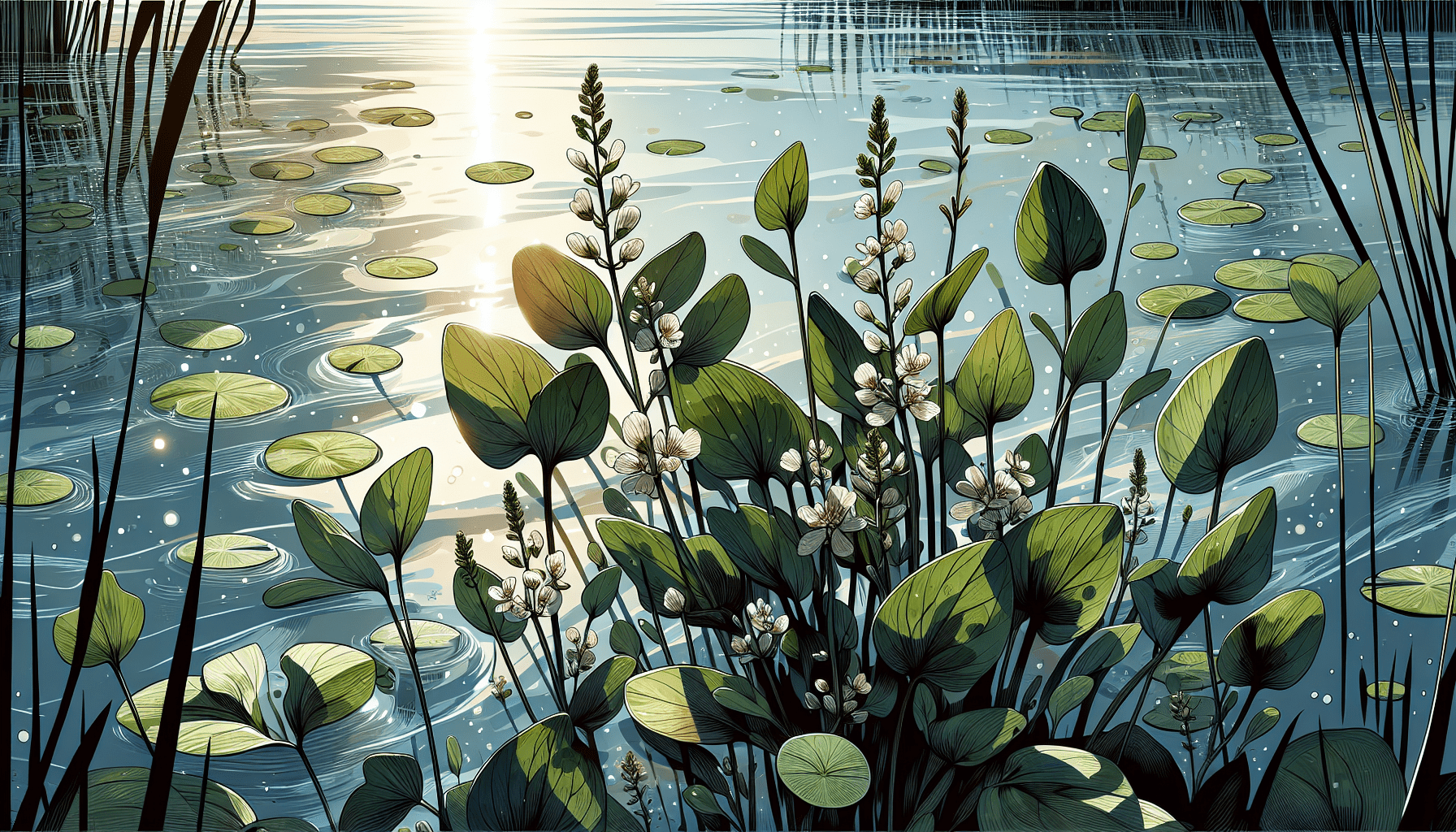
Overview of Narrow-leaved Water Plantain
What the plant is
The Narrow-leaved Water Plantain is an aquatic plant characterized by its eponymous narrow leaves and its unique flower formation. This perennial plant boasts an extensive root system, making it a sturdy and reliable resident in a wide variety of water bodies across the globe.
Botanical name and classification
Narrow-leaved Water Plantain goes by the botanical name of Alisma lanceolatum. This plant belongs to the Plantaginaceae family, a large family composed primarily of flowering plants, with over 20 different genera and around 200 different species.
Native habitats and global distribution
The plant is native to Europe, but has since spread diffusely around the world. It thrives in aquatic habitats, especially slow-moving or stagnant bodies of water such as ponds, marshes, and swamps. Given its adaptive qualities, it has propagated across both temperate and subtropical climates.
Physical Characteristics of the Plant
Description of leaves, stem and flowers
The leaves of the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain are long and slender, accounting for the nomenclature. The perennial plant produces a compact rosette of basal leaves that are submerged beneath the water or float on the water surface. The flowering stems, which could rise as high as a meter above water, showcase a loose array of small, pale pink or purple flowers.
Size and growth pattern
This plant typically grows to be 30-40 inches tall, although its height can vary depending on its environment. The growth pattern for the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain is rhizomatic, meaning the plant tends to spread horizontally across the ground, creating new off-shoots and developing its widespread root system.
Characteristic features distinguishing it from other species
Apart from the unique characteristics of narrow leaves and pale flowers on tall stalks, the plant also has small, ribbed seeds which other species in the Alisma genus do not. These seeds and the root system allow it to propagate robustly and survive in different conditions.
Life Cycle and Growth Traits
Germination and growth
After the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain propagates its seeds, the plant begins the germination process, which depends heavily on sunlight exposure and water temperature. Its growth can be considerably efficient, given favourable conditions.
Flowering and seed production
The flowering season for the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain falls within the summer months. Following this, seeds maturing within the fruit ripen and are ready for dispersion. This seed production extends throughout the plant’s lifespan.
Seasonal changes and adaptations
Given its hardy nature, the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain is well adapted to seasonal changes. During colder months, the plant would appear dormant, with smaller leaves, while in warmer seasons, it rejuvenates with wider foliage and flowers.
Ecological Roles and Interactions
Roles in aquatic ecosystems
As an aquatic plant, it plays a significant role in water ecosystems. Besides providing food and habitat to water-loving insects and birds, the plant also contributes to stabilising ponds and other bodies of water by reducing the rates of erosion along the banks.
Interactions with other plants, animals and microorganisms
In terms of interactions, the plant has many mutualistic relationships. Beneficial microbes help decompose the plant matter, enriching the overall ecosystem. Likewise, animals, such as certain species of waterfowl, often consume the seeds aiding in their dispersal, indirectly supporting the propagation of the plant.
Effect on water quality and habitat diversity
The ability of this species to grow in various conditions contributes to overall habitat diversity. Furthermore, the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain can positively affect water quality by absorbing excess nutrients and pollutants present in the water, thereby maintaining ecological balance.
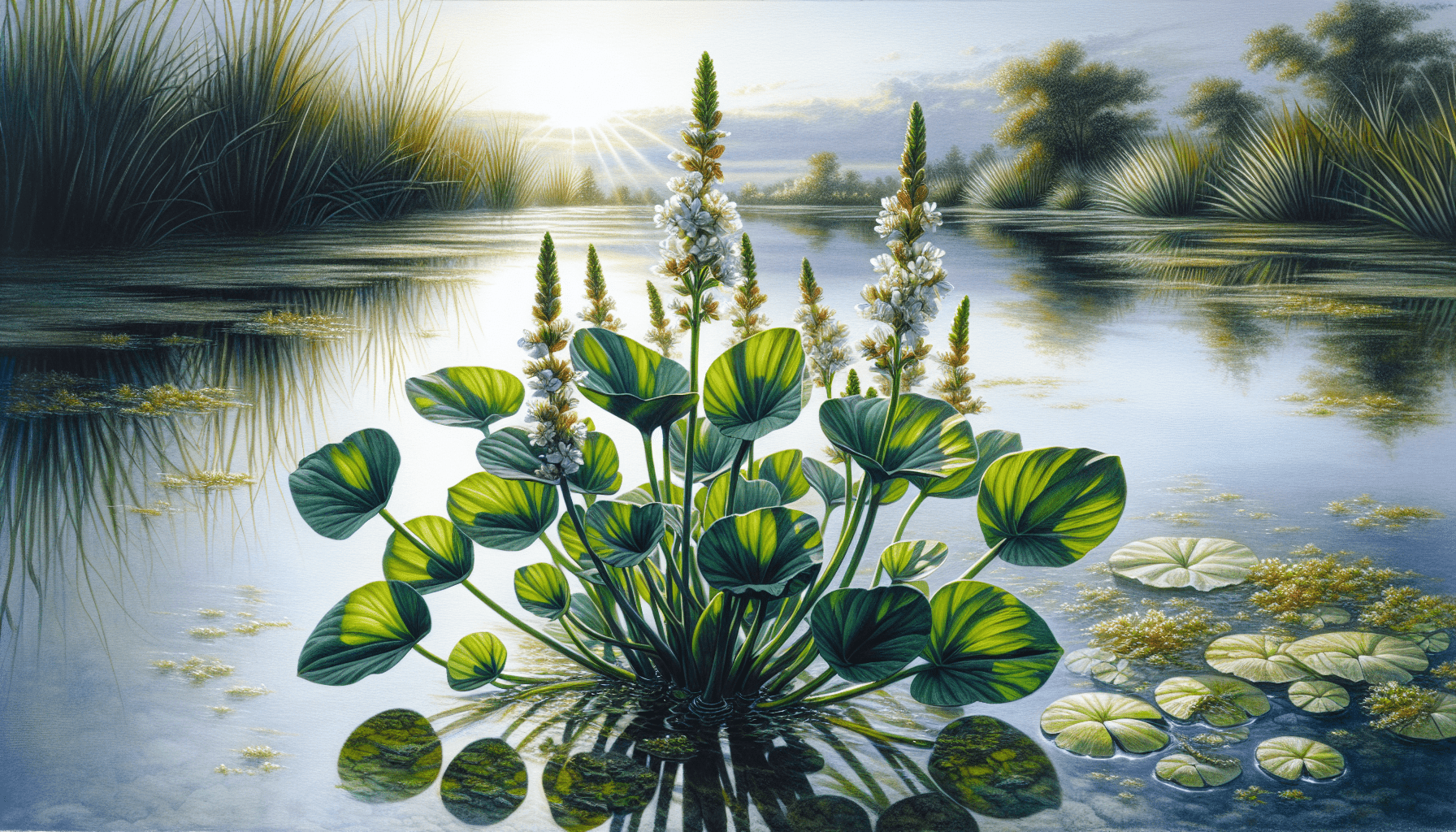

Cultivation and Care
Preferred conditions and planting tips
It prefers marshy locations for growth and its seeds can be directly sown outside after any danger of frost has passed. It should be kept under full sunlight or light shade, ensuring the roots remain submerged in the water.
Water and nutrient requirements
Given it is an aquatic plant, steady water intake is vital. As for nutrient requirements, it can endure in poor nutrient conditions, although adequate nutrients ensure healthy growth of the plant.
Common pests and diseases and how to prevent them
The plant typically exhibits strong resistance towards pests and diseases. However, one must be vigilant for waterlogged conditions that might promote rot in the roots. Similarly, slugs and snails are a known pest for the plant.
Uses and Applications
Historical and cultural uses
Historically, indigenous communities have used the Narrow-leaved Water Plantain for medicinal purposes, as it is believed to possess healing qualities.
Current uses in landscaping, aquaculture and other fields
In the contemporary world, it is commonly used in water gardens or bog gardens due to its hardiness and aesthetic appeal. It also aids in water filtration in aquaculture, being an organic solution to regulation of water ecology.
Potential future uses and research
Given the potential application in ecological preservation and water filtration, there is demand for advanced research to maximize its use in sustainable development.
Conservation Status and Threats
Current conservation status
Due to its widespread distribution, the plant currently has a wildlife risk rating of least concern.
Threats to survival and factors affecting populations
Excessive collection and loss of habitat could be a potential threat to the population. Likewise, climate change and rising temperatures could adversely impact its preferred habitats.
Conservation efforts and measures
Since it is not an endangered species, extensive conservation measures have not been legislated. However, preserving and endorsing its usefulness can be instrumental in maintaining the plant’s health.
Legal Regulations and Restrictions
Local, regional and international regulations
There are currently no specific regulations or prohibitions regarding the growth or distribution of Narrow-leaved Water Plantain.
Restrictions on collection, transplantation and trade
The plant is not under any restrictions when it comes to collection, transplantation, or trade due to its non-endangered status.
Implications for growers, landscapers and hobbyists
Given its unique beauty and ease of care, it is a profitable acquisition for those interested in horticulture, gardening or aquatic environmentalism.
Study and Research
Historical and recent scientific research
Historically, research has been focused on the plant’s biochemistry and ecology. More recent studies are inspecting its role in water purification and its potential use in eradicating water pollution.
Current study areas and findings
Currently, numerous laboratories and botanical institutes continue studies on the species with interest in its ecological roles, optimal growth conditions, and medicinal properties.
Opportunities and challenges for future research
Though promising in its multifarious uses, its potential is relatively untapped in mainstream research due to inadequate funding or interest, offering ample opportunities for future exploration.
Additional Resources
Books, articles and websites for further reading
A host of resources like botanical encyclopedias, horticultural guides, university press publications and dedicated plant databases can assist in further understanding of the plant.
Organizations, networks and online forums
Botanical societies, horticultural organizations and online plant forums also offer opportunities for discussion, exploration and collaboration to enthusiasts.
Where to buy or see Narrow-leaved Water Plantain
Garden outlets, water plant nurseries, botanical gardens and gardening websites are ideal to purchase or view this plant.