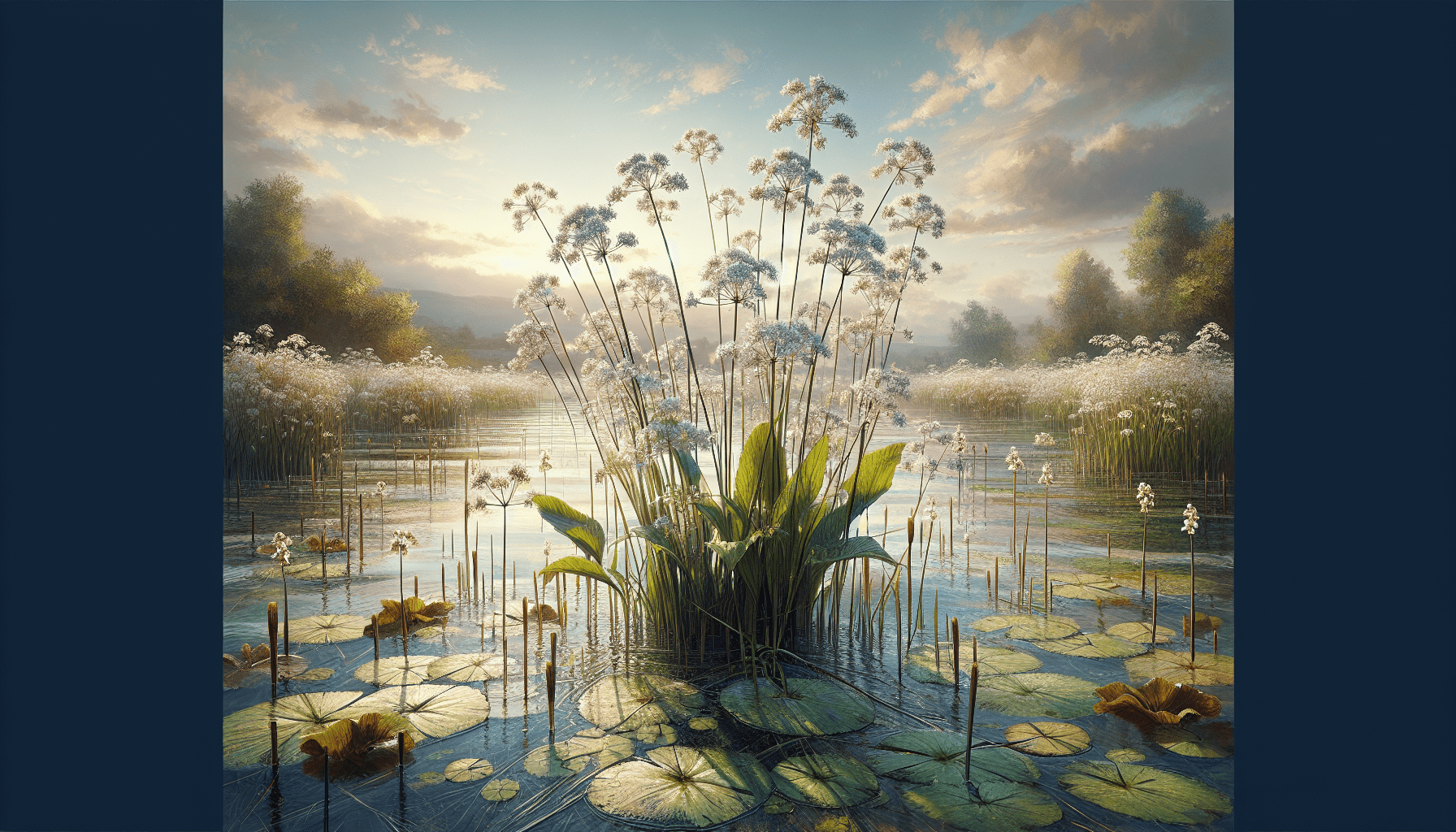
As someone with a keen interest in aquatic botany, you might find the lesser water-plantain fascinating. The lesser water-plantain, scientifically known as Baldellia ranunculoides, is renowned for its distinctive characteristics and uses. This article elucidates the in-depth understanding of this peculiar aquatic plant, exploring its biology, lifecycle, habitat, and potential applications. Furthermore, it delves into its significance in maintaining a balanced aquatic ecosystem. In essence, this article seeks to shed light on every pertinent aspect related to the lesser water-plantain, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this unique species.

Definition of Lesser Water-plantain
Botanical name and classification
The Lesser Water-plantain is scientifically known as Baldellia ranunculoides. This plant belongs to the Alismataceae family, widely known as the water-plantain family. This family comprises approximately 85 known species of aquatic plants.
Basic description and appearance
The Lesser Water-plantain is an aquatic perennial herb typically distinguished by its subtle yet distinct features. It generally reaches a height of about 5 to 30 cm. Their leaves are long and narrow, with petioles that emerge directly from the plant’s base. Lesser Water-plantain’s simple, glabrous, and basal leaves run the length of 2 cm to 8 cm, and its width trails the breadth of 1 cm to 3 cm, resembling an elliptical to ovate figure in shape with entire margins. The flowers bloom into star-like structures usually with three white petals.
Habitat of Lesser Water-plantain
Ecosystem preferences
The Lesser Water-plantain prefers wet and aquatic environments, and it’s most frequently spotted thriving in ponds, marshes, and ditch margins. It also adjusts well to waterlogged soils, inhabiting the silty and peaty banks of slow moving streams.
Geographical distribution
This plant has a wide geographical distribution, primarily known to inhabit Europe and Asia. However, it has also been reported to appear sporadically in the northeastern region of the United States.
Ideal growing conditions
The Lesser Water-plantain ideally grows under sunny exposures and prefers acidic to neutral pH for an optimum growth rate. The species can withstand shallow water habitats and it is frost resistant. It requires moist or wet, well-drained soil that can be loamy or peaty in texture.
Structure and Morphology of Lesser Water-plantain
Root system
Like many aquatic and marshland plants, the Lesser Water-plantain has a fibrous root system. This helps it anchor itself in the often unstable environments it calls home and provides an effective means of absorbing the necessary nutrients from the waterlogged soils.
Stem and leaf structure
The plant has a creeping stem or rhizome, which allows it to propagate throughout its habitat. The leaves are basal and simple, providing a smooth, shinier surface area that can enable the process of photosynthesis efficiently even in its aquatic environment.
Flower and fruit features
The Lesser Water-plantain showcases umbrella-like clusters of small, brilliant white flowers, each typically composed of three petals. The flowering part of the plant is called an inflorescence, which bears unisexual flowers. The fruit of the Lesser Water-plantain is a small, spherical capsule that consists of numerous tiny seeds, which allows for wide dispersion.

Life Cycle of Lesser Water-plantain
Germination process
After the plant’s fruit is mature, it releases its many tiny seeds into the surrounding aquatic environment. These seeds then induce germination under ideal moist conditions, instigating the beginning of the Lesser Water-plantain’s life cycle.
Growth and development stages
Once the seeds germinate and the seedlings have successfully been established, the plant goes through a series of growth stages. The seedlings initially develop into young plants, which then mature into fully grown Lesser Water-plantains, exhibiting a lush presentation of its white flowers.
Flowering and fruiting period
The flowering period of the Lesser Water-plantain is between late spring and early summer, wherein the plant displays its radiant white inflorescences. Fruits usually develop soon after the flowering period, maturing and releasing seeds, thereby completing the life cycle and ensuring the continuation of the species.
Ecological Role of Lesser Water-plantain
Role in the aquatic ecosystem
The Lesser Water-plantain plays an integral role in aquatic ecosystems. This species contributes to filtering water by absorbing harmful pollutants and it adds oxygen to its habitat, which supports the surrounding aquatic life.
Interaction with other species
Several aquatic insects and animals engage with the Lesser Water-plantain for shelter and food. Moreover, waterfowl are known to consume the seeds; therefore, this plant aids in the diet of certain wildlife.
Importance for animals and insects
It serves as a food source for numerous insect larva such as moths and butterflies. Certain species of waterfowl and other birds use the plant as a food source, specifically targeting its fruit for consumption.
Cultivation and Management of Lesser Water-plantain
Cultivation techniques
Lesser Water-plantain can be propagated by seed or by division of its rhizomes. The seeds can be sown at a shallow depth in wet soil or waterlogged conditions. The divison of rhizomes can be conducted in spring or fall, wherein the divided pieces are then planted individually.
Management strategies
The plant requires minimal management. It is typically adequate to ensure that the plant has access to a stable water body and is afforded sufficient sunlight. However, it might be necessary periodically to check for any potential pests or diseases and take appropriate controlling measures.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting Lesser Water-plantain is fairly straightforward. The entire plant, including leaves, stems, and roots, can be harvested during its growing season. The harvested plant can either be used fresh or dried for later use.
Uses of Lesser Water-plantain
Medicinal uses
Historically, the Lesser Water-plantain has been used in traditional medicine for its diuretic and antiseptic properties. It’s been utilised for urinary tract and kidney disorders as well as for its potential wound healing properties.
Culinary uses
Although not the most common use, some cultures do incorporate the plant into their local cuisine. The leaves are often eaten raw or cooked like spinach, and the seeds have been used as a grain substitute.
Landscape and garden uses
The Lesser Water-plantain can be an attractive addition to a water garden due to its small white flowers and lush green leaves. It also serves essential ecological functions even when planted on a smaller scale in domestic environments.
Threats and Conservation of Lesser Water-plantain
Common pests and diseases
As of present knowledge, Lesser Water-plantain doesn’t have any specific diseases or pests predominantly affecting its spread. However, like all plant species, it’s possible for common aquatic plant diseases or pests to occasionally bother this plant.
Conservation status
The Lesser Water-plantain is not currently under any significant threat and is not listed on the IUCN Red List of threatened species. Nevertheless, like any other species, it is vulnerable to loss of habitat due to human activities or climate change.
Efforts for preservation and protection
Preserving their waterlogged habitats from pollution or conversion is crucial for the conservation of the Lesser Water-plantain. Ensuring that water management planning and development activities accommodate the growth and health of this species is instrumental.
Benefits and Importance of Lesser Water-plantain
Benefits to ecosystem
Lesser Water-plantains are beneficial to their ecosystems both as sources of food for animals and insects and as bio-remediators that filter pollutants from their aquatic habitats.
Socio-economic significance
While the Lesser Water-plantain does not currently hold substantial economic value, its potential medicinal uses and contribution to maintaining water quality could enhance its socio-economic significance in the future.
Potential for scientific and medical research
The plant’s traditional use in medicine piques the interest of researchers. Further scientific studies could potentially unveil more medicinal properties of this plant that could be useful in drug development and therapeutic interventions.
Summary of Lesser Water-plantain
Critique of current knowledge
While we know a fair amount about the Lesser Water-plantain’s ecology and potential uses, there is still much to be explored. Comprehensive studies on the plant’s potential health benefits are lacking, and more research is needed about the plant’s ecological roles.
Potential areas for future research
Future research could expand upon the potential medicinal and therapeutic uses of the Lesser Water-plantain. In addition, studies could also delve deeper into its role in the ecosystem, particularly its interactions with other species and its bio-remediation capabilities.
Importance of public awareness and education
Public awareness about the Lesser Water-plantain and similar native species is crucial for their conservation. Education about their benefits and ecological roles can help ensure these plants are valued and protected.
In summary, the Lesser Water-plantain is a valuable player in the aquatic ecosystem, offering both ecological benefits and potential medicinal uses. By appreciating and understanding these plants, we are one step closer to preserving their habitats and utilising their potential for the betterment of humanity and our environment.