In this informative scholarly exploration titled “What Is The Aquatic Plant Large Madagascar Lace Plant,” the central focus is detailed examination of the eponymous species known for its majestic aesthetic in aquatic environments. The aquatic plant large Madagascar lace plant, a staple in the world of water gardening, presents an intriguing topic which you are invited to comprehend through this comprehensive dissection. From its unique biological features to its cultivation methods, every fundamental aspect pertaining to this fascinating aquatic plant will be meticulously discussed to equip you with a profound understanding of its integral role in ecosystem and aquarium alike.
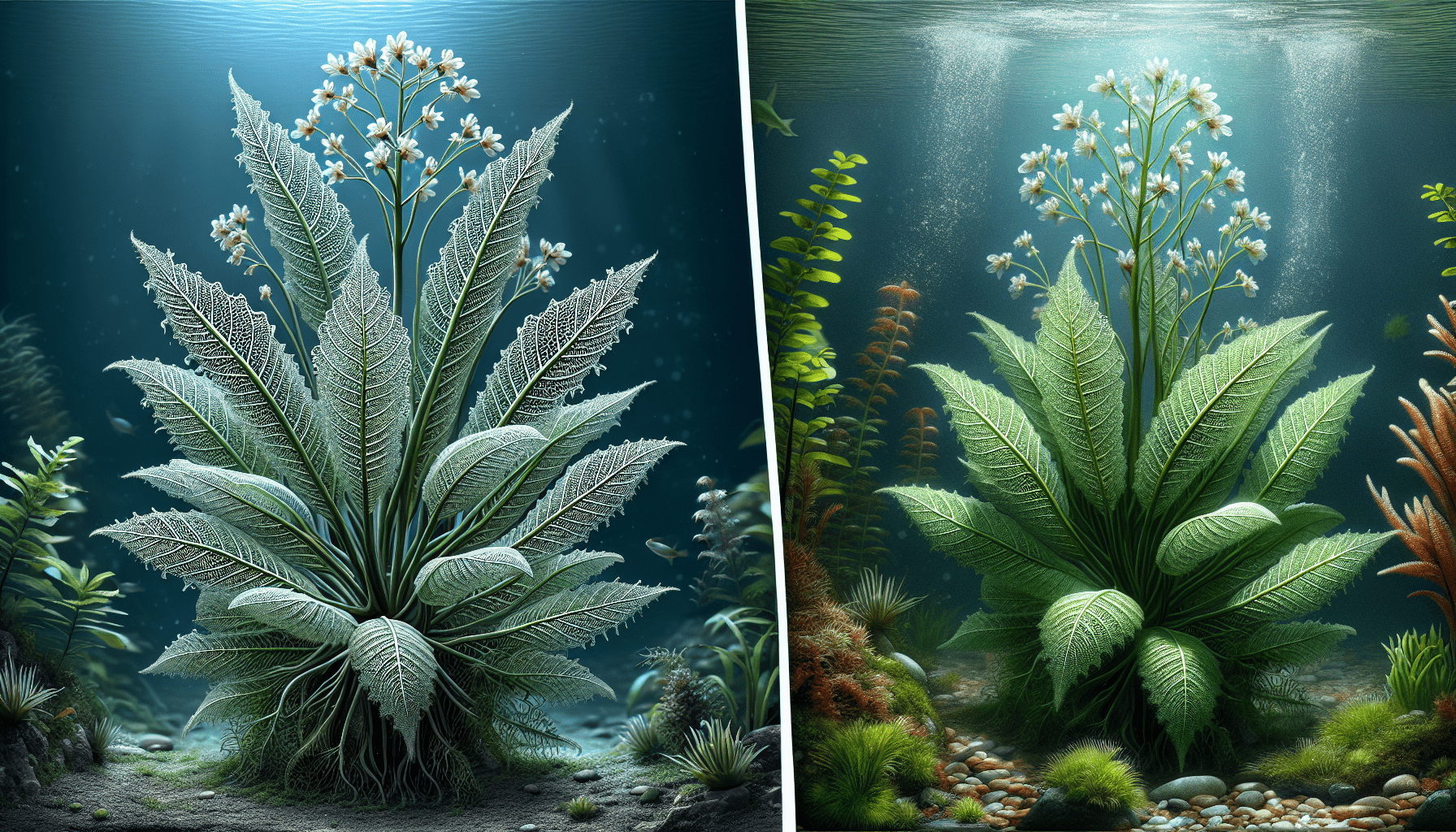
Characteristics of Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Physical Appearance
The Large Madagascar Lace Plant, also known as Aponogeton madagascariensis, is a sight to behold. It is predominantly distinguished by its lace-like leaves that exude an air of delicacy and complexity. These leaves, extending up to a length of two feet, are a vibrant, translucent green, interspersed with a lattice of thin, dark veins. Intricately formed holes give the leaves their signature perforated look. The plant usually grows several long-stemmed leaves and a tall, elongated flower spike.
Growth Habit
As a perennial herbaceous aquatic plant, the Large Madagascar Lace Plant exhibits a growth habit that befits its watery domain. Its tuberous rhizome is rooted in the underwater substrate from which multiple leaves dynamically emerge. Their orientation is usually towards the surface of the water, where they often form a floating rosette.
Distinct Features
Beyond the unique lace-like structure of its leaves, the Large Madagascar Lace Plant boasts two key exceptions that further set it apart. Firstly, it bears substantial, tubular inflorescences that carry numerous tiny white flowers, hinting at its tropical lily heritage. Secondly, its ability to perform photosynthesis even in reduced light, thanks to its glass-like leaf structure, enhances its position as a crucial ecological inhabitant.
Origins and Habitat of Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Natural Habitat
Evocative of its name, the Large Madagascar Lace Plant is indigenous to the marshy waters of Madagascar. It thrives in subtropical freshwater bodies, such as ponds, swamps, and streams, laden with high nutrient content. The suitable depth and current of water lets the plant anchor itself securely and fulfill its photosynthetic needs.
Geographical Distribution
While the Large Madagascar Lace Plant was initially confined to the marshes and ponds of Madagascar, its exquisite beauty led to its wide cultivation. It is now globally distributed, predominantly serving as a centerpiece in public water features and private aquariums.
Climatic Conditions Preferred
During its history, this plant has adapted to subtropical climatic conditions. Given its aquatic nature, it prefers warm temperatures, ideally between 20 to 26 degrees Celsius. Ample sunlight, but not direct exposure, enables it to photosynthesize effectively.
Lifecycle of Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Seed
The lifecycle of the Large Madagascar Lace Plant begins with the germination of a seed. These seeds are enclosed in an envelope, which represents the true fruit of the plant. Upon being dispersed in water, the seeds initiate their growth journey.
Sprout
The sprouting phase sees the emergence of a small shoot from the seed, which grows downwards, anchoring itself into the substrate of the water body. Concurrently, leaves start to sprout from the shoot, initiating a cycle of photosynthesis necessary for the plant’s survival.
Flowering
Flowering is the most vibrant stage of its lifecycle. A long stalk bearing clusters of flowers emerges from the water surface. Successful blooming leads to the formation of seeds, which once dispersed, sustain the species’ continuation.
Propagation
Like most aquatic plants, asexual reproduction is commonly observed in Large Madagascar Lace Plants. It involves the development of new shoots from the rhizome, which mature to form independent plants.

Large Madagascar Lace Plant’s Ecological Role
Water Quality Influences
The Large Madagascar Lace Plant contributes to maintaining water purity by absorbing excess nutrients, thereby preventing nutrient pollution. Its extensive root network also helps to stabilize the water body and reduce soil erosion.
Habitat for Aquatic Animals
The intricate maze of this plant’s leaves provides a sanctuary for various aquatic creatures, acting as a spawning ground, nursery, or a hideaway from predators.
Role in Ecosystem
In the ecosystem, this plant plays a vital part in promoting biodiversity. Moreover, it aids in the oxygenation of water, crucial for the survival of multiple aquatic organisms.
Cultivation of Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Propagation
Propagation, primarily carried out by bulb or tuber division, is relatively straightforward. Once set in a suitably warm, well-lit tank with nutrient-rich substrate, the Lace Plant grows effectively.
Suitable Aquatic Conditions
These involve warm waters with a mild neutral pH range and a well-aerated environment, which imitates their natural habitat.
Maintenance and Care
Regular trimming of decayed leaves, monitoring of water quality, and prevention of overpopulation are essential practices for the plant’s well-being.
Potential Issues in Growing Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Common Diseases and Pests
The most frequent issues usually stem from imbalances in water quality, leading to diseases and pest infections. Proper monitoring and intervention can help mitigate these risks.
Optimal Growth Problems
Optimal growth can be hindered by different factors, including inadequate nutrients, inappropriate light conditions, or frequent disturbances within the tank.
Techniques for Addressing Issues
Addressing these concerns involves nurturing a balanced environment, ensuring optimal light and nutrient conditions, and promptly responding to signs of plant distress.
Uses of Large Madagascar Lace Plant
In Aquariums
Due to their aesthetic appeal, these plants serve as beautiful accents in freshwater aquariums. They also offer a natural habitat for aquatic pets and help maintain water quality.
For Ornaments
Their intricate latticed leaves and pleasing green color make them favored decorative elements in both private and public water features.
Research and Medicinal Applications
Research into this species, owing to their unique physical attributes and survivability, might yield significant insights into plant biology. Anecdotal references also suggest their potential medicinal uses.
Study and Research on Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Existing Studies and Findings
Current research uncovers the large Madagascar Lace Plant’s unique photosynthetic capabilities and its purpose in preserving water bodies. These insights hint at the species’ potential for broader ecological roles.
Ongoing Research Projects
Research is being conducted to understand its ornamental and medicinal value further, along with an examination of its evolutionary history and adaptive traits.
Potential Future Research Directions
Future exploration could delve into the possibilities of harnessing the lace plant’s unique attributes to address broader environmental challenges like water purification and erosion control.
Conservation Status of Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Conservation Efforts
Given their ecological significance, conservation efforts for Large Madagascar Lace Plants are essential. Stringent measures to protect their natural habitats and wise cultivation strategies can ensure their survival.
Threats to Species
Habitat destruction, over-harvesting, and climate change pose substantial threats to their existence.
Role of Human Activities
As custodians of the Earth, we must understand the impact of our activities on these plants. Encouraging responsible cultivation and reducing destructive practices can go a long way in preserving this unique species.
Fun Facts about Large Madagascar Lace Plant
Little Known Features
This plant’s leaf patterns are not just ornamental; they facilitate the plant’s survival in low light conditions, which is quite exceptional in the plant kingdom.
Interesting Discoveries
While known for their underwater growth, these plants can also survive on land, albeit in extremely humid conditions – a testament to their adaptability.
Trivia and Records
Being one of the world’s most beautiful aquatic plants, the Madagascar Lace Plant holds a unique position in the Guinness World Records for its elegance and architectural beauty, reflecting Nature’s own blend of form and function.