Immersing oneself in the world of aquatic plants can often lead to inspiring exhibitions of the often-overlooked biodiversity found within our waters. This piece, “What Is the Aquatic Plant Flower Water Milfoil,” invites you into a comprehensive exploration of one such botanical wonder: the water milfoil. This aquatic perennial, known for its whorl of featherlike leaves and petite blooms, brings life and balance to many freshwater ecosystems. Embark on a journey into the remarkable adaptive abilities and ecological importance of the water milfoil, offering insightful observations about its general biology, propagation, and role in aquatic biodiversity enrichment.
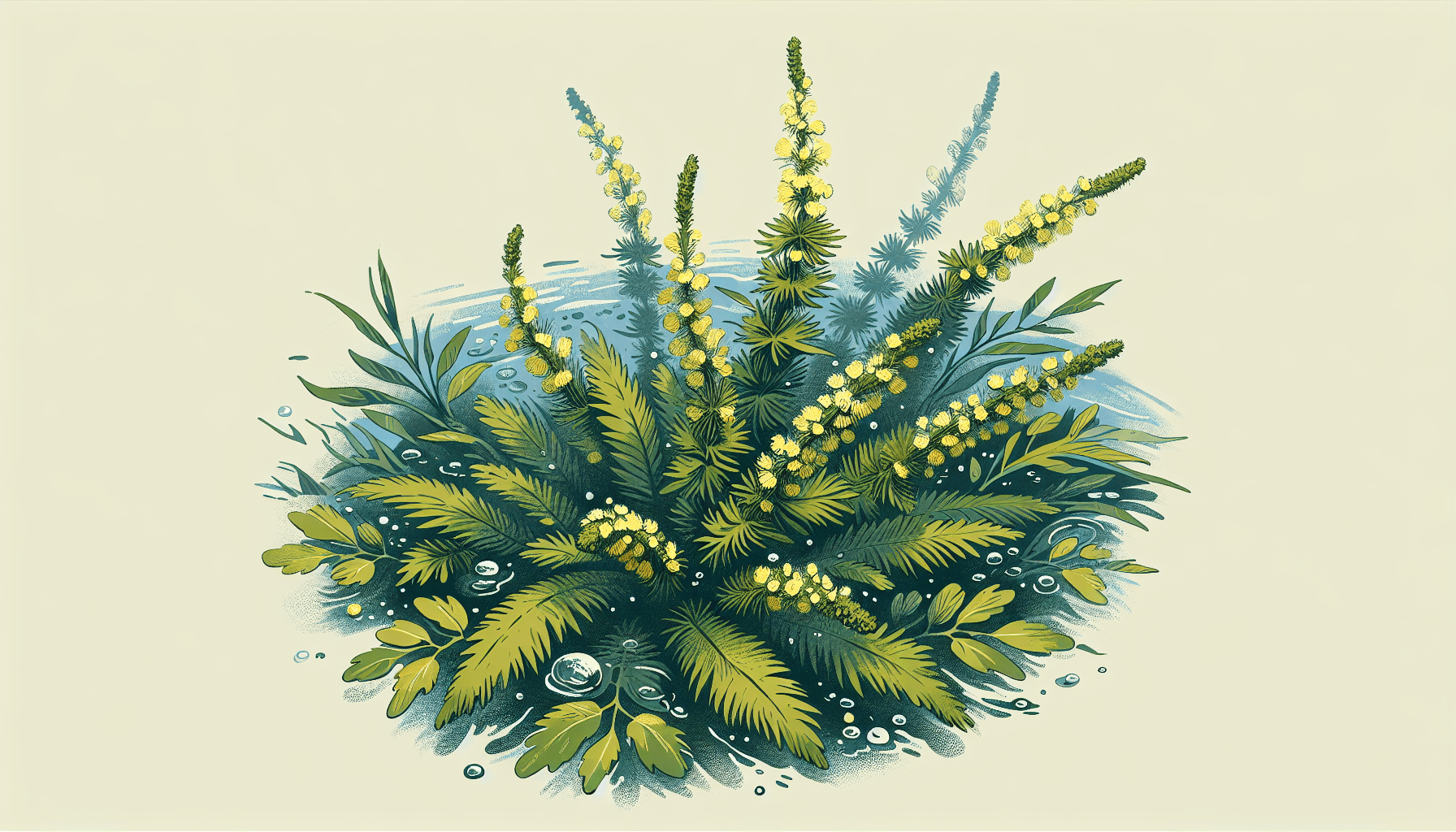
Understanding Water Milfoil
Understanding the diverse range of species categorized under the umbrella of aquatic life is no small feat. A particularly fascinating organism within this category is water milfoil—a genus of roughly 69 aquatic plant species known scientifically as Myriophyllum.
Definition of water milfoil
Water milfoil is an aquatic plant typically found in freshwater environments such as lakes, ponds, reservoirs, and even some slow-moving water bodies. These plants are part of the Haloragaceae family.
Common names and species
The water milfoil genus (Myriophyllum) consists of many species, some of which have multiple common names. Common names for different types of water milfoil include spiked water milfoil, whorl-leaf milfoil, and the Eurasian water milfoil, just to name a few.
Physical appearance and characteristics
A characteristic feature of water milfoil plants is their feather-like submerged foliage that range in color from bright green to reddish-brown. The leaves, arranged in circular whorls around the stem, are typically divided into thread-like leaflets. This plant often produces small, unassuming flowers which float on the water’s surface.
Habitat and Distribution
Unraveling the intricacies of water milfoil’s habitat and distribution provides a rich perspective on its ecology.
Natural habitats
Water milfoil thrives particularly well in still or slow-moving bodies of fresh water. These could range from ditches and canals to lakes and ponds.
Geographical distribution
Geographically, water milfoil species are widely distributed and can be found across the globe, from North America and Europe to Asia and Australia.
Season and conditions for growth
Water milfoil grows most prolifically during the warmer months of the year but can survive in both cool and warm climates. Optimal growth conditions include well-lit water with a depth of no more than three meters.
Lifecycle of Water Milfoil
The lifecycle of water milfoil is worth examining, as it provides insight into the plant’s adaptability and resilience.
Stages of the water milfoil lifecycle
The lifecycle of water milfoil consists of four main stages: germination, growth, flowering, and seed production. Its most aggressive growth stage occurs during the late spring to early summer period.
Length of each stage
The length of each stage varies depending on environmental conditions. However, high water temperature and light availability can significantly speed up the plant’s lifecycle, enabling it to complete a full cycle within a season.
Environmental factors affecting growth and reproduction
Water milfoil’s growth and reproduction are influenced by several external factors. High light availability, warmer temperatures, and nutrient-rich water are all conducive to the plant’s rapid growth.
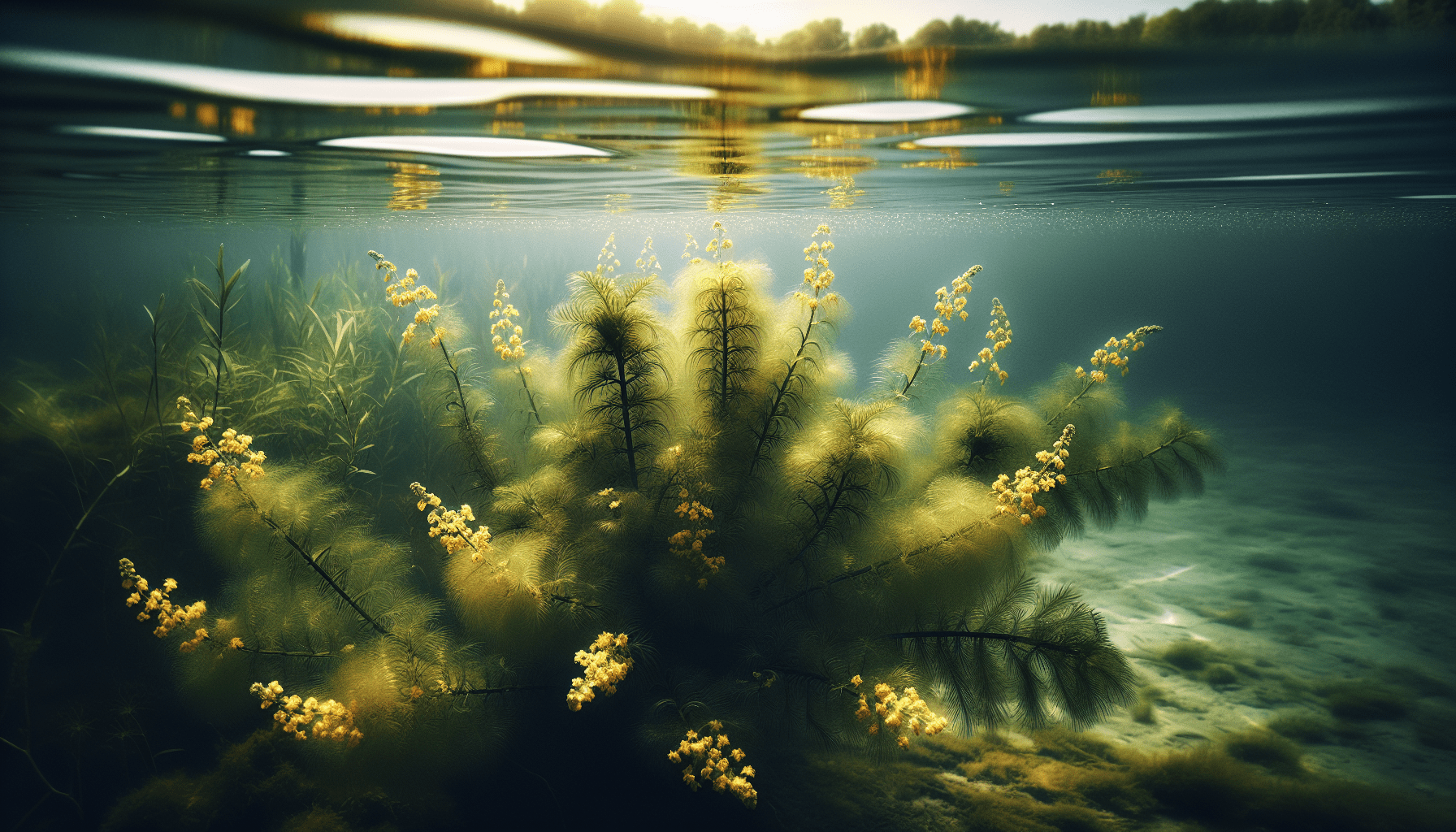

Importance to Aquatic Ecosystems
An appreciation for the role water milfoil plays in its ecosystem enables a better understanding of its overall ecological significance.
Role in sustaining aquatic life
Water milfoil supports a diverse range of aquatic life, serving as a habitat and food source for numerous species. Various micro and macro invertebrates and fish species depend on milfoil for cover and forage.
Contribution to water quality
Surprisingly, water milfoil contributes to water quality. It does this by stabilizing sediment and reducing wave action, which decreases the resuspension of sediments and thereby improves water clarity.
Interaction with other aquatic plants
Water milfoil’s rapid growth can hinder other aquatic plants by blocking light and absorbing nutrients. However, this same characteristic can also facilitate biodiversity by creating dense habitats.
Water Milfoil as Invasive Species
Despite their integral role in aquatic ecosystems, some species of water milfoil can become invasive, outcompeting native species and disrupting their habitats.
Identification of invasive milfoil species
Eurasian water milfoil (Myriophyllum spicatum) is a notable invasive water milfoil species, identifiable by its feather-like leaves whorled in groups of four to five around the stem and its reddish flowers.
Impact on native flora and fauna
Invasive water milfoil can significantly affect native flora and fauna by outcompeting them for resources and drastically altering their habitat, which can lead to a decrease in biodiversity.
Strategies to control and manage invasive milfoil species
Various strategies are undertaken to manage invasive water milfoil, including mechanical removal, use of herbicides, and the introduction of natural predators.
Reproduction and Dispersal
Understanding the plant’s methods of reproduction and dispersion provides further insight into its ability to colonize various habitats.
Reproduction methods
Water milfoil reproduces through both sexual and asexual means. Sexual reproduction occurs via flowering and seed production, while asexual reproduction involves the plant fragmenting and the fragments producing new plants.
Factors influencing successful reproduction
Well-lit conditions, warm temperatures, and nutrient-rich waters contribute to successful water milfoil reproduction.
Methods of dispersion
Mainly, water milfoil spreads through plant fragmentation—a piece of the plant stem or root breaking off and regenerating into a new plant. Seeds and fragments may also be transported by water currents or on the feathers or coats of animals.
Uses of Water Milfoil
Beyond its ecological contributions, water milfoil boasts uses in traditional medicine and as a decorative component in aquariums.
Utilization in traditional medicine
Water milfoil has been used in traditional medicine for its purported anti-inflammatory, sedative, and antibacterial properties.
Guidelines for harvesting
Harvesting water milfoil must be carried out responsibly to ensure the preservation of the species and prevent the potential spread of invasive species.
Safety considerations for use
As with any plant, it’s essential to verify the species correctly before usage. This is especially critical for water milfoil, as some species may be toxic or harmful to certain organisms.
Threats to Water Milfoil
Water milfoil species face various threats—both environmental and caused by human activity—that can impact their survival.
Common environmental threats
Environmental threats to water milfoil include changes in water temperature, reduced light availability due to pollution or turbidity, and competition from other plant species.
Impact of human activity
Human activity—such as pollution, habitat disruption, and the introduction of invasive species—can significantly impact water milfoil populations.
Resulting ecological consequences
The decrease or loss of water milfoil populations can have significant ecological repercussions, as they play a critical role in providing habitats and moderating water clarity.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are crucial in protecting water milfoil from threats and ensuring the species continue to support their ecosystems.
Existing conservation efforts
Current conservation efforts range from public education and responsible harvesting practices to habitat preservation and the control of invasive species.
Future proposals for protection
Future proposals may include strengthened legislation, further research to inform management approaches, and community-led initiatives.
Community engagement in conservation
Engaging the community in conservation efforts can result in more meaningful, lasting outcomes. This could involve involved stewardship programs or citizen scientist initiatives.
Research on Water Milfoil
Scientific research has and continues to play a key role in understanding water milfoil and informing its management and conservation.
Scientific interest in water milfoil
Water milfoil piques scientific interest for its resilience, adaptability, ecological importance, medicinal properties, and potential as bioindicators.
Key findings to date
Significant findings include the plant’s reproductive strategies, its role in aquatic ecosystems, the threats faced by different populations, and successful management techniques for invasive species.
Future areas of research
Future research will likely delve further into water milfoil’s interactions with its environment, its specific ecological contributions, and how best to balance its conservation with the management of invasive species.