In the intricate realms of botanical and ecological studies, you may find a hidden gem called ‘Aquatic Plant Floating Islands.’ This seemingly fantastical name actually refers to a scientifically fascinating phenomenon that combines the versatility of aquatic plant species, engineering innovation, and ecological enhancement. As an inquisitive reader, your curiosity might pique at the amalgamation of these diverse ideas. This article will elucidate what exactly these ‘floating islands’ are, their origin, underlying principles, and environmental implications. Moreover, in your journey of understanding Aquatic Plant Floating Islands, you will also uncover their increasing relevance in contemporary ecological restoration and water management strategies.

Understanding the Concept of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
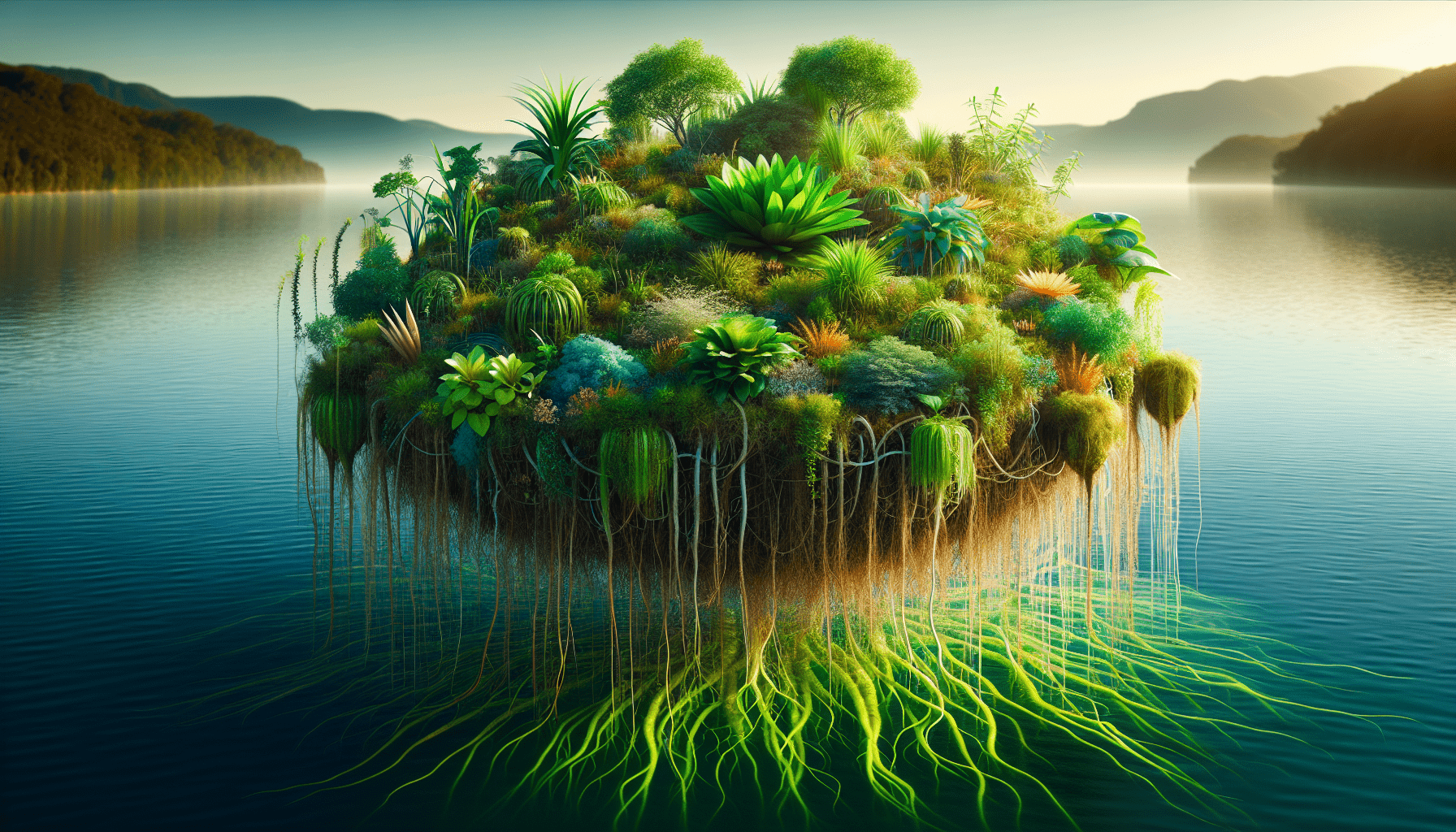
Definition and basic understanding of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Aquatic Plant Floating Islands are naturally occurring or man-made collections of aquatic plants, soil, and organic matter that form a mass which floats on bodies of water. They can be found in various forms and sizes, ranging from a few square meters to several hectares. They are delightfully distinct ecosystems, fostering a diverse range of flora and fauna that contribute significantly to biodiversity.
History and evolution of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Historically, Aquatic Plant Floating Islands have been documented for centuries in texts and tales globally. Their development and evolution are largely linked to natural processes such as erosion, vegetation growth, and decomposition, which create conditions for their formation and nourishment. Over time, these floating ecosystems have adapted to different environmental conditions, leading to uniqueness in composition and function.
Composition of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Types of plants found on floating islands
Floating islands are populated by a wide range of plant species. Typically, robust and adaptable aquatic plants, such as reeds, grasses, mosses, and ferns, dominate these islands. They are joined by water-tolerant tree species and many types of flowering plants, creating a vibrant and diverse botanical landscape that creates a myriad of micro-habitats.
Role of water, soil and organic matter
Water, soil, and organic matter play an integral role in the composition of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands. Water, being the primary medium, lends buoyancy to the islands. The soil builds up over time from dead and decomposing plant materials, particulate matter from the water column, and dropped organic debris. This fertile organic sediment provides vital nutrients for plant growth.
Importance of microbes and insects in the ecosystem
Microbes and insects vastly influence the function and structure of these floating ecosystems. They play an indispensable role in organic matter decomposition, nutrient cycling, and disease suppression. Furthermore, insects partake in the pollination of many plant species found on the islands, thereby influencing their propagation and survival.
Formation of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Natural occurrence of floating islands
Natural floating islands typically form through a process called vegetative rafting, where aquatic vegetation collects and holds together organic and inorganic debris creating a mass buoyant enough to float. They can also form from peat bogs breaking away from a river bank or land due to erosion.
Man-made floating islands: Methods and Materials
Man-made floating islands are constructed using a variety of materials such as bamboo, plastic, and polystyrene blocks, providing buoyancy. They are then planted with suitable aquatic or semi-aquatic plants which, over time, further enhances the stability and buoyancy of the island through root growth and accumulation of organic matter.
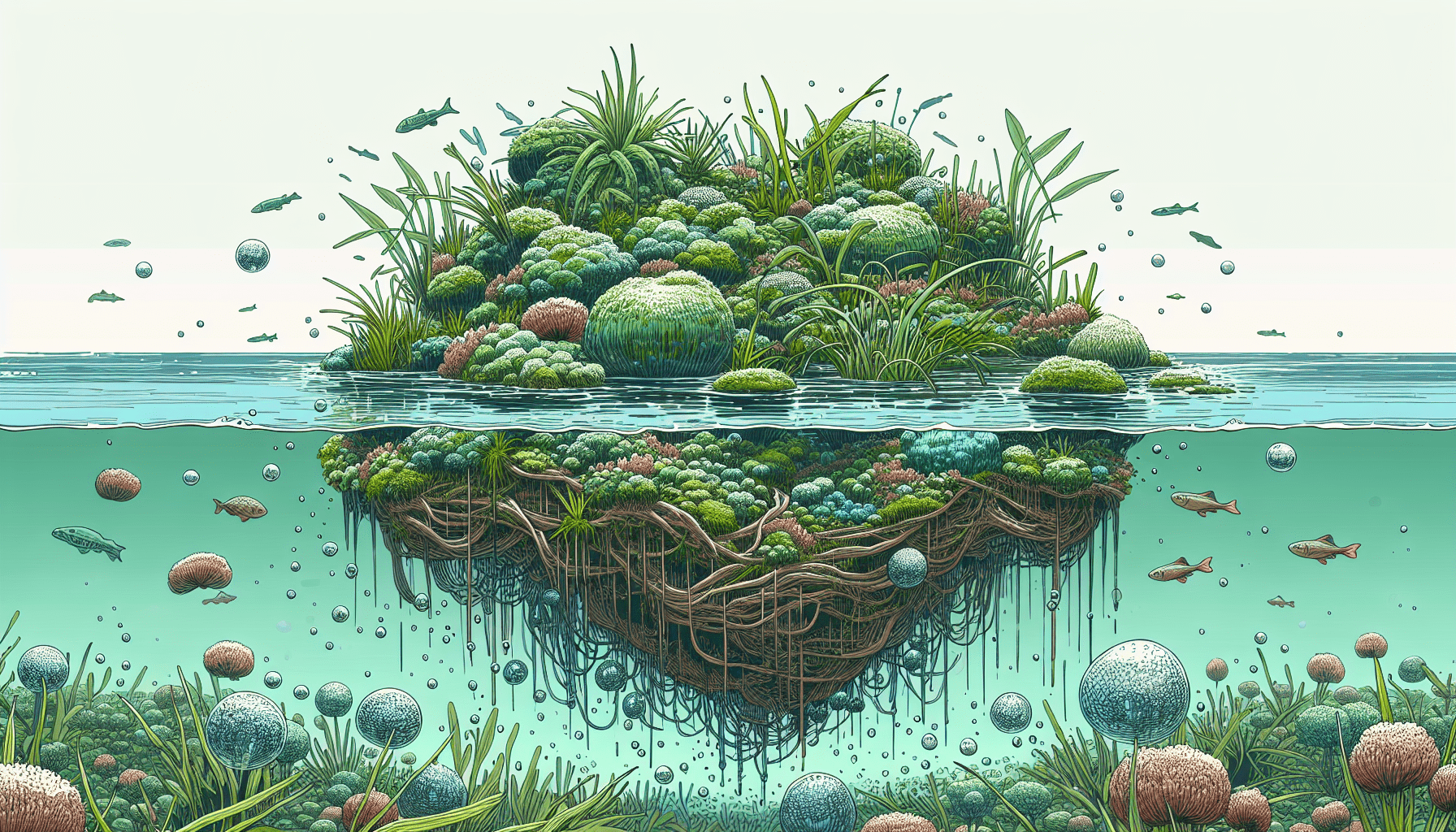
Habitats Provided by Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Bird and insect habitats
Floating islands provide birds with nesting and feeding sites, and for some migratory bird species, essential resting places during their long journeys. Moreover, the myriad of plant species on these islands attracts a wide variety of insects and provides them with diverse habitats and food sources.
Aquatic life beneath floating islands
The underside of floating islands provides a suitable environment for a rich array of aquatic life such as invertebrates, crustaceans, amphibians, and fish. They seek shelter, breed, and hunt beneath these islands, as the dense root systems provide ample hiding spaces and breeding grounds.
Plant species found on floating islands
The high nutrient content of the floating islands allows for the growth of diverse plant species. Beyond aquatic and semi-aquatic plants, these islands can support tree saplings, ferns, moss, and a host of flowering plants that contribute to the biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Ecological Role of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Biodiversity and ecosystem services
Floating islands act as habitats for a wide variety of species, contributing to increased biodiversity. They provide a range of ecosystem services, including nutrient cycling, habitat provision, and primary productivity, essential for supporting marine life.
Carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation
Aquatic Plant Floating Islands sequesters carbon, acting as a vital carbon sink. They help mitigate climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in plant biomass and soil.
Management of water quality
Floating islands improve water quality by filtering out pollutants, heavy metals, and excess nutrients through the process of phytoremediation. The plant roots and associated microbial communities play a crucial role in this process, thus contributing to healthier aquatic environments.
Importance to Aquatic Fauna
Role in fish breeding and survival
Aquatic floating islands provide sheltered breeding grounds for various fish species. The complex root systems and the shade provided by the plants offer refuge and protection to juvenile fish and contribute to their survival.
Food source for many water creatures
Floating islands are essential food sources for many aquatic species. Insects, amphibians, and waterfowl eat the plants directly, while the decomposing plant matter provides food for a wide variety of microbes and invertebrates.
Habitat for uncommon or endangered species
By creating unique habitats, floating islands can support rare or endangered species. Some species have adapted to thrive within this ecosystem, and its preservation supports their continued survival and propagation.
Threats and Challenges to Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Impact of pollution and human interference
Pollution and human interference pose significant threats to Aquatic Plant Floating Islands. Overfishing, habitat destruction, marine littering, and effluent discharge degrade the water quality, impacting the health and survivability of these islands and their inhabitants.
Climate change and rising water levels
Rising temperatures and sea levels brought about by climate change pose an existential threat to floating islands. Such changes can affect the water’s chemistry and physical properties, disrupt the growth of plants, and alter the overall integrity of the islands.
Invasive species and their effect on ecosystem balance
Invasive plant or animal species can threaten the delicate ecosystem of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands. Non-native creatures can outcompete local species for resources and alter the biodiversity imbalance, potentially disrupting the entire ecosystem.
Importance in Human Cultures
Aquatic Plant Floating Islands in folklore and tradition
Floating islands have been a part of folklore and tradition in many cultures, often associated with tales of mystery, magic, or spiritual significance. They symbolise fertility and abundance, given their capacity to harbor and sustain life.
Use for agriculture and fishing practices
In many parts of the world, humans have harnessed the productive potential of floating islands for agricultural and fishing practices. The fertile soil of the islands is ideal for cultivating certain types of crops, and their aquatic position provides easy access to fishing.
Countries or regions known for floating islands
Certain regions are known for their floating islands. For instance, the Uros people of Lake Titicaca in Peru live on large, man-made floating islands. In India, the Loktak Lake is famous for its natural floating islands called “phumdis.”
Conservation Efforts for Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Measures taken by governments and environmental bodies
Governments and environmental bodies worldwide have undertaken measures to protect and conserve Aquatic Plant Floating Islands. These include formal legislation, environmental education initiatives, and restoration projects designed to maintain these unique ecosystems.
Successful case studies of conservation
Several successful case studies showcase the recovery and restoration of these lands through targeted conservation efforts. These cases emphasize the importance of community involvement, sustainable practices, and strategic intervention in ensuring the survival of these unique ecosystems.
The role of community involvement and eco-tourism
Community involvement plays a vital role in the conservation of floating islands. Many communities have taken ownership of local floating islands, caring for them as precious resources. Additionally, eco-tourism has emerged as a sustainable means of promoting conservation while offering socio-economic benefits to the local communities.
Future Perspectives for Aquatic Plant Floating Islands
Innovative uses for sustainable living
The future may see more innovative uses of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands for sustainable living. From floating gardens to self-sustaining habitats, the potential applications are vast and could play a significant role in addressing some of our most pressing environmental challenges.
Potential risks or benefits in the context of climate change
In the context of climate change, floating islands could face threats from rising temperatures and sea levels. However, they could also offer potential benefits in terms of carbon sequestration and serving as sanctuary habitats for species displaced by climate change.
Ongoing research and scientific discoveries
Ongoing research and scientific discoveries continue to uncover more about these fascinating ecosystems. From their role in preserving biodiversity to their potential for mitigating climate change, every new finding contributes to the growing body of knowledge that underscores the importance and complexity of Aquatic Plant Floating Islands.