In the exploration of “What Is The Aquatic Plant Floating Heart”, the thrust of the narrative remains centered on this distinctive flora that graces our water bodies. In the forthcoming article, your comprehension of the floating heart, a fascinating variety of water hyacinth, will be considerably enhanced, as the discussion perambulates through its morphology, ecological significance, and role in various cultures. As you immerse yourself in learning about this aquatic plant, anticipate enriching your knowledge and nourishing your intellectual curiosity in environmental biodiversity.

Overview of Floating Heart
Floating Heart, a charming aquatic plant, exudes a whimsical beauty that is enchanting to observe yet poses significant ecological implications due to its aggressive, invasive tendencies. This member of the Nymphoides family is distinguished by its heart-shaped leaves and small, striking flowers. Notwithstanding its aesthetic appeal, the Floating Heart’s ability to rapidly colonize bodies of water often wreaks havoc on aquatic ecosystems.
Scientific Classification
The scientific classification of a Floating Heart belongs to the plant kingdom, specifically the Angiosperm phylum within the Asterids class. It falls under the Gentianales order, and is part of the Menyanthaceae family. Its genus is Nymphoides, a group commonly referred to as floating heart or water fringe.
Native Regions
The natural habitat of the Floating Heart species is primarily in Asia, particularly in countries including Japan, the Philippines, and Thailand. However, it has successfully spread and adapted to various other parts of the world, emphasizing its ability to survive in a range of climatic conditions.
Common Names
Aside from the Floating Heart, this plant is commonly known as water fringe, crested floating heart, small floating heart, and water snowflake. The diversity of names is largely credited to the plant’s wide distribution and unique aesthetic features.
Physical Characteristics of Floating Heart
The Floating Heart, despite being an invasive species, is undoubtedly a visual delight. The combination of its leaf and flower structure presents a captivating sight.
Shape and Size
The Floating Heart tends to grow approximately 6 inches in height. The plant, true to its name, consists of small, heart-shaped leaves that float on the water’s surface. These leaves typically have a span of about 2 inches.
Leaf Description
The leaves are heart-shaped, light green in color, and are arranged alternately along the stem. Remarkably, the leaves have a waxy coating making them water-repellent. During warm weather, leaves emerge above the water surface, while during cooler periods, they float directly on the water.
Flower Description
The flowers of the Floating Heart are its most remarkable feature. These are small, yellow or white flowers with fringed petals, infusing a delicate and ethereal beauty to a water body.
Habitat and Distribution
Floating Heart’s widespread distribution reveals its inherent adaptability and resilience across various habitats.
Preferred Environment
Floating Heart thrives in aquatic environments. Ponds, lakes, canals, and slow-moving rivers are the primary habitats for this species. The plant prefers freshwater bodies with a neutral to slightly alkaline pH.
Global Distribution
Despite originating from Asia, Floating Heart has successfully invaded various regions worldwide. It is found in North America, Australia, and parts of Africa, demonstrating its global presence.
Indigenous vs Invasive Presence
While Floating Heart is indigenous to parts of Asia, in many regions, it’s an invasive species. Its rapid proliferation and spread often disturbs local aquatic ecosystems, making it a concern for conservationists.
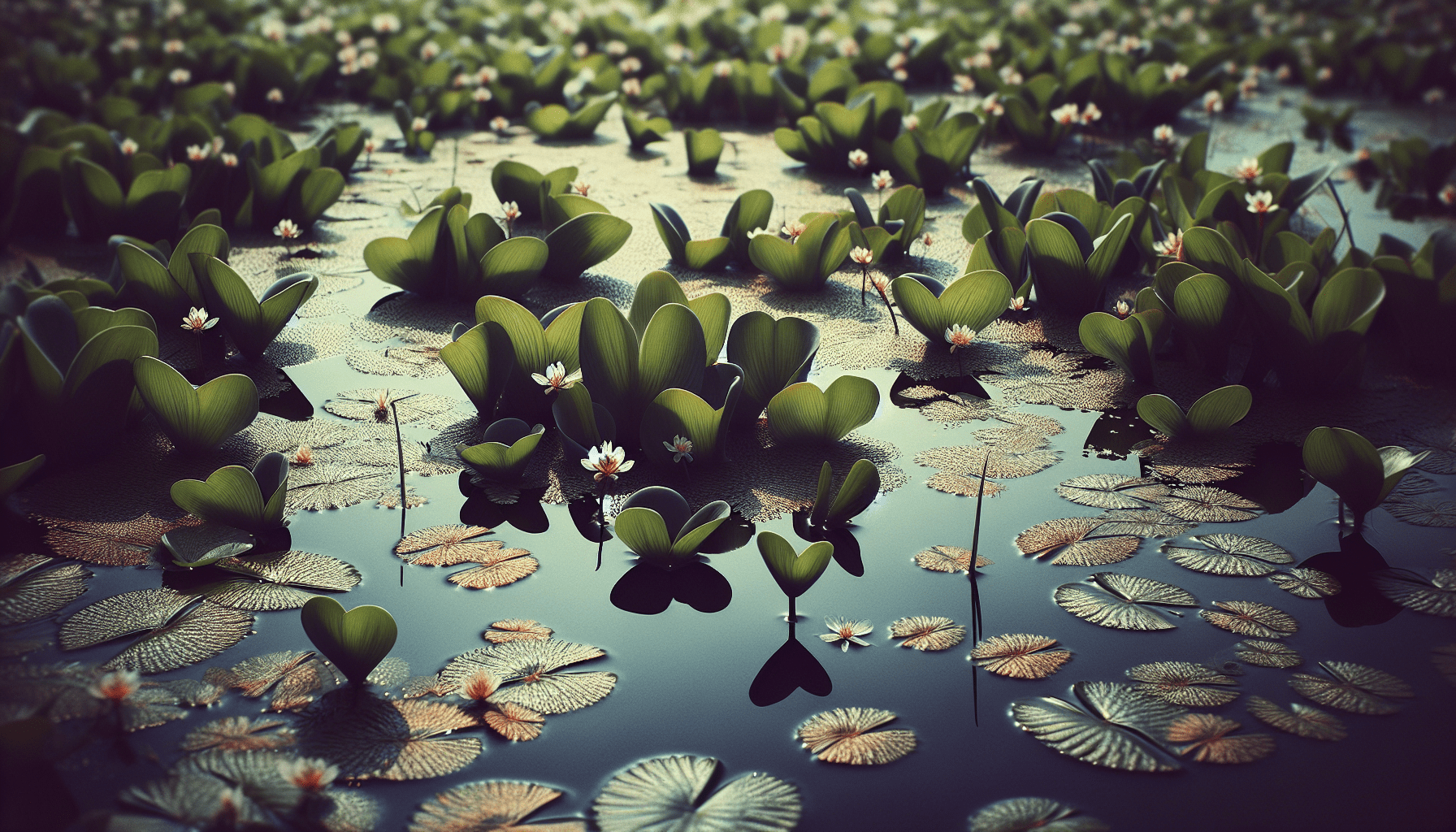
Life Cycle of Floating Heart
Floating Heart’s life cycle is characterized by rapid growth, effective reproduction, and impressive longevity under optimal conditions.
Growth Stages
Floating Heart grows through a sequence of vegetative and flowering stages, a common growth pattern in many aquatic plants. The vegetative stage witnesses the spread of the plant across the water surface, followed by the flowering stage when small, delicate buds evolve into fringed, charming flowers.
Reproductive Strategy
Floating Heart reproduces both sexually through seeds and asexually through stolons. The ability to reproduce vegetatively allows it to colonize large areas rapidly, contributing significantly to its invasive potential.
Life Span
While the exact lifespan of Floating Heart is not well documented, like many perennial aquatic plants, it likely survives for several years given favorable conditions.
Ecological Role
Despite being an invasive species, the Floating Heart plays significant roles within the aquatic ecosystem including interaction with fauna, ecological contributions, and impact on water quality.
Interaction with Aquatic Fauna
Floating Heart can provide habitat and food for various aquatic fauna. However, when overgrown, it can displace native species and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem by monopolizing resources.
Role in Aquatic Ecosystem
Floating Heart helps to oxygenate the water which can support the aquatic life. Still, its rapid spread can eventually lead to over-shading of the water and deoxygenation, often causing harm to the aquatic life.
Impact on Water Quality
While Floating Heart helps in water purification by reducing nutrient pollution, its overgrowth can cause dissolved oxygen levels in the water to plummet, negatively impacting water quality.
Floating Heart as an Invasive Species
Floating Heart, due it’s rapid growth and reproductive capacity, is considered an invasive species in many regions outside its native range.
Issues Caused by Invasive Presence
The main issue caused by its invasive presence is the significant alteration and often deterioration of aquatic ecosystems. It can outcompete native plants for space and resources, churn out dense mats of vegetation that restrict light penetration and contribute to the depletion of dissolved oxygen in the water.
Methods of Spread
Floating Heart spreads through both seeds and fragmentation. Pieces broken off by water currents, animals, or human activities can result in new plant colonies.
Efforts to Control Spread
Controlling the spread of Floating Heart involves both mechanical and chemical methods. Manual removal is a labor-intensive but non-polluting option. However, in cases of large infestations, herbicides may be used.
Cultivation and Care of Floating Heart
While Floating Heart is relatively low maintenance, specific conditions and care measures can enhance its growth.
Ideal Growing Conditions
Floating Heart prefers full sunlight to partial shade and thrives best in neutral to slightly alkaline freshwater bodies. It also appreciates a rich nutrient base.
Common Pests and Diseases
Floating Heart is relatively resilient to pests and diseases. However, it must be protected from cold temperatures, as it is not frost-tolerant.
Maintenance Requirements
Pruning or manual removal of excess vegetation can help control the plant’s spread, crucial to prevent potential invasiveness.
Utilization and Benefits
While Floating Heart does hold certain risks, it also offers various benefits.
Use in Aquatic Gardening
Floating Heart, due to its lovely flowers and leaves, can add beauty to ponds and water gardens. However, its growth and spread must be carefully monitored to prevent invasiveness.
Potential Medicinal Uses
Though largely unexplored, some believe that Floating Heart offers potential medicinal benefits. Based on traditional usage in parts of Asia, it’s seen as a potential source of natural remedies.
Culinary Uses
In certain regions, young floating heart leaves and shoots are consumed as a vegetable. However, this use is relatively limited and localized.
Myths and Symbolism associated with Floating Heart
Floating Heart, with its unique, charming appearance, has been subjected to a range of myths and symbolism.
Cultural Significance
In several Asian cultures, Floating Heart is seen as a symbol of purity and peace due to its tranquil, serene appearance.
Common Myths
A common myth associated with Floating Heart is that the presence of this plant can predict rainfall. This belief, however, is more folklore than fact.
Symbolism in Literature and Art
Floating Heart often features as an emblem of love and affection in art and literature, given its heart-shaped leaves and delicate, charming flowers.
Conservation Status and Threats
The Floating Heart’s conservation status and associated threats are primarily associated with its invasive nature.
Current Conservation Status
While not globally assessed for conservation status, in regions where it is invasive, efforts are focused not on its conservation but on its control to safeguard local biodiversity.
Threats to Population
In its native range, potential threats may arise from habitat degradation or pollution. In regions where it is invasive, control measures to limit its spread pose a threat to its populations.
Conservation Efforts
In native regions, no specific conservation efforts are noted for Floating Heart. In invaded territories, efforts aim at the containment and management of this species to protect local aquatic biodiversity.