Set to unveil the complexities of the aquatic flora world, this discourse precisely concerns the captivating yet largely misunderstood entity known as Flatsedge. This everlasting, resilient aquatic plant is increasingly becoming a pivotal species in wetland ecosystems. But what exactly is Flatsedge? How does it survive amidst the harsh realities of its challenging habitat? From unraveling Flatsedge’s biological features and ecological role, to reflecting upon its real-world importance, it promises to be an enlightening journey through the theory and practice of aquatic plant botany, centred around this quiet but influential player of water-laden landscapes. Every aspect of the flora veneer is gradually revealed, allowing you to gain a complete understanding of the mysterious Flatsedge, an unsung hero in the aquatic plant kingdom.
The Definition of Flatsedge
Flatsedge represents a group of perennial graminoides, part of the Cyperaceae, or sedge family. This category includes grass-like flowering plants that are typically found in wet habitats across the globe. Being a cosmopolitan species, flatsedge has adapted to various environmental conditions yet retaining its unique characteristics and playing significant roles in both the ecosystem and human activities.
General characteristics of flatsedge
Flatsedge presents a fascinating mix of properties, which serve as identification markers. Its three-ranked leaves sprout off from an unbranched stem, which has a notably triangular cross-section. Moreover, the flowers, usually small and inconspicuous, appear at the stem tips, often enclosed by a group of leaf-like bracts. This unique combination of traits sets flatsedge apart from other grasses and water plants.
Botanical attributes
Botanically, flatsedge distinguishes itself through its anatomy and reproductive traits. Its stem (culm), characterized by nodes and internodes, usually ends in a compact inflorescence called a spikelet. The flowers, minus petals, embrace a modified leaf or scale that engulfs the ovary. The fruit, an achene, creates a hard outer shell to safeguard the seed within.
The Flatsedge species
The flatsedge genus, Cyperus, consists of approximately 600-690 species. They appear in different forms, ranging from dwarf species hardly reaching several centimeters to large ones that can grow over a meter tall. Some of the commonly recognized species include the Cyperus papyrus, famed for its use in Ancient Egypt, and the Cyperus esculentus, otherwise known as the yellow nutgrass, well-regarded for its edible tubers.
Physical Description of Flatsedge
Understanding the physical structure of flatsedge, including its leaf architecture, root system, and flower and seed characteristics, is crucial in its identification and classification.
Leaf structure
The leaves of flatsedge are generally flat and blade-like, growing from the base of the plant in three ranks. This three-ranked design forms a characteristic pattern that goes up the stem in a spiral fashion, making flatsedge distinguishable from other plants.
Root system
Flatsedge features a fibrous root system that is shallow and spreads horizontally, often forming thick mats. Sometimes, the roots form underground stems known as rhizomes, which aid in the plant’s propagation. This diverse root system equips it for survival in various conditions, particularly waterlogged environments.
Flower and seed characteristics
Flatsedge flowers are unique, often inconspicuous, formed in clusters or solitary, and lack petals. They are typically surrounded by bracts, giving the impression of a single flower head. After flowering, the plant forms a small, dry fruit called an achene, which typically contains a single seed. These seeds can remain viable for several years, aiding in the plant’s widespread dispersion and longevity.
Habitat and Distribution of Flatsedge
Flatsedge is a cosmopolitan species known for its adaptive power and expansive geographical spread across diverse habitats.
Common locations and environments
Typically, flatsedge thrives in damp and wet locations, including marshes, bogs, wetlands and along water bodies like rivers, lakes, and ponds. They excel in poorly drained soils and can tolerate a certain degree of waterlogging, making them a familiar sight in swamps and wet pastures.
Adaptation to aquatic habitats
Being largely semiaquatic, flatsedge has evolved several adaptations, including its fibrous root system, which allows it to withstand waterlogged conditions. Its ability to grow in both standing water and on dry soil, along with its tolerance for varying pH levels, substantiates its adaptability in diverse aquatic habitats.
Geographical distribution of the species
Flatsedge species are globally distributed, with notable presence across temperate, tropical, and sub-tropical regions. They are native to parts of North and South America, Africa, Europe, and Asia. This cosmopolitan distribution is largely due to their tolerance to a wide range of environmental conditions and their efficient dispersal mechanism.
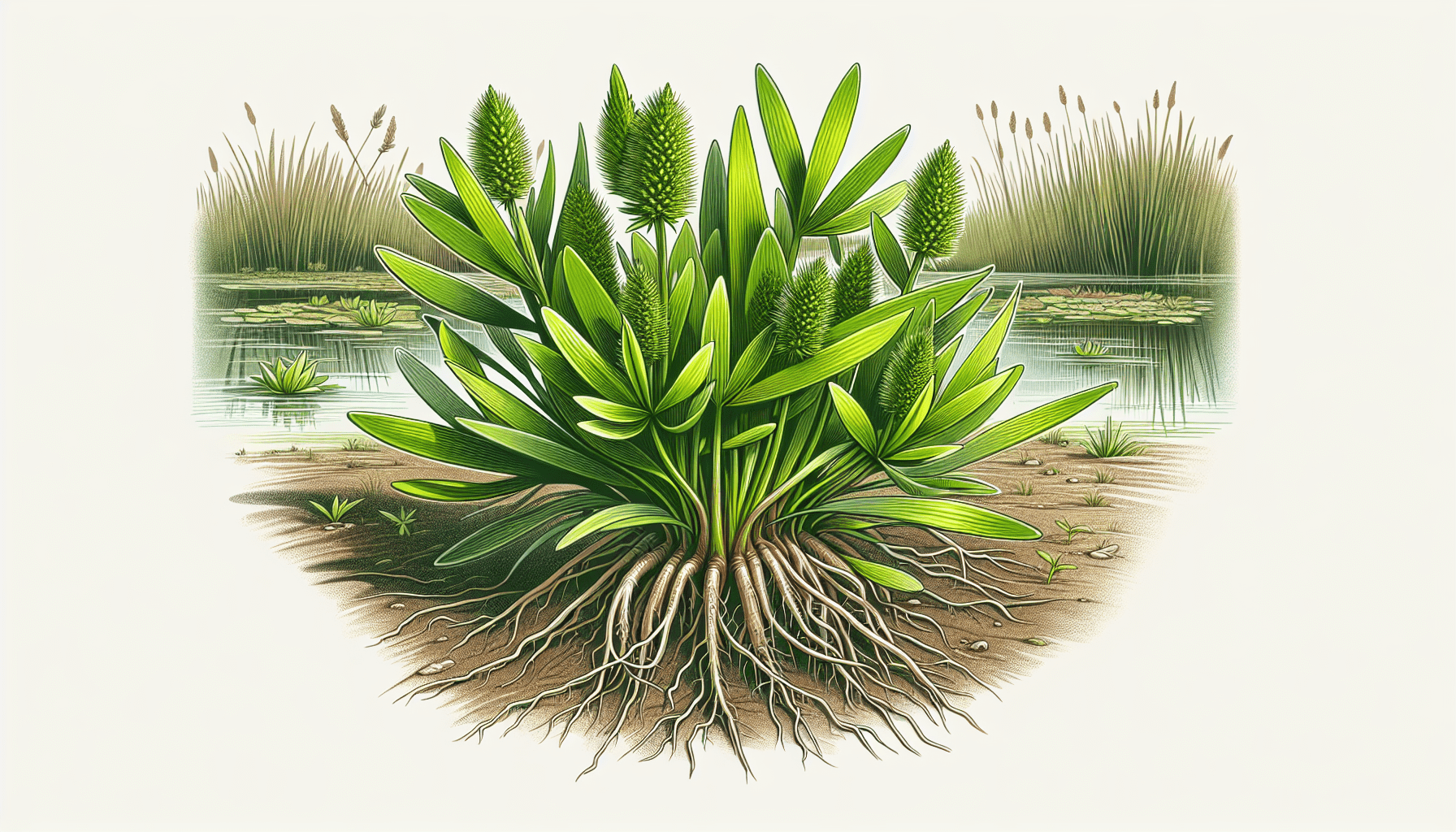
Flatsedge as an Aquatic Plant
As an aquatic plant, flatsedge plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance, providing habitat, and contributing to biodiversity.
Common aquatic varieties
While many flatsedge species are terrestrial, a few thrive as aquatic plants. Possibly the most famous is the Cyperus papyrus, an aquatic perennial native to Africa. Another species, Cyperus alternifolius, often dubbed the umbrella papyrus, is equally suited for water gardens and ponds.
Role in aquatic ecosystems
In their aquatic environment, flatsedge plants contribute to several ecosystem functions. They help in filtering runoff water, thus improving water quality. They also provide food and habitat for an array of wildlife, hence maintaining the biodiversity balance.
Adaptations for aquatic life
Flatsedge adaptation for aquatic life is facilitated by their unique structural features, such as their robust root system, which enables them to anchor firmly in water or waterlogged conditions. In addition, their fibrous roots also aid in exchange of gases, making them suitable for such low-oxygen environments.
Flatsedge in Agriculture
Despite being perceived famously as a troublesome weed in agriculture, flatsedge has potential benefits if effectively managed.
Use in crop rotation
Flatsedge can play a part in crop rotation due to its ability to survive in waterlogged soils. This attribute allows it to be planted between main crop seasons, improving soil structure and preventing erosion.
Impact on crop yields
Nevertheless, flatsedge can also have a negative impact on crop yields. Certain species, like the Yellow nutsedge, are considered invasive weeds. They compete with cultivated crops for resources, affecting crop growth and resulting in yield reduction.
Managing Flatsedge in agricultural settings
Managing flatsedge in agricultural settings is crucial to optimize crop yields. This can be achieved through various methods, including correct water management, frequent field monitoring, targeted application of herbicides, and employing biological control agents.
Importance for Wildlife
The extensive network between the biodiversity and flora is conspicuous in the case of flatsedge. It provides nourishment, habitats, and contributes to biodiversity.
The plant as a food source
Flatsedge seeds are a significant food source for numerous bird species. In addition, some species of waterfowl are known to feast on their rhizomes and tubers thereby receiving nourishment.
Habitat provision for insects and birds
With its dense growth habit, flatsedge provides ideal habitats for a variety of insects and birds. The intricate web of leaves and stems offers protection to nesting birds and small mammal species.
Contribution to biodiversity
The presence of flatsedge in an ecosystem contributes to local biodiversity. It provides food and shelter to a number of organisms, which in turn attracts other species creating a cycle of life that sustains biodiversity.
Cultural Significance of Flatsedge
Flatsedge has enriched history, culture, and even folk medicine, making it noteworthy beyond its botanical identity.
Historical uses of Flatsedge
Historically, some species of flatsedge, especially Cyperus papyrus, were held in high esteem. The ancient Egyptians used this plant to make papyrus paper, boats, mats, and other items. Additionally, some species’ edible tubers have been used as a food source.
Cultural symbolism
In certain cultures, flatsedge has symbolic interpretations. For instance, in Christian iconography, it’s sometimes used to symbolize humility due to its common and unassuming nature.
Flatsedge in folk medicine
In folk medicine, several species of flatsedge have been used traditionally to treat a variety of ailments. Extracts from these plants have been taken to address issues like stomach disorders, skin diseases, and fever.
Environmental Impact of Flatsedge
Flatsedge interaction with the environment results in various impacts, both positive and negative.
Erosion control
Flatsedge plays a critical role in erosion control, particularly in wetland environments. Its dense root system holds the soil together, reducing soil erosion during heavy rains or flows.
Water quality improvement
Through a process called phytoremediation, flatsedge helps to improve water quality. It can absorb heavy metals from the water, aiding in cleaning polluted water bodies.
Invasive species concerns
However, not all aspects of flatsedge are beneficial. Some species, such as the Yellow nutsedge, can turn invasive in certain conditions, disrupting local ecosystems and outcompeting native plant species.
Cultivation and Care of Flatsedge
Cultivating flatsedge requires understanding of its growing conditions, propagation methods, and the ongoing care and maintenance it requires.
Ideal growing conditions
Flatsedge generally thrives in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. Wet, poorly drained soils serve as the ideal planting medium, although it can tolerate a range of soil conditions, including sandy, loamy, or clay.
Propagation methods
Flatsedge propagation is primarily through seeds or division of rhizomes. The seeds can be sown directly into the soil or started indoors before transplanting. Rhizomes can be dug up, divided and planted in early spring or fall.
Ongoing care and maintenance
Ongoing care for flatsedge generally involves ensuring that the planting medium remains moist. Additonally, flatsedge usually requires little to no pruning, but removing dead or yellowing leaves keeps the plant looking fresh.
Potential Threats to Flatsedge
Flatsedge faces several potential threats, including pests, diseases, and impact from climate change.
Pests and diseases
Flatsedge is relatively disease-free, but it can be affected by certain pests. Root-knot nematodes and aphids are the primary concern for this plant, while fungal diseases like rust can occasionally be an issue.
Environmental pollution
Environmental pollution through heavy metals can also create conditions that are toxic for flatsedge. Despite the plant’s ability to absorb certain heavy metals, excessive pollution can hinder its growth and development.
Climate change and its impact
Climate change presents potential challenges to flatsedge’s survival, particularly due to shifts in rainfall patterns. As a plant that thrives in inundated soils, prolonged periods of drought can have detrimental effects on flatsedge populations. On the other hand, extreme flooding could also disrupt the plant’s normal lifecycle patterns. Therefore, the prevalence and health of this species can serve as a bioindicator of climate change.