Extending your knowledge about aquatic flora, your intrigue will soon be directed towards a particular species known as the Dwarf Anubias (Anubias nana). This tropical freshwater plant, native to West Africa, holds immense prominence in the world of aquariums due to its dynamic resilience and minimalistic care requirements. In this article, you will obtain a comprehensive understanding of the biology, growth behavior, propagation and its noteworthy role in aquatic ecosystems. By the conclusion of your reading, you should be well equipped with the necessary insights to cultivate and appreciate the splendor that dwells within this robust aquatic plant, the Dwarf Anubias.
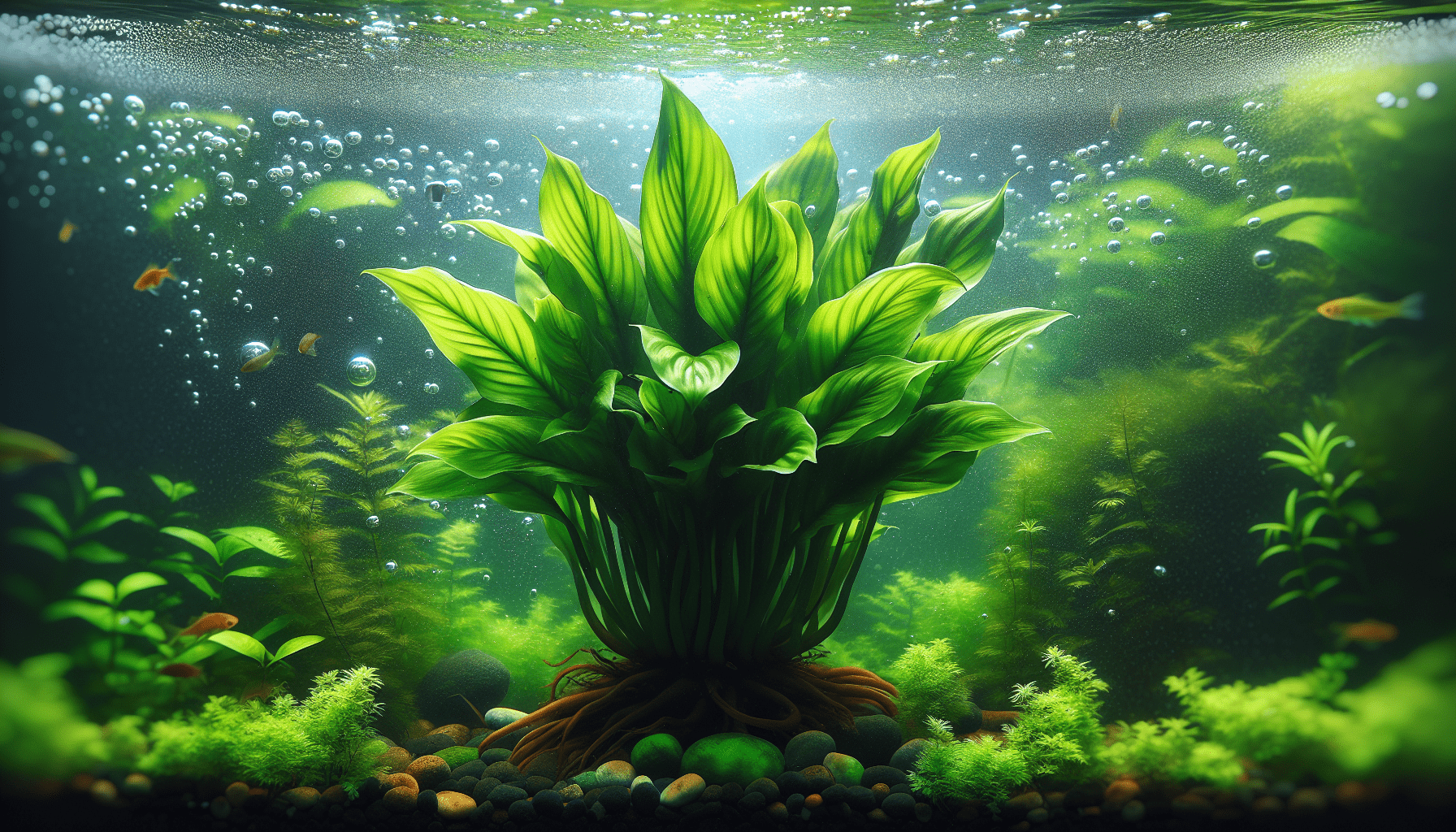

Overview of Dwarf Anubias
Dwarf Anubias, scientifically called ‘Anubias nana’, is a perennial, aquatic plant native to central and west Africa. This plant is popular among aquarium enthusiasts for its hardy nature and beautiful green foliage that bring aesthetic value to aquariums or fish tanks. This section provides a brief description, the origin, and the classification of Dwarf Anubias in the plant kingdom.
Description of the plant
Dwarf Anubias is an aquatic plant that features dark green, attractive, waxy leaves that feel leathery to the touch. The plant reaches up to a height of 5-10 cm and spreads to a width of 10-15 cm, making it an ideal candidate for foreground planting in aquariums. The plant has a slow growth rate, adding to its easy maintenance factor.
Origin and discovery of Dwarf Anubias
This plant is native to the tropical rainforests of central and west Africa. It was first discovered by botanists in the late 19th century. Its scientific name ‘Anubias’ was derived from ‘Anubis’, an Egyptian god, as the plant was wrongly identified as native to Egypt during its early discovery years.
Classification in the plant kingdom
Dwarf Anubias is classified under the order Alismatales and the family Araceae, often called the aroid or arum family. The genus Anubias contains approximately 30 species, all originating from Africa. Dwarf Anubias or ‘Anubias nana’ is one of the most popular species well-adored by aquarium hobbyists worldwide.
Physical Characteristics of Dwarf Anubias
Dwarf Anubias is a short, semi-aquatic plant possessing a robust structure and visually appealing foliage, making it a favorable choice for aquatic landscaping. Its physical features include specific characteristics of its stem, leaves, and the intriguing aspects of its growth pattern.
Description of the stems and leaves
The rootstock (rhizome) of Dwarf Anubias is robust and creeping. The leaves, measuring up to 12 cm in diameter, grow sparsely from the rhizome. The leaf margins are smooth and entire, and they are dark green, oval-shaped, and somewhat heart-shaped at the base.
Description of the flowers and seeds
Dwarf Anubias produces small, yellowish-green flowers that rarely bloom under submersed growth conditions. These flowers are not spectacular and are barely noticed by aquarists. An interesting fact about Anubias plants is the presence of heat-producing organ, called spadix, inside their flowers. Seeds follow the flowers, however, seed production is relatively rare.
Growth pattern and rate
Being a slow-growing plant, the Dwarf Anubias usually grows one leaf per month. The slow growth pattern makes it relatively easy for the owners to manage the plant in an aquarium setting. The plant thrives in varied conditions, provided slow modification to changes in the environmental parameters takes place.
Aquatic Habitat of Dwarf Anubias
Aquatic environments with specific parameters provide the optimal habitat for Dwarf Anubias to thrive. Understanding the preferred water conditions, temperature, light settings, and the plant’s natural geographical distribution can be instrumental for the successful cultivation of this plant.
Ideal water conditions
The hardiness of Dwarf Anubias enables it to adapt to varied water conditions. However, optimum growth can be achieved in clear and slow-moving waters with a slightly alkaline to neutral pH (6.0 to 7.5) . Though Anubias can tolerate lower light and poor nutrient conditions, providing adequate light and nutrients can enhance its vitality.
Preferred temperature and light settings
Dwarf Anubias thrives well in temperatures ranging from 22 to 28 degrees Celsius. This species, unlike many other aquatic plants, can survive and flourish in low-light conditions, making it an attractive choice for novice aquarium hobbyists. But, it’s important to maintain moderate lighting conditions as too low light can hinder the growth.
Natural habitat and geographic distribution
Anubias nana, true to its African origin, is specifically native to the dense forests of Cameroon and Nigeria. The plant is usually found in tropical rainforest ecosystems, attached to rocks and driftwoods, or sometimes rooted in the soil along the margins of the rivers and streams.
Cultivation and Care of Dwarf Anubias
Despite its ability to tolerate a range of conditions, specific culture practices can significantly aid in the successful cultivation and care of the Dwarf Anubias. These practices involve understanding and implementing the appropriate planting process, maintaining desirable water conditions, meeting its lighting needs, and implementing effective pruning strategies.
Planting process
In an aquarium, Dwarf Anubias is usually attached to rocks, driftwoods, or decorations using a fishing line or cotton thread. The roots should not be buried deep into gravel or sand, as such could lead to the rot of the rhizomes. In nature, the plant grows attached to various substrates but also grows in soil.
Water treatment and filtration
A slow-moving water current promotes the optimal growth of Dwarf Anubias. However, stagnant water conditions may promote the growth of algae on the leaves. Implementing a proper filtration system enhances water movement and prevents the build-up of toxic elements.
Lighting needs
Though the plant can survive in low light conditions, moderate lighting levels are ideal for it to flourish. Placing the plant in an area that receives indirect sunlight is beneficial, as direct sunlight may result in an influx of algae.
Trimming and pruning practices
The plant’s slow growth reduces the need for frequent pruning. Removal of yellow or spotted leaves to ensure healthy growth is generally enough. One should never cut the rhizome as the new leaves originate from it.
Propagation of Dwarf Anubias
The assiduous life cycle of Dwarf Anubias offers multiple propagation methods, both sexual and asexual. However, the propensity for asexual reproduction, specifically rhizome division, is stronger due to certain complexities involved in seed production.
Asexual reproduction through rhizome division
Rhizome division ranks as the most preferred method for Anubias nana propagation. With the presence of several leaves and roots, the rhizome can be divided into several sections, each capable of giving rise to a new plant, ensuring successful propagation.
Sexual reproduction through seed
In contrast to asexual reproduction, sexual propagation through seeds can be quite challenging because of the rarity of flower production and the subsequent seed formation under submerged conditions. However, if the flowers are pollinated, they can form berries containing the seeds.
Timeline and steps for successful propagation
Anubias nana propagation usually involves cutting a piece of the rhizome with a sharp knife, ensuring each piece has at least a couple of leaves. Upon replanting these pieces, new growth can be observed within weeks if optimum conditions are maintained.
Benefits of Dwarf Anubias in Aquariums
Beyond its ornamental attributes, Dwarf Anubias serves important ecological functions in aquarium settings. It’s credited for enhancing aesthetics, contributing to oxygen production, and nutrient cycling, as well as offering shelter to aquatic creatures.
Aesthetic advantages
With its lush green, glossy leaves and compact size, Dwarf Anubias significantly enhances the visual appeal of an aquarium. It is commonly used in the foreground or mid-ground and is often used in ‘Aquascaping’, a craft of arranging aquatic plants, rocks, and driftwood aesthetically in an aquarium.
Oxygen production and nutrient cycling
Anubias nana plays a crucial role in infusing oxygen into the aquarium water through photosynthesis. It also helps in nutrient cycling by absorbing excess nutrients, thereby maintaining water quality.
Shelter and habitat for fish and other aquatic creatures
With its broad, dense leaves, Dwarf Anubias provides a secure hiding spot for small fish and shrimps. They also provide substrates for fish to attach their eggs. Thus, this plant is a significant addition to a breeding aquarium.
Common Pests and Diseases Affecting Dwarf Anubias
Despite Dwarf Anubias’s resilience, it is susceptible to certain pests and diseases. Identifying common threats and implementing preventative measures can ensure the long-term health and vibrancy of the plant.
Types of common diseases
Brown or yellow spots on the leaves are the common symptoms of disease in Anubias nana. These symptoms usually signal deficiencies or excesses of certain nutrients. For example, yellow leaves could indicate iron deficiency, while brown spots might be a sign of potassium deficiency.
Pest infestations
‘Black beard algae’ is the most common pest infestation that affects this hardy plant. The algae appear as small black tufts on the leaves or stems and can stunt the plant’s growth. Other pests include snails, which can cause damage to the plant’s leaves.
Preventative measures and treatments
Addressing the nutrient deficiencies by adding the missing nutrients presents a common remedy for the diseases. For pest infestations, manual removal or introducing natural predators like shrimps or a Siamese Algae Eater can be effective. Regular checking and maintenance can also prevent the pests from establishing.
Role of Dwarf Anubias in Ecosystems
Dwarf Anubias’s role extends beyond aquariums, as it plays a significant role in natural ecosystems. Its contribution to biodiversity and nutrient cycling, along with its interactions with other organisms, shapes the ecosystem dynamics.
Contribution to biodiversity
Anubias nana contributes to biodiversity by providing shelter, breeding grounds, and food sources for various aquatic organisms. It’s broad, leathery leaves are a common site for certain fish species to deposit their eggs.
Role in nutrient cycling
Just like in aquariums, Dwarf Anubias in the wild plays an important role in nutrient cycling. It extracts nutrients from the water column, aiding in nutrient control and water purification, thus contributing to the health of its aquatic ecosystem.
Interaction with other organisms, both symbiotic and competitive
The plant has both competitive and symbiotic relationships with other organisms in its environment. While it competes with other plants for nutrients and light, it also shares a symbiotic relationship with fish and other aquatic creatures that rely on it for shelter and egg deposition.
Dwarf Anubias in Research and Medicine
Dwarf Anubias is of more value than just an aquarium plant. Its use in scientific research is ever expanding, and the potential medicinal benefits it may possess opens a new avenue for exploration.
Use in scientific research
Given its ability to thrive in various conditions, Dwarf Anubias is commonly used within scientific research focused on aquatic plant ecology. In addition, given its slow growth rate and low maintenance, it proves useful in long-term experiments.
Potential medicinal properties
While there is no documented evidence of its medicinal properties, the plant’s adaptability to varied conditions broadens the scope for research in phyto-remediation and potential medicinal properties.
Future prospects for Dwarf Anubias in medicine and biotechnology
The prospect of Dwarf Anubias’s future use in medicine and biotechnology lies primarily in genetic research. With advancements in technology, researchers are keen on exploring its genetic makeup to understand its adaptive mechanisms that could possibly unearth promising medical applications.
Conservation Status of Dwarf Anubias
Despite its popularity in aquarium trade, the discussion around the conservation status of the Dwarf Anubias, the threats it faces, and the urgency to protect them becomes crucial.
Current conservation status
As of the current knowledge, there is no specific documentation on the threatened status of Dwarf Anubias. However, like other aquatic plant species, it is certainly subject to habitat loss due to deforestation and aquatic life trafficking.
Threats and challenges to Dwarf Anubias populations
Possibly the most significant threats to Dwarf Anubias are habitat loss due to deforestation and the subsequent destruction for agriculture. Illegal collection and unregulated commerce for the pet trade also potentially threaten the plant populations in their natural habitats.
Efforts to protect and conserve Dwarf Anubias
There are continual efforts in place to protect the habitats of aquatic plants, including Dwarf Anubias. Captive breeding programs and sustainable agriculture practices can help relieve the pressures on the wild populations. Further research and knowledge about this plant species are instrumental in creating effective conservation strategies.
Dwarf Anubias, with its lush foliage and hardiness, proves to be more than just an ornamental plant. While it adds aesthetic value to aquariums, it serves significant ecological functions too. Its possibilities in research and potential medicinal applications broaden its relevance in today’s scientific landscape. A modicum of carefully planned care ensures the health and vibrancy of this plant, making it a popular choice among aquarium enthusiasts and researchers alike.