Embarking on a closer examination of particular floras, you may find yourself intrigued by the intricate realm of aquatic plants. Among these water-dwelling species, the Distant Flatsedge stands distinctly as a specimen you should most certainly be aware of. This article serves as an informative discourse on this unique aquatic plant, exploring its various characteristics, biological classifications, and its significance in the natural world. As you immerse yourself further, you will develop a deeper understanding of the Distant Flatsedge, fueling your knowledge in aquatic botany.
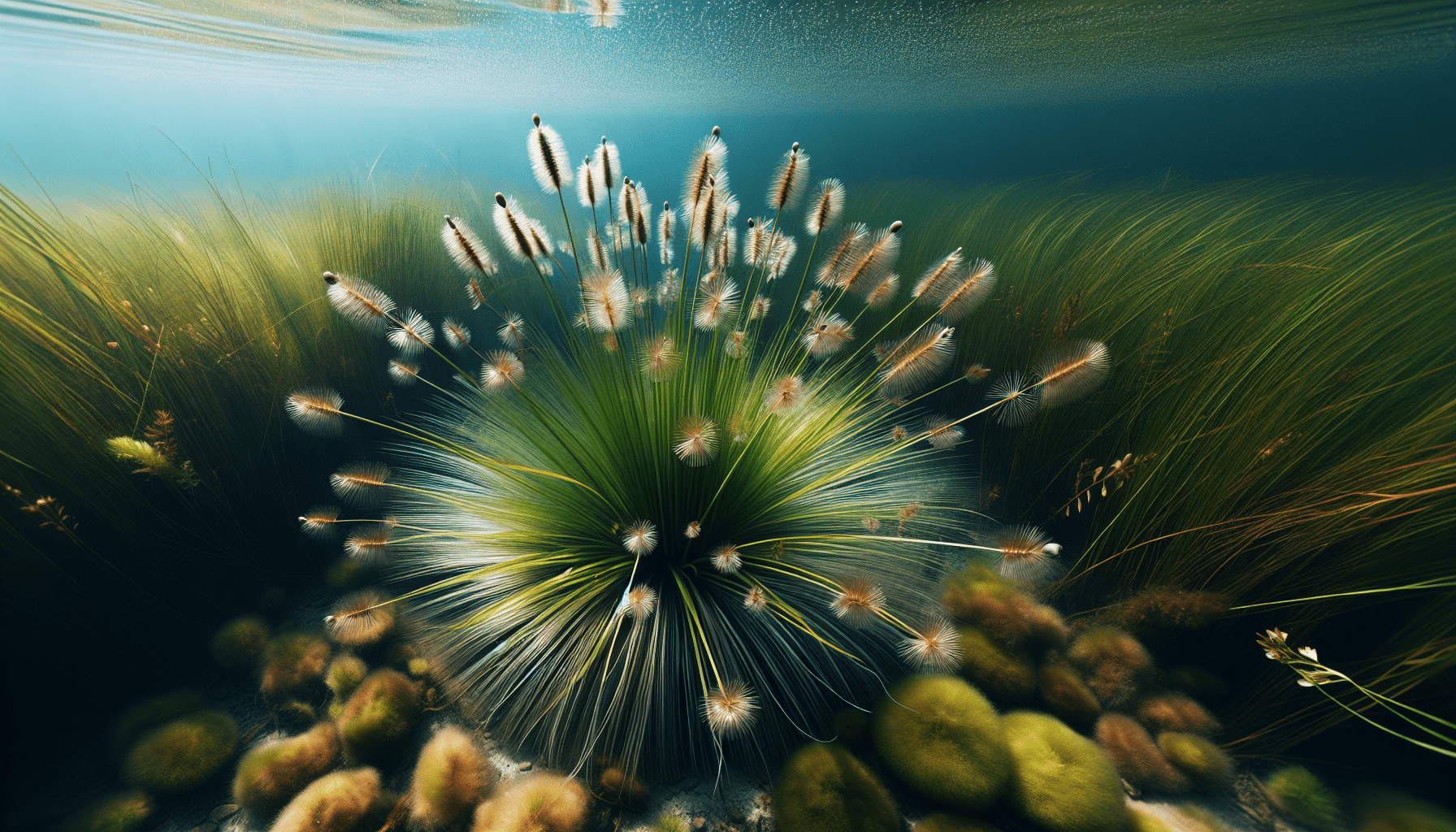

Overview of Distant Flatsedge
Distant Flatsedge is an intriguing aquatic plant species that piques the interest of botanists, ecologists, and horticulturists alike. This perennial weed from the Cyperaceae family is abundant in tropical and subtropical regions around the world and possesses an incredible adaptability to varied environmental conditions.
Scientific Classification
Scientifically, Distant Flatsedge is classified as Cyperus distans. It falls under the Kingdom Plantae, and is a part of the Tracheophyta phylum, after which it belongs to the class Liliopsida, order Cyperales, family Cyperaceae, and genus Cyperus.
Common Names and Synonyms
Alternatively, Distant Flatsedge is recognized by several common names across different regions, such as Umbrella Sedge and Faraway Flat Sedge. Some of the synonyms of the plant include Mariscus distans and Cyperus pygmaeus.
General Description
Distant Flatsedge is often recognized by its distinctive fascicled (bundled/meeting at a single point) culms which typically grow around 10-60 cm. The plant has a rhizomatous (horizontal, underground stem) nature, which aids in its growth and propagation.
Habitat and Distribution
Global Range and Distribution
A versatile plant species, Distant Flatsedge, is found in a wide range of distribution across the globe, particularly in tropical and subtropical climates. You will commonly encounter this plant in the South Central, Southeast, and North regions of the United States and in countries like India, China, and African countries.
Preferred Habitat Conditions
Distant Flatsedge naturally prospers in moist, damp habitat conditions. It is typically spotted thriving in wetlands, along the freshwater bodies, marshy areas, and low-lying pastures that are regularly flooded.
Physical Characteristics
Stem and Leaf Structure
The stem of Distant Flatsedge, also referred to as culms, is often trigonous (triangular in cross-section) and erect, with a height spanning between 10-60 cm. The leaves, on the other hand, are generally three-ranked, linear, and flat, with a glabrous (smooth) surface.
Flower and Fruit Characteristics
The inflorescence of Distant Flatsedge exhibits a compound anthela (a form of floral arrangement) and is commonly enclosed by leaf-like bracts. The flowers are small and regularly brownish-yellow. The fruits, usually achene (a single seeded fruit), are oblong or ellipsoid and brown in color.
Root System
The root system of the plant features a well-developed, extensive network of rhizomes that contributes significantly to the plant’s survival and aids in its proliferation across different habitats.
Life Cycle of Distant Flatsedge
Germination and Growth
Distant Flatsedge exhibits a fairly typical germination process to that of other aquatic plants. The cycle begins with the dispersion of seeds, which under suitable conditions, germinate into seedlings. Throughout the growth phase, the plants utilize their rhizomes for nutritional support and the extension of the plant’s reach.
Flowering and Seed Production
Flowering in Distant Flatsedge generally happens during the warmer months of the year. Following successful pollination, the flowers give way to achenes, which encapsulate the plant’s seeds.
Regeneration Capabilities
Distant Flatsedge can regenerate through seeds and vegetatively via its extensive rhizome system. As such, even a single rhizome fragment can result in a new plant when conditions are favorable.
Ecological Role
Role in the Ecosystem
Distant Flatsedge plays a vital role within the ecosystem. Its rhizomes often serve to stabilize the soil and prevent erosion in areas of its growth.
Importance for Wildlife
Various wildlife species are known to feed on Distant Flatsedge. The seeds serve as food for birds and small mammals, while the leafage is consumed by larger mammals.
Interactions with Other Plant Species
Distant Flatsedge, through its competitive growth pattern and extensive rhizome network, often out-competes other plant species for resources in the immediate vicinity.
Adaptations to the Aquatic Environment
Water and Nutrient Uptake
Distant Flatsedge’s rhizomes not only provide structural stability but also aid in the water and nutrient uptake from the saturated soils of its habitat, ensuring its survival in aquatic environments.
Survival Under Waterlogged Conditions
Its ability to thrive in waterlogged conditions can be attributed to the aerenchyma tissues (air-filled cavities) within its stem and roots that facilitate oxygen transport to underwater roots, thereby preventing suffocation due to excessive water.
Resistance against Pests and Diseases
The plant’s inherent resistance against several pests and diseases can also be attributed to its unique physiological adaptations, which allow it to survive in often challenging aquatic environments.
Uses of Distant Flatsedge
Culinary Uses
In some cultures, the tubers of Distant Flatsedge are consumed either raw or cooked. They are also transformed into flour and used in making bread.
Medicinal Uses
Distant Flatsedge has been used traditionally in some cultures for its medicinal properties. It has been known to treat issues like digestive problems and skin ailments.
Other Traditional Uses
The flexible and strong culms of Distant Flatsedge have been used in the past for thatching and mat-making.
Conservation Status and Threats
Current Conservation Status
Unlike many aquatic plants, Distant Flatsedge does not feature any significant conservation status or sit on the brink of extinction. This plant is widespread and often considered invasive in some areas due to its aggressive growth.
Potential Threats and Challenges
Potential threats for Distant Flatsedge primarily revolve around habitat destruction and pollution, which could hamper its growth and proliferation.
Efforts for Preservation
Given the current robust populations and its invasive potential, active preservation efforts for Distant Flatsedge are minimal. However, researchers and ecologists continue to monitor its growth patterns to avoid possible ecological imbalances.
Cultivation and Management
Cultivation Requirements
Being a robust and flexible plant, Distant Flatsedge demands little to begin cultivation. It thrives in moist and waterlogged conditions and can withstand a range of light conditions, from full sun to partial shade.
Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning and maintenance requirements are pretty basic for this plant. Manual removal of unwanted young plants can be done to manage its population.
Propagation Techniques
Propagation can be achieved through seeds dispersed from the achenes, or vegetatively, using rhizome sections.
Research and Studies on Distant Flatsedge
Noteworthy Research Findings
Various studies have been performed to understand Distant Flatsedge’s ecological role, physiological adaptations, and potential uses. One significant finding points to its potential use in hyperaccumulation, which means it could be used to extract pollutants from water bodies.
Ongoing Research Studies
Several ongoing studies on Distant Flatsedge aim to further investigate its ecological role, strategies utilized for survival in aquatic environments, and its potential medicinal benefits.
Future Research Possibilities
Future research opportunities extend to understanding its extensive network of rhizomes and how it could be potentially used in stabilizing eroding lands. Its potential role in treating wastewater and efficacy in phytoremediation also opens the avenue for future research possibilities.