In this discourse, you will gain a deeper understanding of the aquatic plant known as Cutleaf Water Milfoil. As a reader, your perceptions of the plant, its relevance and applications within the field of botany and environmental sciences will be broadened. Coverage will include exploring the plant’s unique morphology, ecological significance, and how it comes into play in aquatic ecosystems. The intention here is to shed light on the fascinating world of Cutleaf Water Milfoil to heighten your appreciation for the interplay of flora within aquatic habitats.
Scientific Classification
Your focused study on the aquatic plant Cutleaf Water Milfoil begins with its scientific classification. Through a systematic approach, it falls under the Kingdom Plantae, which comprises all green plants. This perennial plant is part of the Phylum Tracheophyta, which groups all vascular plants. Cutleaf Water Milfoil’s Class, Magnoliopsida, is representative of the so-called dicotyledons, and it belongs to the Order Lamiales, characterized by having two stamens and a two-lipped flower. On a more specific level, it is a member of the Family Plantaginaceae, also known as the plantain family. This brings us to its Genus, Myriophyllum, where the common characteristic is the feather-like leaves. Finally, the plant’s Species is pinnatum, which distinguishes it from other species within the Genus Myriophyllum.
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus and Species of Cutleaf Water Milfoil
Cutleaf Water Milfoil, in the taxonomic hierarchy of the biological classification, belongs to the Kingdom Plantae, the Phylum Tracheophyta, the Class Magnoliopsida, the Order Lamiales, the Family Plantaginaceae, the Genus Myriophyllum, and the Species Pinnatum.
Common Names across Different Languages
The names of this plant vary across different languages. It is known as Cutleaf Water Milfoil in English, Cut-leaved Water-milfoil in Irish, and Fougère D’eau in French, showcasing its wide linguistic and geographical spread.
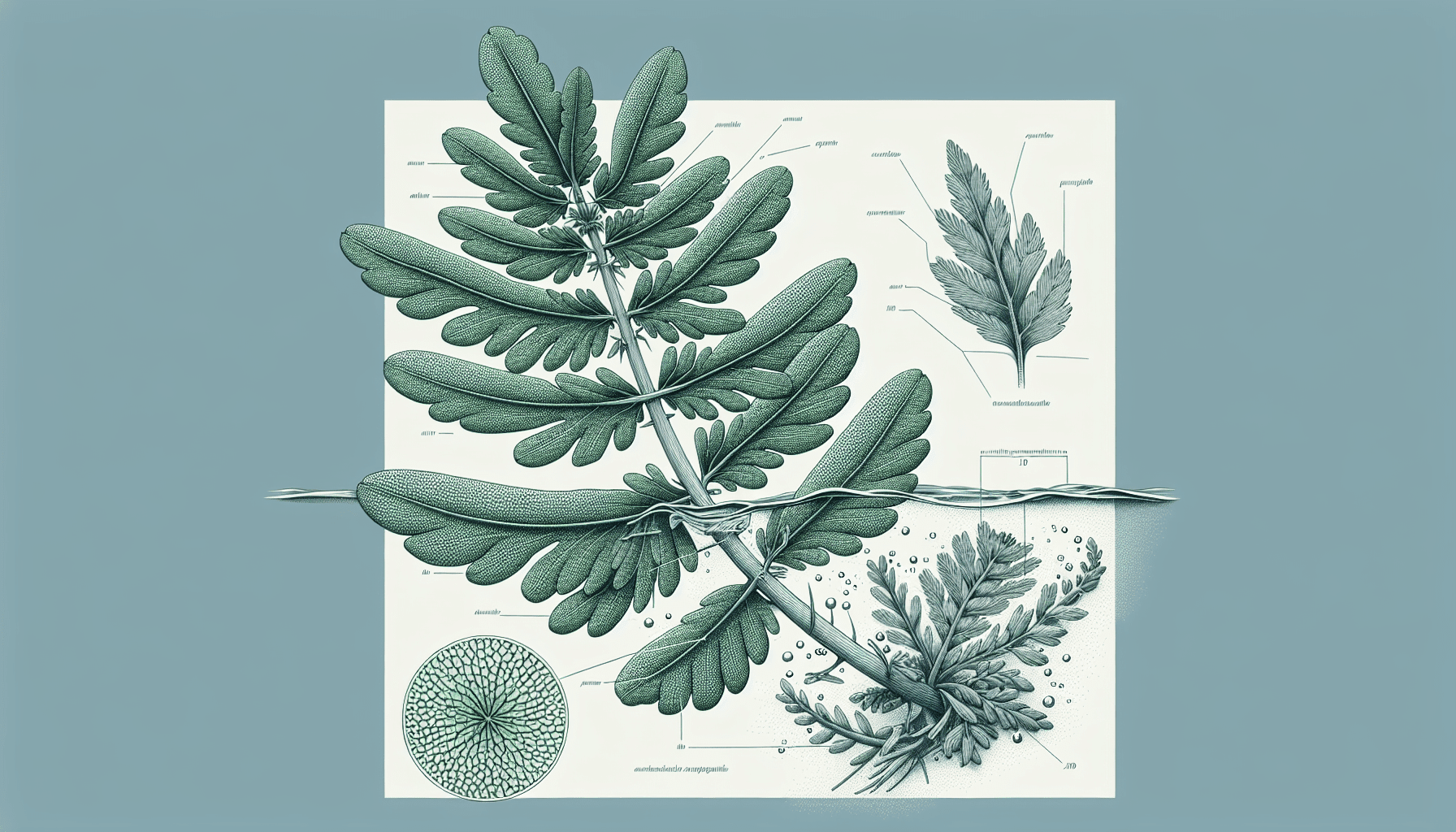
Physical Description
To identify Cutleaf Water Milfoil, it is essential to understand its physical attributes. Its leaves, flowers, stem, and roots all have unique features that differentiate it from other similar aquatic plants.
Leaf Shape and Size
The leaves of Cutleaf Water Milfoil are typically pinnate or feather-like. The size depends on the water temperature and nutrient availability, but they usually range from 1 to 5 cm in length. They are generally submerged, forming a bushy appearance.
Flower Type and Color
The flowers of this aquatic plant are typically small, greenish to purple, and usually bloom from late spring to early summer. They are arranged in a spike-like inflorescence extending above the water’s surface.
Stem and Root Structure
The stem of Cutleaf Water Milfoil is slender, round, and can reach up to 2 meters long, while the roots of this plant are primarily fibrous.
Overall Growth Pattern and Size
Cutleaf Water Milfoil showcases a bushy growth pattern, quickly developing dense stands. Its size varies but can reach up to 2 meters in length depending on the conditions of its environment.
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding the environment where Cutleaf Water Milfoil thrives is pivotal for researchers and conservationists who seek to manage its rapid growth.
Geographic Locations where Cutleaf Water Milfoil Thrives
This plant is native to the temperate regions of Asia, Europe, and North America. It thrives in both fresh and brackish water bodies, including lakes, ponds, canals, and slow-moving rivers.
Preferred Types of Aquatic Environments
Cutleaf Water Milfoil prefers nutrient-rich, shallow waters but can adapt to varying sunlight and depth conditions. It is often found in disturbed areas, suggesting its resilience to environmental changes.

Growth and Propagation
Studying the growth and propagation of Cutleaf Water Milfoil sheds light on its invasiveness and effects on its environment.
Rates of Growth
This plant grows rapidly, with high nutrient availability and warm temperatures accelerating its growth. It can quickly form dense vegetation, crowding out other native aquatic plants.
Season of Growth
Cutleaf Water Milfoil actively grows throughout the growing season, primarily from spring to early fall.
Mode of Reproduction and Spreading
Its mode of reproduction is primarily asexual, through fragmenting stems that root into the sediment. Sexual reproduction through seeds also occurs but is relatively less common.
Conditions for Germination and Rooting
Under optimal conditions, the stem fragments of Cutleaf Water Milfoil quickly form roots and establish new plants. Sediment type, light availability, and nutrient supply impact the success of germination and rooting.
Ecological Impact
The ecological consequences of Cutleaf Water Milfoil are vast. Its invasive nature significantly alters the aquatic ecosystem.
Impact on Aquatic Ecosystem
The rapid growth of Cutleaf Water Milfoil can result in dense vegetation, altering the physical structure of the aquatic habitat, and negatively impacting the biodiversity.
Interactions with Wildlife
Cutleaf Water Milfoil provides refuge for smaller aquatic organisms and is also a food source for herbivorous wildlife. However, it can also compromise the habitat of other species, affecting the overall wildlife population.
Impact on Water Quality
This plant impacts water quality by changing oxygen levels and increasing sedimentation. It can cause algal blooms through nutrient leaching, which can have negative impacts on other aquatic life.
Roles in Human Activities
Despite its detrimental environmental effects, Cutleaf Water Milfoil also plays a vital role in human activities.
Use in Aquascaping and Decorative Use
Due to its attractive, feathery leaves, Cutleaf Water Milfoil is commonly used in aquascaping. It plays a pivotal role in creating aesthetically pleasing aquatic environments and is also used for decorative purposes in ponds and water gardens.
Potential Medicinal Use
Historically, Cutleaf Water Milfoil has been used in traditional medicine for its potential medicinal uses. Its therapeutic potentials are currently being further explored.
Consideration as an Invasive Species in Some Regions
In some regions, Cutleaf Water Milfoil is considered an invasive species due to its fast growth and spread, threatening native species and habitats.
Methods of Control and Management
Effective control and management strategies are required to mitigate the potentially harmful impacts of Cutleaf Water Milfoil.
Mechanical Removal Methods
Mechanical removal involves physical extraction, such as hand-pulling, dredging, or using specially designed equipment. While this method can be effective, it may also inadvertently lead to further spread if not executed correctly.
Biological Control Methods
Biological control involves utilizing other organisms to manage the growth of Cutleaf Water Milfoil, such as insects, fish, or other competing native plants.
Chemical Control Methods
Chemical control involves applying specific herbicides to kill or inhibit the growth of Cutleaf Water Milfoil. It requires careful consideration due to potential impacts on non-target species and the overall aquatic environment.
Cutleaf Water Milfoil and Environmental Change
Understanding the interplay between Cutleaf Water Milfoil and environmental change is critical for anticipating its future distribution and impacts.
Impacts of Climate Change on Its Spread and Distribution
As global temperatures rise due to climate change, Cutleaf Water Milfoil’s geographical range may expand, and its growing season may lengthen, potentially exacerbating its invasive behavior.
Adaptation to Changes in Water Quality and Temperature
Cutleaf Water Milfoil has demonstrated adaptability to diverse environmental conditions, suggesting it may continue to thrive, or even increase, as aquatic environments change due to human activities and climate change.
Comparison to Other Aquatic Plants
Understanding how Cutleaf Water Milfoil compares to other aquatic plants provides context for studying its growth, propagation, and impacts.
Similarities and Differences with Other Milfoils
While Cutleaf Water Milfoil shares similar feathery leaves and invasive growth behavior with other milfoils, distinct differences include its asexually dominant mode of reproduction.
Comparison to Other Common Aquatic Plants
In comparison to other common aquatic plants, Cutleaf Water Milfoil’s ability to form dense mats on the water’s surface is unique, as is its tolerance for varying light and nutrient levels in its environment.
Current Research and Studies
Staying informed on the latest scientific research provides insights into management strategies and potential opportunities for harnessing Cutleaf Water Milfoil’s growth.
Latest Findings on Cutleaf Water Milfoil
Recent studies have discovered genetic variations within Cutleaf Water Milfoil, suggesting potential for development of region-specific management strategies.
Ongoing Research and Potential Breakthroughs
Current research is exploring the potential for using DNA technology in controlling Cutleaf Water Milfoil’s reproduction and growth. It is hopeful that such breakthroughs could revolutionize our approach to managing this complex and impactful aquatic plant.
