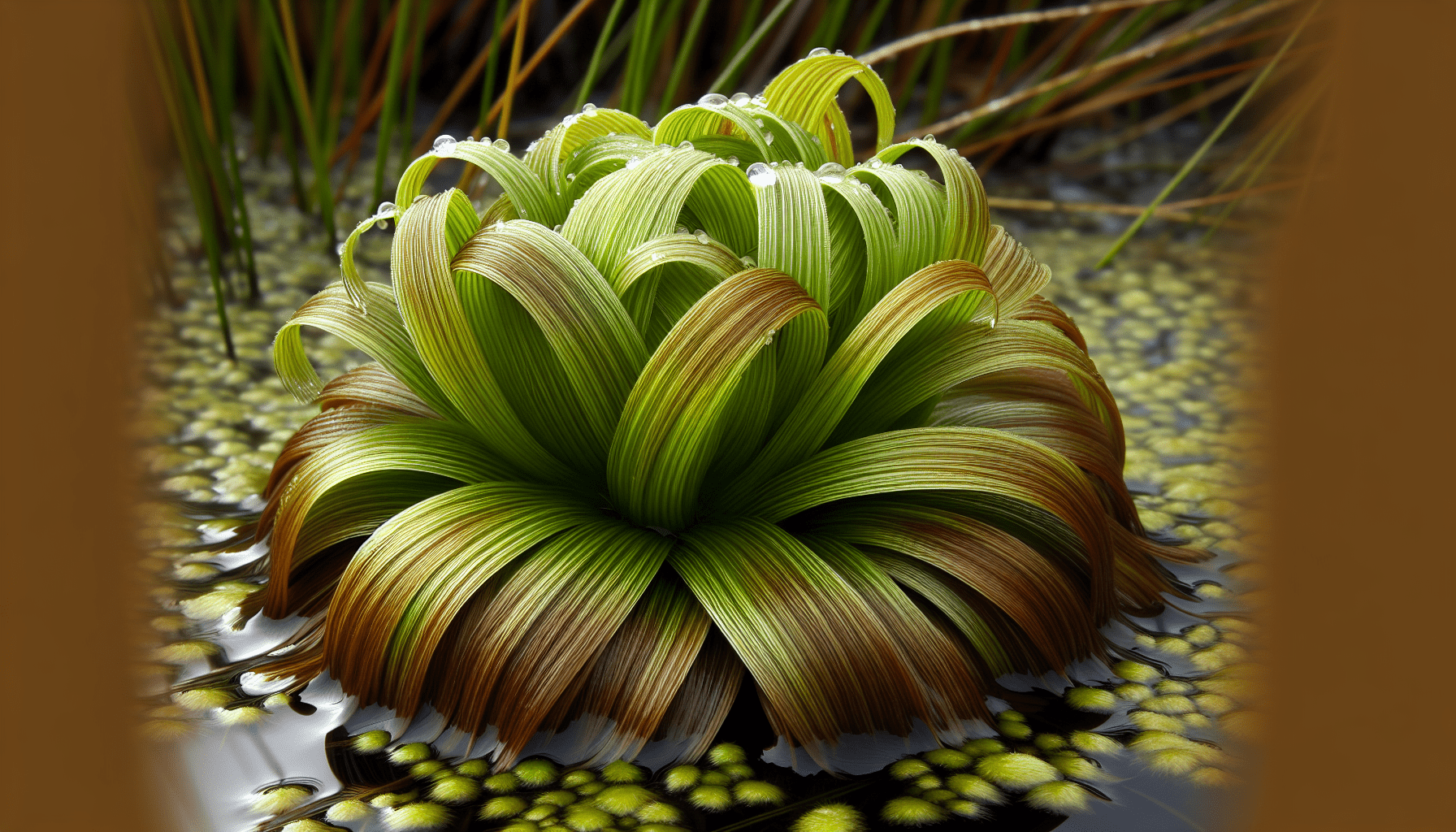
As you engage in a study of the aquatic biosphere, it’s inevitable to come across a myriad of flora that serve as cornerstones in aquatic ecology. Among the cornucopia of aquatic vegetation, one particular specimen stands out – the Bulbous Flatsedge. In the following article, considerable detail is offered regarding its taxonomy, biological characteristics, and role in the aquatic ecosystem, thus enriching your understanding of this exceptional plant species. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll gather insights into the interconnectedness of life within water bodies and the myriad, fascinating adaptations that enable life forms to thrive in diverse environments.
Defining Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants, as the name implies, are plants that live in or near water bodies. This categorization of plants encompasses a broad array of botanical life, ranging from the smallest microalgae to the towering water lilies. Just as land plants, these possess roots, stems, leaves, and sometimes flowers, but with modifications that allow them to flourish in aquatic environments.
Characteristics of Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants exhibit certain characteristics that distinguish them from their terrestrial counterparts. Their cell structure is modified to enable the absorption and retention of water and nutrients from their surroundings. They have thin leaves and flexible stems that enable them to float in water and resist the currents. Moreover, many aquatic plants have air spaces within their tissues, known as aerenchyma, which facilitate respiration even when underwater.
Types of Aquatic Plants
Aquatic plants can be broadly sorted into three types. Emergent aquatic plants are those whose roots are submerged but other parts extend above the water surface. Submerged plants live completely under the water, with leaves and stems adapted to the aquatic environment. Floating varieties, as the moniker implies, float on the water surface with their roots anchored in the sediment or freely floating on the water.
Role of Aquatic Plants in the Environment
Aquatic plants play a crucial role in the environment. They are primary producers in the ecosystem, converting sunlight into organic substances through photosynthesis, which in turn serves as food for other organisms. These plants also provide shelter and breeding grounds for various aquatic and semi-aquatic animals. Furthermore, aquatic plants significantly contribute to maintaining water quality by absorbing nutrients and pollutants from the water.
Understanding Bulbous Flatsedge
Bulbous Flatsedge (Cyperus bulbosus) is an example of an aquatic plant found in various water bodies across the world. It is part of the sedge family, marked by its grass-like appearance, with a unique bulbous base that gives it its name.
General Description of Bulbous Flatsedge
As a member of the Cyperaceae family, the Bulbous Flatsedge stands out for its bulbous base and the clusters of flower spikes at the ends of its stalk. It typically grows up to a height of 60 centimetres, featuring narrow, grass-like leaves that usually originate from the base of the plant.
Scientific Classification of Bulbous Flatsedge
Scientifically, Bulbous Flatsedge falls under the Plantae kingdom and is part of the Cyperaceae family. Its Genus is Cyperus and bulbosus is its specific epithet, referring to the characteristic bulbous base.
Common Habitats of Bulbous Flatsedge
Bulbous Flatsedge is predominantly found in damp or moist habitats, including marshes, swamps, bogs, and bodies of still or slow-moving water. It can adapt to varying water depths but typically prefers shallow, freshwater environments.
Life Cycle of Bulbous Flatsedge
Understanding a plant’s life cycle can give insights into its survival strategies and reproductive methods. Having a fibrous root system and perennial growth habit, Bulbous Flatsedge can survive for multiple years, growing in the active growing season and becoming dormant in the off-season.
How Bulbous Flatsedge grows
The Bulbous Flatsedge first initiates growth from a bulbous structure present in the root system, which contains abundant reserves of starch and proteins. The stored nutrients support the growth of new shoots and leaves that reach towards the water surface or the sunlight above.
Phases in the Life Cycle of Bulbous Flatsedge
The life cycle of the Bulbous Flatsedge, like other perennial plants, progresses through various stages. These include the vegetative phase, where the plant focuses its energy on growth, followed by the reproductive phase, where flowering and seed production occur, and finally the senescence stage where energy is diverted back to the rhizomes for storage and the plant prepares for dormancy.
Reproduction Methods of Bulbous Flatsedge
Bulbous Flatsedge reproduces through both sexual and asexual means. The sexual reproduction involves the production of seeds following the pollination of its flowers, similar to other flowering plants. Asexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves the development of new plants from the bulbous bases or the spreading rhizomes.

Morphological Attributes of Bulbous Flatsedge
Morphological descriptions of plants are crucial for their identification and for understanding their adaptations. Bulbous Flatsedge is characterized by various distinguishing features, including its leaves, stems, rhizome structure, and its flower and seed structure.
Description of Leaves and Stems
The leaves of Bulbous Flatsedge resemble those of grass, being linear and flat. The long, slender leaves usually arise from their bulbous bases. The stems, or culms as they are referred to in sedges, are unbranched and round in cross-section, which helps support the plant in water currents.
Understanding the Rhizome Structure
The bulbous base of the Flatsedge is actually a thickened rhizome which contains the food reserves for the plant. The rhizomes help in the asexual reproduction of the plant, as new shoots can sprout from these structures, resulting in the spread of the plant in its habitat.
Characteristics of Flowering and Seeds
The flowers of the Bulbous Flatsedge are arranged in clusters or umbels at the end of each stem, each one consisting of a few to several spikelets. Each spikelet carries several flowers, which upon fertilization produce fruits that are small nuts or achenes.
Ecological Significance of Bulbous Flatsedge
The ecological value of the Bulbous Flatsedge is inherent in its contribution to its habitat. It plays a role in the ecosystem balance of the water bodies it occupies, provides support for wildlife and contributes to water quality.
Bulbous Flatsedge Role in Water Bodies
This aquatic plant plays a multifaceted role in the water bodies it inhabits. It helps to stabilize the soil with its fibrous root system, combating erosion.
How Bulbous Flatsedge Supports Wildlife
As an aquatic plant, Bulbous Flatsedge offers an important sanctuary and steady food source for a variety of wildlife. Invertebrates, fish, and birds often feed on the seeds of this plant, while amphibians and smaller fish species use the plant as shelter.
Effect of Bulbous Flatsedge on Water Quality
Bulbous Flatsedge, like many other aquatic plants, contributes to maintaining water quality. By absorbing nutrients and particles from the water, it can both clarify it and limit the development of harmful algae.
Bulbous Flatsedge Distribution Worldwide
Bulbous Flatsedge can be found in several regions around the world. It has a wide geographical spread, benefits significantly from certain climate conditions, and faces influences from human-induced factors that can affect its distribution.
Geographical Distribution of Bulbous Flatsedge
Bulbous Flatsedge is native to much of the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia. However, it has been introduced to other regions, such as North America, thanks to its ability to adapt to a variety of conditions.
Climate Conditions Favoring Bulbous Flatsedge Growth
It generally thrives in warmer temperate climates, though it is adaptable and can withstand a variety of weather conditions. It primarily seeks out damp or moist habitats such as marshes, swamps, bogs, and still or slow-moving shallow water bodies.
Human-Induced Factors Affecting Its Distribution
Human activities such as land use changes, drainage of wetlands, aquatic pollution, and climate change can greatly affect the distribution and survival of Bulbous Flatsedge.
Conservation Status of Bulbous Flatsedge
The conservation status of the Bulbous Flatsedge varies by region. It may face threats from habitat loss, pollution, and invasive species, but its widespread existence reduces its vulnerability to extinction.
Threats to Bulbous Flatsedge
Habitat loss due to land reclamation and drainage of wetlands is perhaps the most significant threat to the Bulbous Flatsedge. Aquatic pollution from agricultural runoff carrying excess nutrients can also harm this species by promoting the growth of algal blooms that overshadow the plant and suffocate aquatic life.
Current Conservation Status
To the best of current knowledge, the Bulbous Flatsedge is not listed as threatened or endangered on any international conservation list. Its large native range and ability to grow in various conditions provide it with a certain degree of resilience.
Programs and Initiatives for Its Protection
There are no specific programs or initiatives aimed at the conservation of Bulbous Flatsedge. However, broader efforts to conserve wetlands and aquatic habitats do benefit this species indirectly.
Bulbous Flatsedge and Human Use
Humans have found various uses for this aquatic plant, such as utilizing it as a food source, for medicinal purposes, and potentially for other purposes.
Bulbous Flatsedge as a Food Source
Some parts of the Bulbous Flatsedge, including the seeds and roots, can be consumed by humans. The seeds can be ground into a flour to make bread, while the roots are often used in stews or roasted as a potato alternative.
Medicinal Uses of Bulbous Flatsedge
While the scientific validation is still lacking, several traditional medicinal uses of Bulbous Flatsedge have been documented. These include utilizing it as an astringent, diuretic, or to alleviate certain skin conditions.
Other Potential Uses and Benefits to Humans
Future research may reveal additional benefits of Bulbous Flatsedge to humans. Meanwhile, the plant’s role in stabilizing soil and maintaining water quality has indirect benefits for people living in or near their habitats.
Effects of Climate Change on Bulbous Flatsedge
The impact of climate change on Bulbous Flatsedge is a multifaceted issue. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and sea-level rise may all potentially affect its habitats and survival.
Impacts of Rising Temperatures on Growth
If the global temperatures continue to rise at the current rate, the growing conditions for the Bulbous Flatsedge—like many other plants—may be adversely impacted. These conditions include changes in water temperature or increased evaporation rates that can alter the plant’s optimal habitats.
Effects of Changing Precipitation Patterns
Changes in rainfall patterns caused by climate change may alter the availability and distribution of habitat for Bulbous Flatsedge. If areas become drier, their habitats may disappear, while if areas become wetter, new habitats may be created.
How Sea-Level Rise May Affect Bulbous Flatsedge Habitats
Rising sea levels may inundate coastal habitats, leading to an increase in the salinity of the water in these habitats. This could potentially affect the distribution of Bulbous Flatsedge, as it is primarily a freshwater species.
Future Research Directions in Bulbous Flatsedge
There is still much to learn about the Bulbous Flatsedge. Some research gaps need to be addressed, and technological innovations can facilitate this studying process.
Key Research Gaps
Important research gaps include a better understanding of its reproductive biology, response to climate change, and potential uses in phytoremediation or other human applications.
Potential Applications for Future Studies
There is potential for future studies to explore the incorporation of Bulbous Flatsedge in wetland restoration efforts, given its role in soil stabilization and water filtration. The plant’s potential for bioengineering and phytoremediation is yet another topic worth exploring.
Technological Innovations in Studying Bulbous Flatsedge
Technological advancements, including genomic sequencing or satellite remote sensing technologies, can be utilized to enhance the understanding of Bulbous Flatsedge’s evolutionary history, its functional traits, or to track its distribution and growth patterns.