As you explore the intriguing realm of aquatic botany, a fascinating specimen that may garner your attention is the Broadleaf Arrowhead. Plunge into this engrossing discourse to expand your cognizance of this exceptional plant, commonly stationed in marshes and pond margins. You will travel through its distinctive morphology, critical ecological role, notable uses, and intriguing folklore. Fostering a well-rounded comprehension of the Broadleaf Arrowhead will offer you a profound understanding not merely of this specific species, but further of the interconnected dynamics underlying our complex aquatic ecosystems.
Definition of Broadleaf Arrowhead
Broadleaf Arrowhead, scientifically known as Sagittaria latifolia, is an aquatic plant that is native to North America. This perennial herb is part of the Alismataceae family, which consists of plants that grow in water or marshes.
Scientific classification
From a taxonomic standpoint, the Kingdom of broadleaf arrowhead is Plantae, indicating its plant nature. The Order for this species is the Alismatales, families of monocots that are amphibious, and semi-aquatic. Its Binomial Name is Sagittaria latifolia, a classification that is universally recognized by the scientific community. The Family is Alismataceae, a group that’s generally found in wet places or water.
Common names
Broadleaf Arrowhead holds other common names with which it is identified, such as duck potato, Indian potato, or wapato. These names often represent its features or implications in various cultures.
Physical characteristics
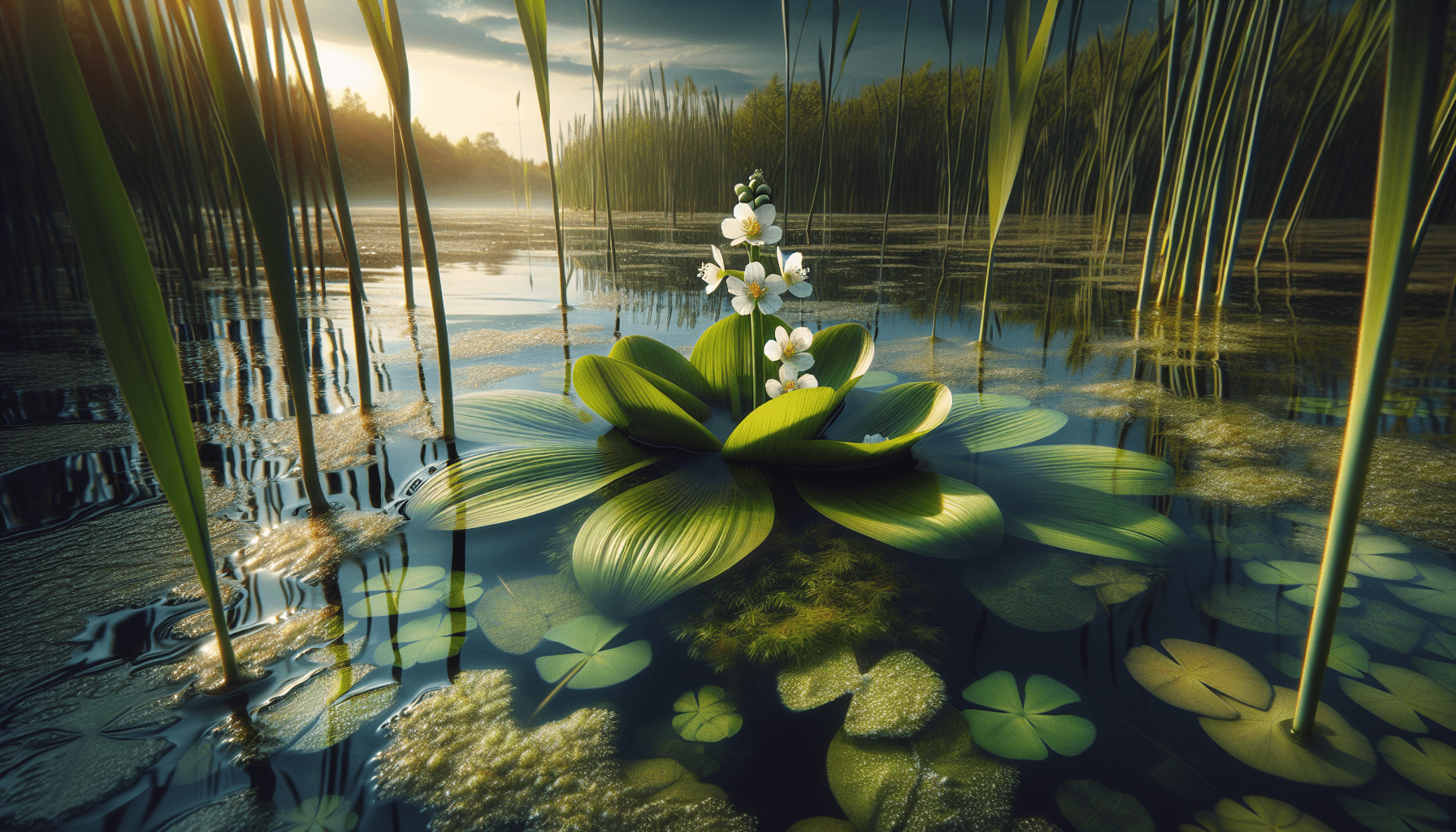
The Broadleaf Arrowhead plant is distinctive, characterized by its arrowhead-shaped leaves, hence the name. Additionally, they produce three-petalled white flowers during the blooming season, often appearing in whorls of three.
Natural habitat
Broadleaf Arrowhead typically grows in slow-moving water bodies, wetlands, and marshes. It is primarily found in shallow water or mud, enabling the sprouting of the unique leaves above the water surface.
Cultural Relevance of Broadleaf Arrowhead
In several cultures, the Broadleaf Arrowhead plant holds a significant role.
Culinary use in Native American culture
Historically, Native American tribes consumed the tubers of the plant, which were harvested by pushing the feet in the mud to dislodge them and collect them when they floated to the surface. These tubers, hence the name ‘duck potato’, could be cooked or ground into a flour for bread making.
Symbolic meanings and legends
In various cultures, Broadleaf Arrowhead’s unique shape is associated with protection and strength. Legends often include this plant as an important symbol highlighting various properties.
Conservation status
Currently, Broadleaf Arrowhead is not known to be under any specific conservation status. However, the habitats where this plant thrives are under constant threat due to climate change and other human activities.
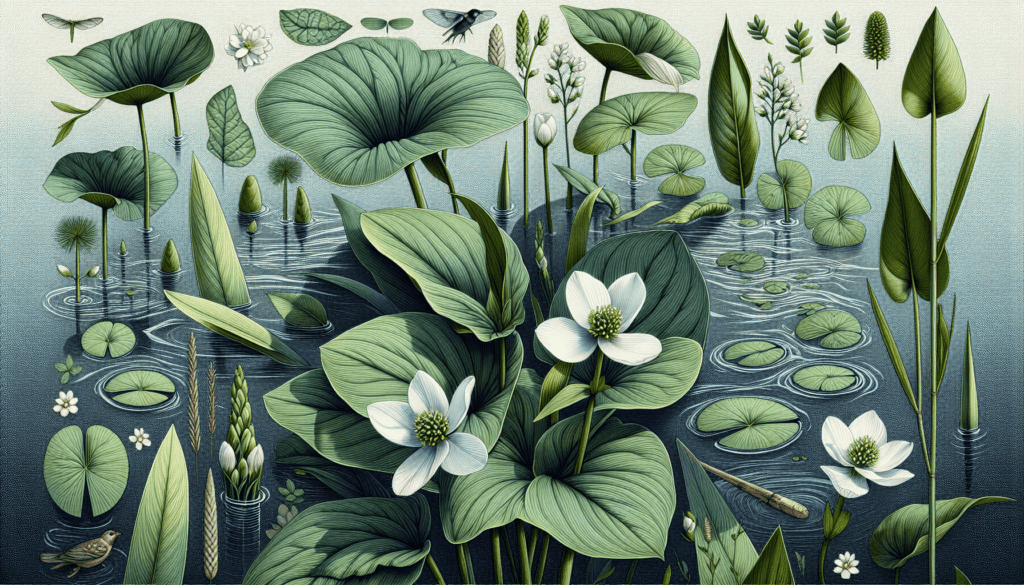

Lifecycle of the Broadleaf Arrowhead
Broadleaf Arrowhead has an interesting lifecycle and distinctive growth phases.
Growth stages
Initial growth of Broadleaf Arrowhead is marked by the formation of tubers, which later sprout into seedlings. The plant eventually rises above the water surface, revealing its distinctive arrowhead foliage.
Seasonal adaptations
Broadleaf Arrowhead is a robust plant, showing considerable adaptations to the changing seasons. In winter, the foliage dies back and the plant survives as tubers under the surface, sprouting again when the warmer temperatures return in spring.
Reproductive processes
Reproduction in Broadleaf Arrowhead happens sexually through flowers and asexually through tubers. The flowers are pollinated to produce seeds, while the tubers allow the plant to reproduce under suitable conditions.
Geographical Distribution
Though native to North America, Broadleaf Arrowhead is now commonly found in different parts of the world.
Native regions
The plant is indigenous to the Americas, thriving well within the wetlands, marshes and slow-moving water bodies in this region.
Spread across the world
Over time, Broadleaf Arrowhead has gained acceptance around the globe. With a high adaptability feature, this plant is now naturalized in many parts of Europe, Asia, and Australia.
Current presence in continents and countries
Broadleaf Arrowhead currently thrives in multiple continents including North and South America, parts of Europe, marshy regions of Asia, and Australia.
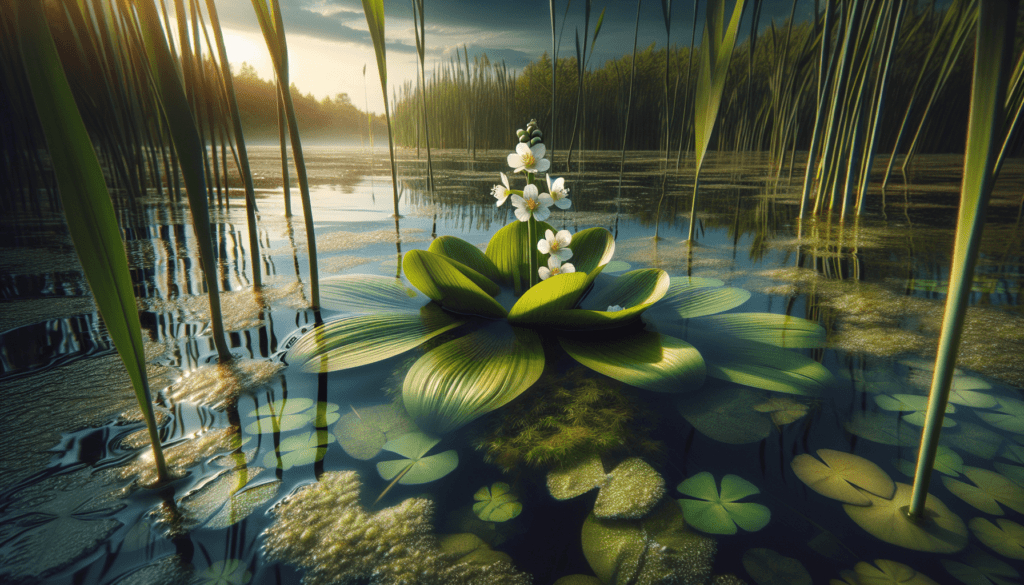

Environmental Conditions Required
The environmental conditions required for the growth of Broadleaf Arrowhead are specific.
Preferred water conditions
The plant requires a marshy, wetland environment or slowly-moving water bodies for optimal growth. Enough moisture ensures its survival, the lack of which might lead to dormant tubers.
Temperature tolerance
Broadleaf Arrowhead is resilient and adaptable to a variety of temperatures. It can survive cold winters as tubers and reblossom with the onset of warmer springs.
Sunlight requirement
The plant prefers full sun to partial shade for optimal growth. Lack of sunlight may hinder its photosynthetic processes, hampering its growth.
Role in the Ecosystem
In its ecological niche, Broadleaf Arrowhead renders a number of functions.
Contribution to biodiversity
The plant adds to the overall biodiversity of a wetland ecosystem. Its tubers often attract animals and insects, contributing to the food chain.
Commodity for wildlife
Broadleaf Arrowhead serves as food for numerous aquatic and terrestrial animals. While ducks are known to consume the plant, beavers and muskrats often feed on the tubers.
Role in shoreline stabilization
The root system of Broadleaf Arrowhead aids in soil stabilization, which is particularly important in preventing erosion along shorelines.
Potential Threats to Broadleaf Arrowhead
Like any other species, the survival of Broadleaf Arrowhead is not free from threats.
Climate change
Climate change implications on wetland ecosystems pose an existential threat to Broadleaf Arrowhead. The rising temperatures may dry out its typical habitats.
Pollution and water quality
Water pollution, particularly due to agricultural runoff filled with phosphates and nitrates can potentially damage these plants and their ecosystems.
Invasive species competition
The introduction of invasive species poses a threat to Broadleaf Arrowhead, as they tend to compete for the same natural resources like sunlight, water, and space.
Cultivation and Care of Broadleaf Arrowhead
While Broadleaf Arrowhead is a relatively easy plant to grow, it does require some specific care.
Propagation techniques
Propagation of Broadleaf Arrowhead can be achieved through seeds or division of tubers.
Maintenance and care requirements
The plant requires a constant supply of water throughout its growth phase. Regular checks for pests and disease infestation ensures healthy growth.
Forcing dormancy and germination
Dormancy can be induced by lowering the water supply and temperature, while germination can be achieved by the resumption of favorable growth conditions.
Applications and Uses of Broadleaf Arrowhead
In addition to its ecological importance, Broadleaf Arrowhead has commercial, culinary and potential medicinal applications.
Commercial uses
As an ornamental plant, Broadleaf Arrowhead can beautify ponds or water gardens. Its unique shape makes it a popular choice for such settings.
Culinary potential
Historically, the tubers were consumed by Native Americans. Resembling potatoes, they can be roasted or boiled, or ground into flour.
Medicinal applicability
Though not widely recognized, some traditions use Broadleaf Arrowhead for medicinal purposes. Research is needed to further explore these properties.
Broadleaf Arrowhead Research and Studies
Further research can help decode this plant’s potential and its role in ecosystems.
Analyzing ecological impact
Understanding the ecological role of Broadleaf Arrowhead can lead to practical applications in wetland conservation.
Potential medical research
While Broadleaf Arrowhead is mentioned in traditional medicine, substantial research is required to validate its medicinal properties.
Conservation strategies and policies
Policies to conserve wetlands and their unique plant species like Broadleaf Arrowhead can help save these ecosystems from further deterioration.
In conclusion, Broadleaf Arrowhead is a uniquely adaptive plant, whose importance spans various facets from ecological roles, cultural significance to potential medical properties. The careful study and conservation of such plants is required, which in turn aids in preserving the intricacies of their respective ecosystems.