Nymphaea caerulea, more commonly known as the Blue Water lily, serves as the focus of this comprehensive study, drawing attention to its multifaceted functions in diverse ecosystems. As you navigate through the paper, an exploration into its unique characteristics, lifecycle, and ecological role will define and articulate the profound presence of this aquatic plant. Subsequently, this analysis of the Blue Water Lily is designed to inform and educate your existing knowledge and perceptions regarding this striking botanical dweller of the water bodies.
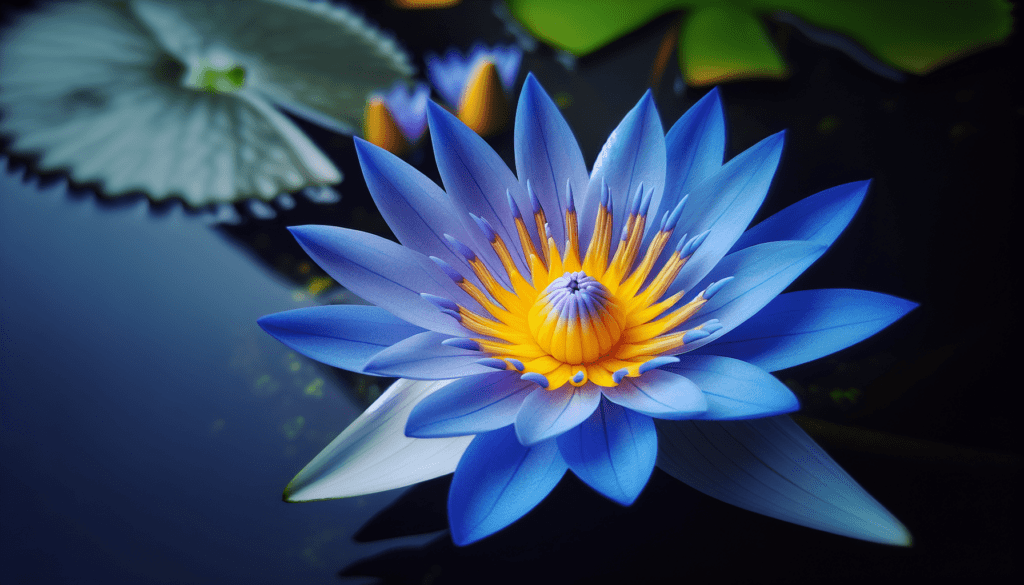

Overview of Blue Water Lily
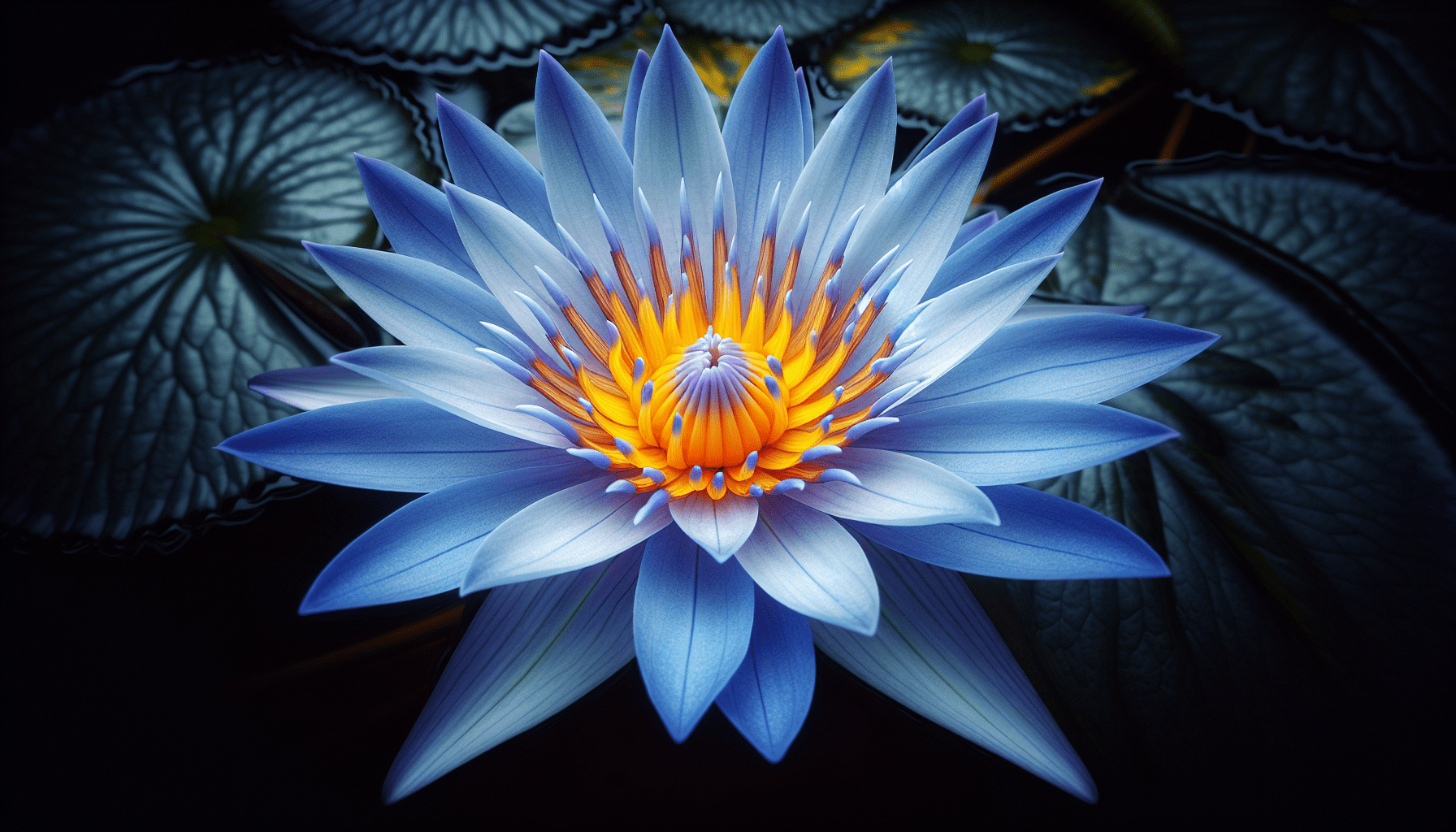
The aquatic plant Blue Water Lily, scientifically named Nymphaea caerulea, also known by colloquial names such as the Blue Egyptian Water Lily or Sacred Blue Lily, is a fascinating subject in the field of botany. It combines unique aesthetic qualities with rich biological traits and cultural significance, making it a symbol of beauty and mystery around the world.
Scientific classification of Blue Water Lily
In the scientific classification or taxonomy, the Blue Water Lily is placed under the Nymphaeaceae family. Its genus Nymphaea encompasses a wide variety of water lilies, differentiating primarily in terms of their color and growth habits. The species under which the Blue Water Lily falls is caerulea, derived from Latin, signifying its distinctive blue color.
Origin and geographical distribution
The origin of the Blue Water Lily is traced back to Ancient Egypt and other parts of Northern and Eastern Africa. From there, it has been introduced to other parts of the world and is now commonly found in freshwater ecosystems. This plant is prevalent across Asia, Europe, North America, and even Australia, often in ponds, lakes, slow-moving streams, and marshes.
Physical description and features
The Blue Water Lily displays broad, circular leaves that float on the surface of the water, ranging in shades from light to dark green often with a reddish underside. What truly captures attention is the beautiful blue flower that blooms from the center, characterized by numerous petals surrounding a yellow or sometimes reddish stamen. Their roots anchor them into the pond bed, allowing the plant to stay afloat and adapt to the water’s movements.
Life cycle of Blue Water Lily
The life cycle of the Blue Water Lily is particularly fascinating and is deeply linked to the environmental conditions of its habitat.
Seeds and germination
Initially, after cross-pollination, the Blue Water Lily develops seeds which are housed within a fruit under the water’s surface. Once ready, these seeds are released where they fall into the sediment below. Depending on the right conditions, they will germinate and produce new plants.
Growth Patterns
The growth of the Blue Water Lily starts with a seed but can also occur through the division of its tuberous root. New plants grow directly from these roots, producing long leaf stalks that penetrate the water surface to enable the leaves to float and capture sunlight.
Flowering and reproduction
Flowering occurs between spring and autumn, with each flower lasting only a few days. Attracting bees, beetles, and flies with its scent and color, this plant uniquely adjusts its temperature to facilitate insect activity and hence ensure successful pollination.
Life span and survival strategies
The Blue Water Lily is a perennial plant, meaning it can live for many years. It has numerous survival strategies including a robust root system for anchorage and resource uptake, the ability to self-reproduce, and adaptability to various water conditions.
Habitat requirements
The habitat requirements for a Blue Water Lily include a blend of precise levels of light, water, and temperature, all pivotal in its growth and survival.
Water and light requirements
As an aquatic plant, the Blue Water Lily naturally needs a significant amount of water in which to thrive. Full sunlight is also key in promoting the development of flowers. Partial shade may be acceptable, but prolonged periods of darkness can inhibit flowering.
Soil conditions
This water lily adapts well to a variety of soil conditions but usually prefers a rich, loamy soil at the bottom of a water body. The roots embed into the underwater soil for anchorage and nutrient uptake.
Temperature preferences
The temperature preferences of the Blue Water Lily ranges from 22 to 30 degrees Celsius during the day. At night, temperatures should preferably not fall below 15 degrees Celsius.
Effects of fluctuating water levels
An important consideration is the effect of fluctuating water levels on the growth of the Blue Water Lily. Rapid changes can create instability and potentially damage the plant or inhibit growth. Therefore, its habitat should ideally maintain stable water levels.
Role in the Ecosystem
The Blue Water Lily occupies a critical role in the ecosystem in which it resides.
Importance as a habitat and food source
These plants provide important underwater habitat for many types of microscopic organisms which are fundamental to a healthy aquatic food chain. The stems, roots, and nearly all parts of the Blue Water Lily serve as a food source for various aquatic animals and birds.
Interactions with aquatic animals and insects
The Blue Water Lily interacts with aquatic animals and insects in more ways than just being a food source. Birds, frogs, and insects often find refuge in their leaves and flowers. Moreover, its flowers act as a captivating site for pollinating insects.
Impact on water quality
Blue Water Lilies can improve the water quality of their habitats by absorbing pollutants and heavy metals from the water. This ability highlights their potential role in the mitigation of water pollution.
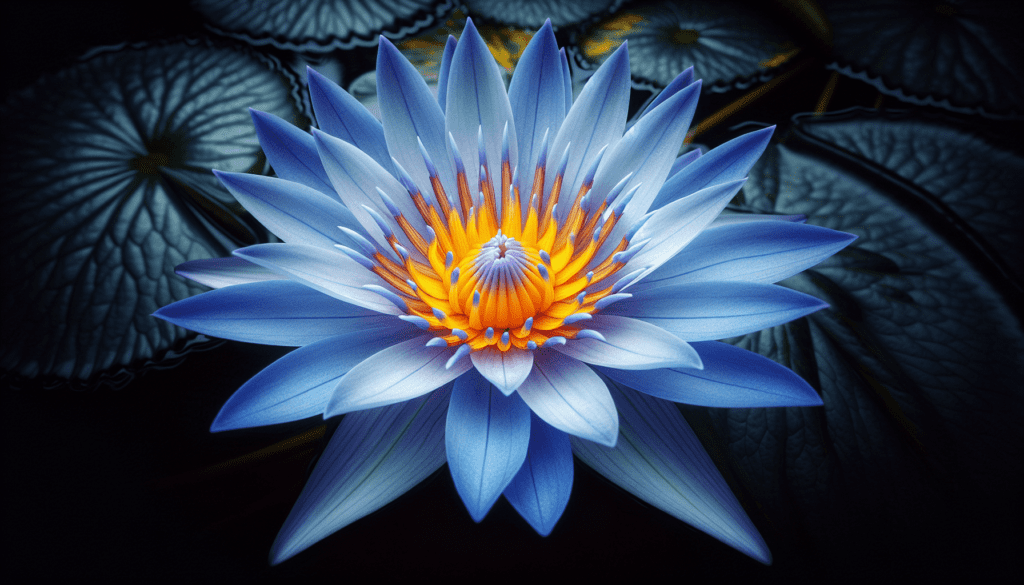

Adaptations of Blue Water Lily
Over time, Blue Water Lilies have developed several physical and physiological adaptations to survive their aquatic environment.
Structural adaptations like waxy leaves and buoyant flowers
One primary structural adaptation is the water lily’s waxy leaves that repel water, allowing them to float and perform photosynthesis above the water surface. Another adaptation is their buoyant flowers which can remain above water even in conditions of increasing water levels.
Physiological adaptations like anaerobic respiration
Physiologically, the underwater portions of the Blue Water Lily can perform anaerobic respiration, which means they can produce energy in the absence of oxygen.
Reproductive adaptations
The Blue Water Lily’s reproduction is aided by its attractive color and fragrance that successfully draw pollinating insects. Moreover, the plant has adapted to regulate its flower’s temperature, encouraging insect activity and thereby enhancing pollination.
Cultural significance
The cultural significance of the Blue Water Lily is deeply rooted in various societies due to its aesthetic appeal and distinct symbolism.
Usage in decoration and landscaping
Blue Water Lilies are widely used for decoration and landscaping. Their vibrant colors and unique blooms make them an appealing choice for ponds and water features in gardens and parks.
Religious and spiritual significance
In many cultures, specifically Ancient Egypt, the Blue Water Lily was considered sacred. It was associated with rebirth and the sun due to the cycle of its bloom. Even today, in various religions and spiritual practices, it symbolizes purity, tranquility, and enlightenment.
Representation in art, literature, and symbolism
The Blue Water Lily has been popularly represented in various forms of art, literature, and symbolism. Its image is often used to represent beauty, serenity and mysticism. In literature, it often serves as a symbol of love, life, and transformation.
Maintenance and cultivation
The maintenance and cultivation of Blue Water Lilies require specific knowledge to ensure healthy growth and longevity.
Promoting flowering and growth
To promote flowering, it is essential to ensure that the Blue Water Lily is planted in full sun and its water requirements are duly met. For growth, nutrient-rich soil conditions are ideal.
Controlling pests and diseases
Controlling pests and diseases include occasional inspection for aphids, beetles, and other pests that might cause harm. When found, one should carefully remove the pests, or use specific safe treatments when necessary.
Propagation techniques
For propagation, the division of the root system is the most common and successful technique. Division should ideally be done in the spring before new growth begins.
Medicinal uses and health benefits
Historically, Blue Water Lily was used for its alleged healing properties and continues to be explored for its potential health benefits.
Alleged healing qualities
Blue Water Lily was used in ancient medicine for its purported healing abilities. It was believed to have sedative and aphrodisiac properties, and was also used for relieving pain and inducing euphoria.
Preparation methods
The preparation of Blue Water Lily for its potential therapeutic benefits might include brewing the petals and bulbs into a tea or infusion. Alternatively, it can be dried and used in tinctures or capsules.
Potential side effects and warnings
While some suggest therapeutic benefits of the Blue Water Lily, it’s essential to note the potential side effects, such as hallucinations or nausea. It should only be used under professional supervision.
Conservation and threats
While not an endangered species, the Blue Water Lily does face threats requiring concerted conservation efforts.
Endangered status
The Blue Water Lily is not currently classified under any immediate endangered status. However, changes in its natural habitats due to human interference could put certain populations at risk.
Threats due to invasive species and pollution
Threats to the Blue Water Lily are due to invasive species that may compete for resources, changing climate, and pollution affecting water quality where they grow.
Conservation efforts
Conservation efforts for the Blue Water Lily revolve around maintaining clean water bodies, controlling invasive species, and preserving their natural habitats.
Research and Studies
Research and studies on the Blue Water Lily have deepened our understanding about the plant and opened new potentials for its use.
Scientific research on the plant’s medicinal properties
Recent scientific research on the medicinal properties of the Blue Water Lily has seen momentum. Studies have thrown light on alkaloids present in the plant that affect the human nervous system, providing a basis for its historical use as a sedative and potentially leading the way for new medicinal applications.
Studies on environmental impact
Research has also been directed at understanding the Blue Water Lily’s impact on its environment – its role in nutrient cycling, ability to absorb pollutants, and the implications of its presence on the biodiversity of an ecosystem.
Future potential and ongoing studies
Ongoing studies continue to explore the Blue Water Lily. From discovering more about its ecological importance to its future potential in human medicine or even as an aesthetic and peaceful addition to aquatic environments, research into the Blue Water Lily promises to uncover more about this fascinating plant.