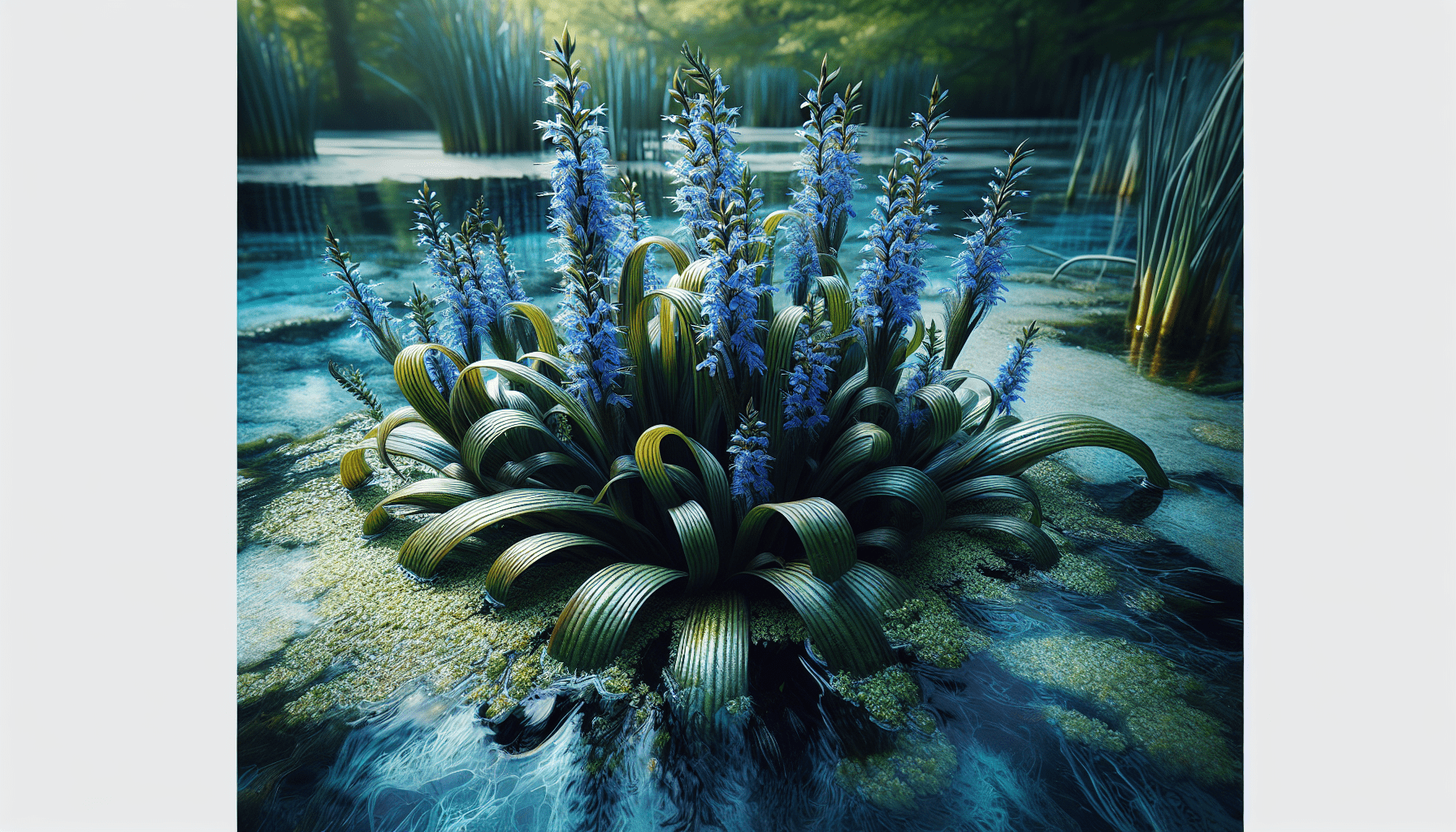
Embarking on your scholastic journey through the realm of aquatic botany, your initial exploration takes you into the verdant world of the Blue Pickerel Plant. This aquatic flora, known scientifically as Pontederia Cordata, unfolds an intriguing story of ecological significance and aesthetic beauty. As you immerse yourself in this article, you will garner an understanding of its native habitat, its ecological role, and its cultural significance, thereby adding depth to your botanical knowledge. From evolutionary adaptations to cultural symbolism, the Blue Pickerel Plant offers an enriching and enlightening exploration of nature’s aquatic tapestry.
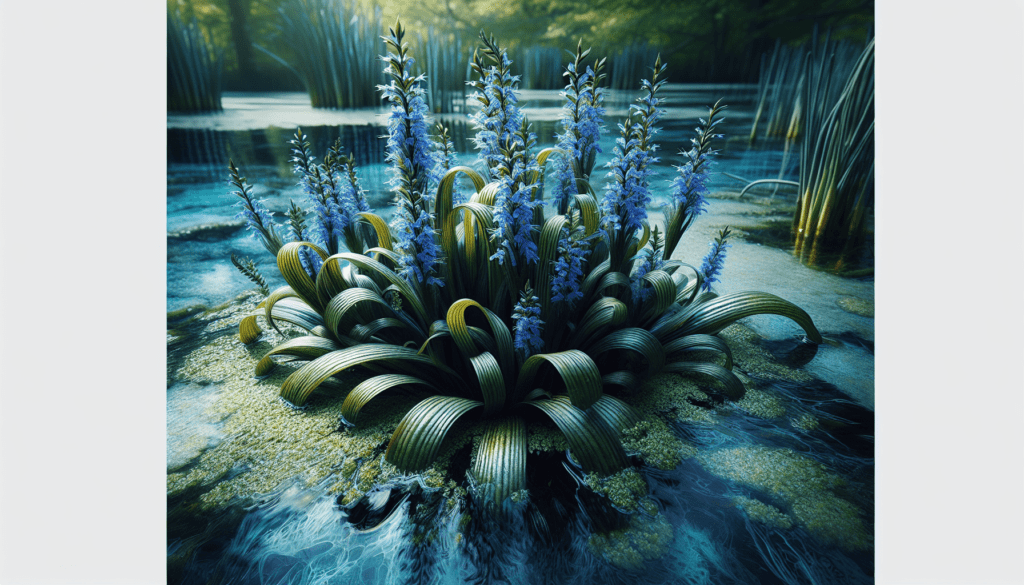

Definition of Blue Pickerel Plant
The Blue Pickerel Plant, known in the scientific community as the Pontederia cordata, is an aquatic species classified within the family Pontederiaceae. This perennial plant is revered for its striking aesthetics and unique adaptive qualities which allow it to thrive in water-rich environments.
Scientific name and classification
The Blue Pickerel Plant identifies with the scientific name of Pontederia cordata, and falls under the Pontederiaceae family. This family consists of approximately 30 species, broadly distributed in tropical and subtropical areas worldwide.
Common names and synonyms
In addition to its scientific name, the plant possesses several common names and synonyms, including Pickerel Weed, Pickerelweed, Pickerel Rush, Heartleaf Pickerelweed, among others. These names often reflect the physical characteristics or environmental preferences of the plant.
Physical Characteristics
The Blue Pickerel Plant possesses several unique and stunning physical characteristics, which contribute to its success in aquatic habitats and popularity in human landscaping projects.
Leaves and Stem
The Blue Pickerel Plant has distinctive, broad, glossy, heart-shaped leaves held high above the water on stout stems. The robustness of these stems enables the plant to withstand the force of water currents without being uprooted or damaged.
Flowers and Seeds
One of the most striking traits is its spike of blue or purple flowers that blooms from late spring to early fall. Each flower gives way to a capsular fruit containing many seeds, providing the primary means of propagation for the species.
Size and Growth Habit
Typically, the Blue Pickerel Plant stands 2 to 4 feet tall in its full maturity with a spread as wide. The plant’s growth habit generally takes on a robust, clump-forming disposition, making it ideal for dense clustering in various landscapes.
Habitat and Distribution
Despite its desirable landscaping qualities, the native habitat of the Blue Pickerel Plant is essential to understand properly for its sustainable cultivation.
Geographical range
The Blue Pickerel Plant primarily finds its home in North America, with a geographical range stretching from Canada to the Argentine Patagonia.
Preferred environmental conditions
The plant prefers shallow freshwater bodies such as ponds, lakes, and streams, thriving in conditions with full to partial sunlight. It can also tolerate a variety of soil types including sandy, loamy, and clay soils provided they remain consistently moist.
Role in Ecosystem
The ecological role of the Blue Pickerel Plant is one of both direct support for specific fauna as well as broader impacts on water-based ecosystems.
Importance to aquatic life
The Blue Pickerel Plant serves as a rich source of food and habitat for many aquatic creatures. Its leaves provide shade, while the stems offer refuge for smaller fishes from predators. Moreover, the plant’s flowers are known to attract butterflies and hummingbirds, adding biodiversity value to their environments.
Its role in nutrient cycling
Beyond just providing habitat and food, the Blue Pickerel Plant plays a part in the nutrient cycling in aquatic environments. The plant absorbs excess nutrients from water bodies, reducing the potential for algal bloom, which could otherwise disrupt the ecological balance.
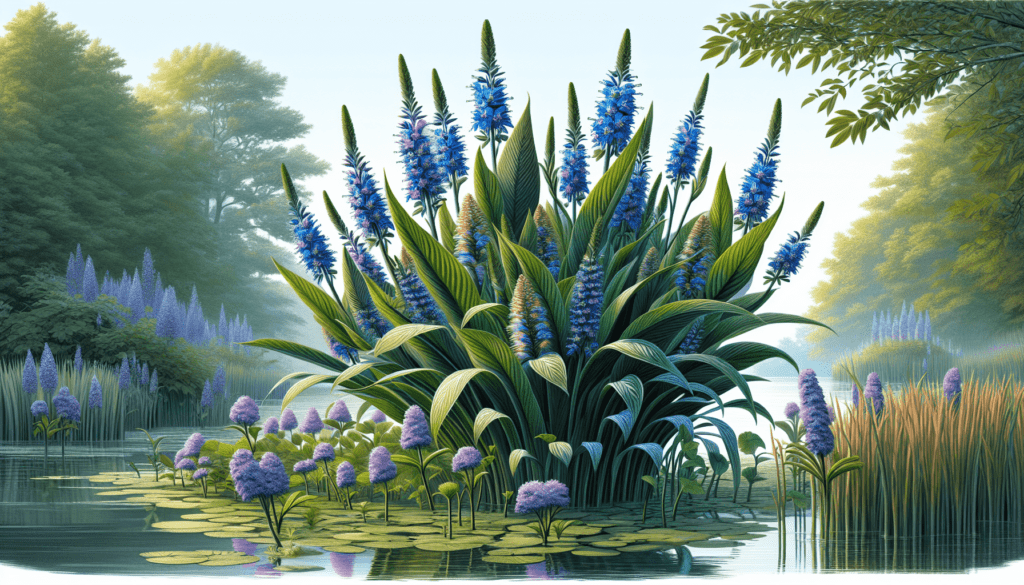

Propagation and Growth
Understanding the natural propagation mechanisms and growth characteristics of the Blue Pickerel Plant can guide effective cultivation strategies.
Methods of propagation
The Blue Pickerel Plant propagates primarily through seed dispersal. However, vegetative reproduction is common, using portions of the roots or rhizomes that produce new plant clusters.
Growth rate and lifespan
This plant exhibits a moderate to fast growth rate and boasts a fairly long lifespan. The leaves appear in early spring and last until the first frost of the fall.
Cultivation and Care
Though hearty, the cultivation and care of Blue Pickerel Plant require certain considerations for optimal growth and longevity.
Ideal planting conditions
The plant prefers consistently wet or boggy soils. Places adjacent to water bodies such as edges of ponds, water gardens, or streams are ideal. Full sunlight and warm temperatures also promote optimal growth.
Care and Maintenance requirements
Blue Pickerel Plants require relatively low maintenance. Frequently checking soil moisture and making sure it remains wet is vital, especially in dry spells. Periodic pruning may promote thicker plant growth.
Potential Threats
Like most plants, the Blue Pickerel Plant faces certain threats that impact its health and longevity.
Common diseases
Fungal diseases and bacterial wet rot are common diseases that can impact this plant. However, given the right conditions, the plant shows remarkable resilience.
Pest issues and management
Pests such as grasshoppers and aphids may sometimes feed on its foliage. Proper inspection and pest control can mitigate this issue, helping to maintain the plant’s health.
Uses in Landscaping
The Blue Pickerel Plant’s aesthetic appeal and environmental tolerance make it a preferred choice for many landscaping projects.
Incorporation in water gardens or ponds
Its love for water, along with its striking beauty, makes the plant an ideal choice for water gardens, ponds, and even aquatic themed containers.
Complementing plants and design suggestions
Blue Pickerel Plants blend well with other aquatic and waterside plants, including water lilies, lotus flowers, or bullrushes. Its blue flowers contrast well with those of other colors, creating an eye-catching range of hues.
Medicinal and Other Uses
The Blue Pickerel Plant is not just visually attractive, but it also holds a few other practical uses.
Uses in traditional medicine
Traditionally, Native Americans used parts of these plants as a poultice to treat wounds or insect stings, proving its medicinal potential.
Other cultural and practical uses
In certain cultures, the plant serves culinary purposes as well. The young, unfurled leaves can be consumed as vegetables!
Conservation Status
Though common in North America, it is crucial to consider the conservation status of the plant to ensure its sustained existence.
Current status according to conservation bodies
Generally, the Blue Pickerel Plant is not considered an endangered or threatened species. However, its status might vary between different regions.
Efforts towards preservation and sustainable use
Despite the presumed safe status, this does not preclude the necessity of conscious preservation efforts. It is crucial to cultivate and use the Blue Pickerel Plant sustainably, preserving its natural habitats, and promoting its use responsibly in human landscaping projects.