In the realm of aquatic botany, a multitude of fascinating plant species can be found, yet one stands out for its distinctive attributes and intrigue – the Amur Pond Plant. This article will explore the characteristics, environmental preferences, and growth patterns of this unique water-dwelling species. So, whether you are a botany enthusiast or a novice gardener keen on expanding your horticultural understanding, prepare yourself for an informative journey into the captivating world of the Amur Pond Plant.
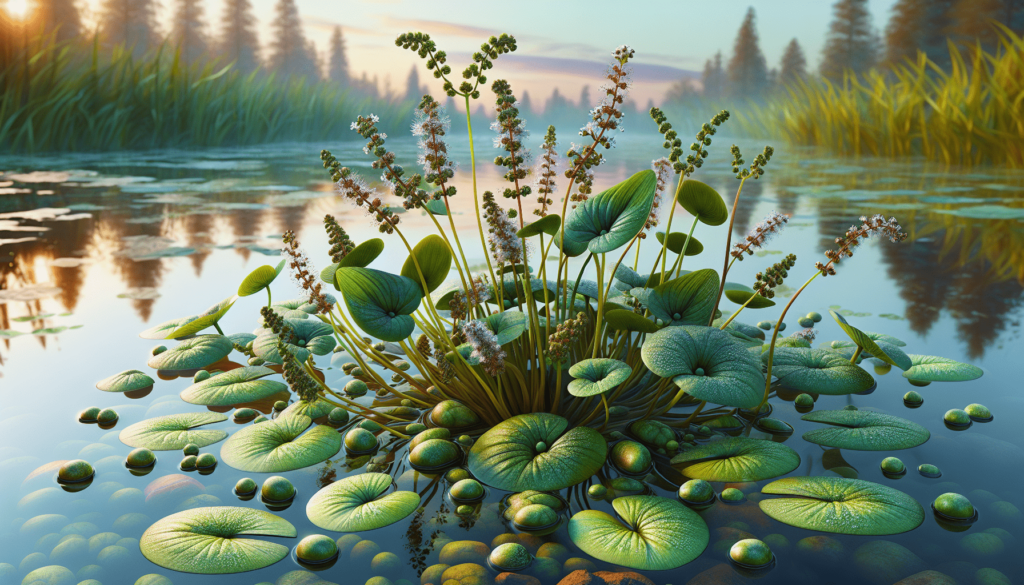

Definition of Amur Pond Plant
General description
The Amur Pond Plant, as the name suggests, is a type of aquatic plant native to the Amur River region. This plant species is characterized by vibrant lush leaves that sprout from a central stem and form a branching pattern. The leaves have a pliable texture and a glossy sheen, which adds to their aesthetic appeal, making these plants popular choices for aquariums and artificial pond setups.
Scientific name and classification
The scientific name for the Amur Pond Plant is Phragmites australis. In terms of taxonomic classification, this plant belongs to the Poaceae family, fondly referred to as the grass family. It falls under the plant kingdom and shares the characteristics typical of a monocotyledonous structure.
Origin and distribution
The Amur Pond Plant originates from the Amur River, which stretches across the eastern part of Russia and forms a natural border with China. However, due to its adaptability and aesthetic charm, the plant’s distribution has to extend well beyond its native region. It can be found in various aquatic ecosystems around the world, including lakes, ponds, and swamps.
Physical Characteristics of Amur Pond Plant
Shape and Size
The Amur Pond Plant exhibits a tall and slender form, with mature plants often reaching up to six feet in height. The leaves, branching out from the central stem, are long and narrow. The plant’s overall structure can be compared to that of common reeds, with similar ramifications and a graceful, bending posture.
Color
The Amur Pond Plant boasts an alluring shade of deep green throughout most of the year. During the bloom period, golden-brown inflorescences lend a contrasting hue to the otherwise monochromatic color profile of the plant.
Flowering period
The Amur Pond Plant typically flowers from late summer through early fall. Its flowering spikes bearing tiny feather-like flowers that add texture and visual interest to the plant’s appeal.
Seeds and fruits
The plant bears fruit following the flowering period. The seeds, similar in size and shape to rice grains, scatter with the wind, facilitating the spread and colonization of the plant over vast distances.
Habitat Preferences
Aquatic environments
As an aquatic plant, the Amur Pond Plant exhibits a preference for still or slow-moving water bodies such as lake edges, riverbanks, and wetlands. They can also proliferate in ditches and marshy environments.
Preferred temperature ranges
The Amur Pond Plant is adaptable to a range of temperature settings but thrives best within mild temperate climates, indicative of its origin.
Soil types
This plant species is not overly particular about soil types and can grow in various substrates provided they remain consistently damp.
Sunlight exposure
Like most aquatic plants, the Amur Pond Plant prefers full sun but can tolerate partial shade.
Lifecycle and Growth of Amur Pond Plant
Germination and Early Growth stages
The seeds of the Amur Pond Plant, once dispersed, require wet conditions to germinate, a process that typically occurs in the early spring. The seedlings develop into fully formed plants by late spring or early summer.
Mature plant
The mature Amur Pond Plant is characterized by a cluster of tall and slender stems topped with dense foliage and bloom spikes.
Reproduction
Reproduction is primarily via seed dispersal. However, this plant is also capable of vegetative reproduction through rhizome division.
Lifespan
As a perennial plant, the Amur Pond Plant can live for several years, regrowing each spring from the root system.
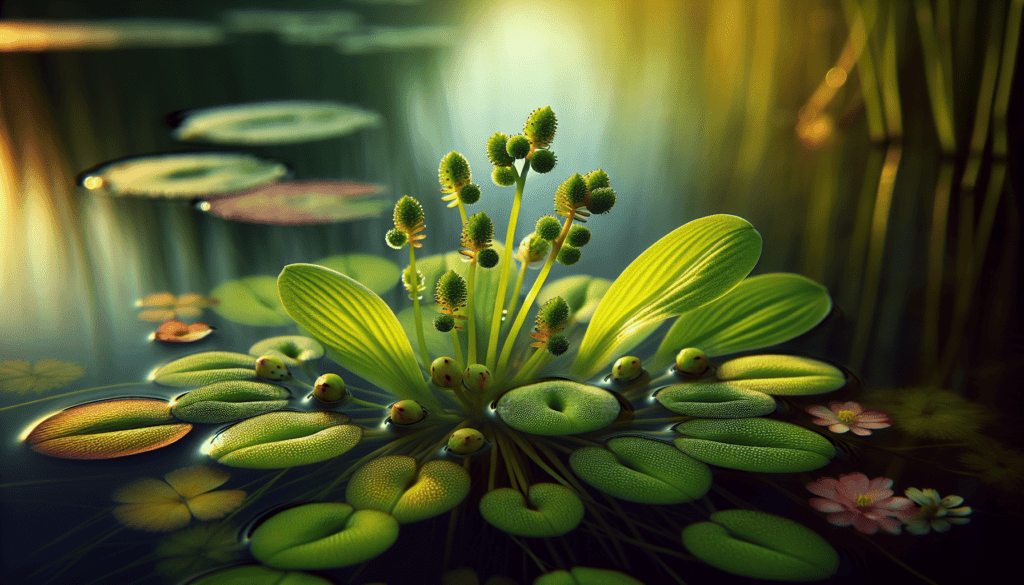

Maintenance and Care for Amur Pond Plant
Watering and nutrition requirements
Given its aquatic nature, the Amur Pond Plant requires consistent moisture and can tolerate periods of waterlogging. It can extract necessary nutrients from the water and surrounding substrate.
Pruning
Pruning can facilitate healthier growth by removing old or damaged stalks. It can also help in controlling the plant’s tendency to spread aggressively.
Disease control and prevention
Though generally robust against diseases, the Amur Pond Plant can occasionally be afflicted by fungal infections or pests. Regular inspection and preemptive measures can prevent such instances.
Regulating growth
Monitoring and controlling the spread of this plant is crucial, given its tendency to become invasive if left unchecked.
Potential Pests and Diseases Amur Pond Plant can Acquire
Common pests
Common pests that can affect the Amur Pond Plant include aphids and stem-boring insects.
Fungal diseases
Fungal diseases such as rust and leaf spot can impact the plant’s health, often indicated by discolored patches on the leaves.
Prevention and treatment
Using environmentally friendly protective measures, such as biopesticides, can help prevent pest infestation and disease spread. Additionally, prompt removal of diseased plants can curtail the spread of pathogens.
Role in the Ecosystem
Beneficial insects attracted
The Amur Pond Plant, with its flowers and seeds, can draw various pollinators and beneficial insects, thereby promoting biodiversity.
Impact on water quality
By absorbing nutrients and pollutants from the water, the plant can improve water quality, contributing to healthier aquatic ecosystems.
Contribution to habitat
The dense growth of the Amur Pond Plant can provide shelter and breeding grounds for a variety of aquatic and semi-aquatic creatures.
Potential Risks and Controversies
Invasive species issues
Due to its aggressive growth and resilient nature, the Amur Pond Plant can become an invasive species if not properly managed, potentially disrupting native flora and fauna.
Potential toxicity
While generally considered safe, the plant may pose ingestion hazards to certain livestock species.
Uses of Amur Plant
Ornamental
The Amur Pond Plant’s lush, vibrant foliage and tall stature make it a popular choice for water gardens and ponds.
Medicinal uses
Historically, certain cultures have used the plant for its purported medicinal properties, although scientific validation of these uses is needed.
Use in aquaponics
In aquaponics, the Amur Pond Plant can help in nutrient cycling and water purification.
Conservation Status and Environmental Concerns
Current conservation status
Given its widespread distribution and adaptive abilities, the Amur Pond Plant is not currently on any conservation status list.
Threats to survival
Despite its resilience, the plant could face threats from unsuitable habitat transformation, aggressive harvesting, or climate change.
Conservation efforts
While not officially conserved, control measures should be in place to prevent the plant from becoming invasive, while still maintaining healthy populations in native habitats.