In the intricate pool of biodiversity, a prevalent aquatic species you may come across is Alisma subcordatum, widely known as the American Water Plantain. This article illuminates the unique attributes of this commensal inhabitant of freshwater environments in North America. As you venture into the ensuing discussion, expect to unfurl layers of knowledge about its botanical anatomy, ecological role, propagation, conservation status, and the plethora of uses it offers. Let your curiosity guide you as you explore the engrossing journey of discovering the American Water Plantain.

Overview of the American Water Plantain
American Water Plantain is a aquatic plant native to the United States. It belongs to the family Alismataceae. This family includes other wetland plants such as arrowheads and narrow leaf mud plantains.
Scientific classification and common names
The scientific name for the American Water Plantain is Alisma subcordatum. Apart from American Water Plantain, this plant has other common names such as Southern Water Plantain and Mud Plantain. It can be found across different regions and thus, the name varies regionally.
Description of its appearance
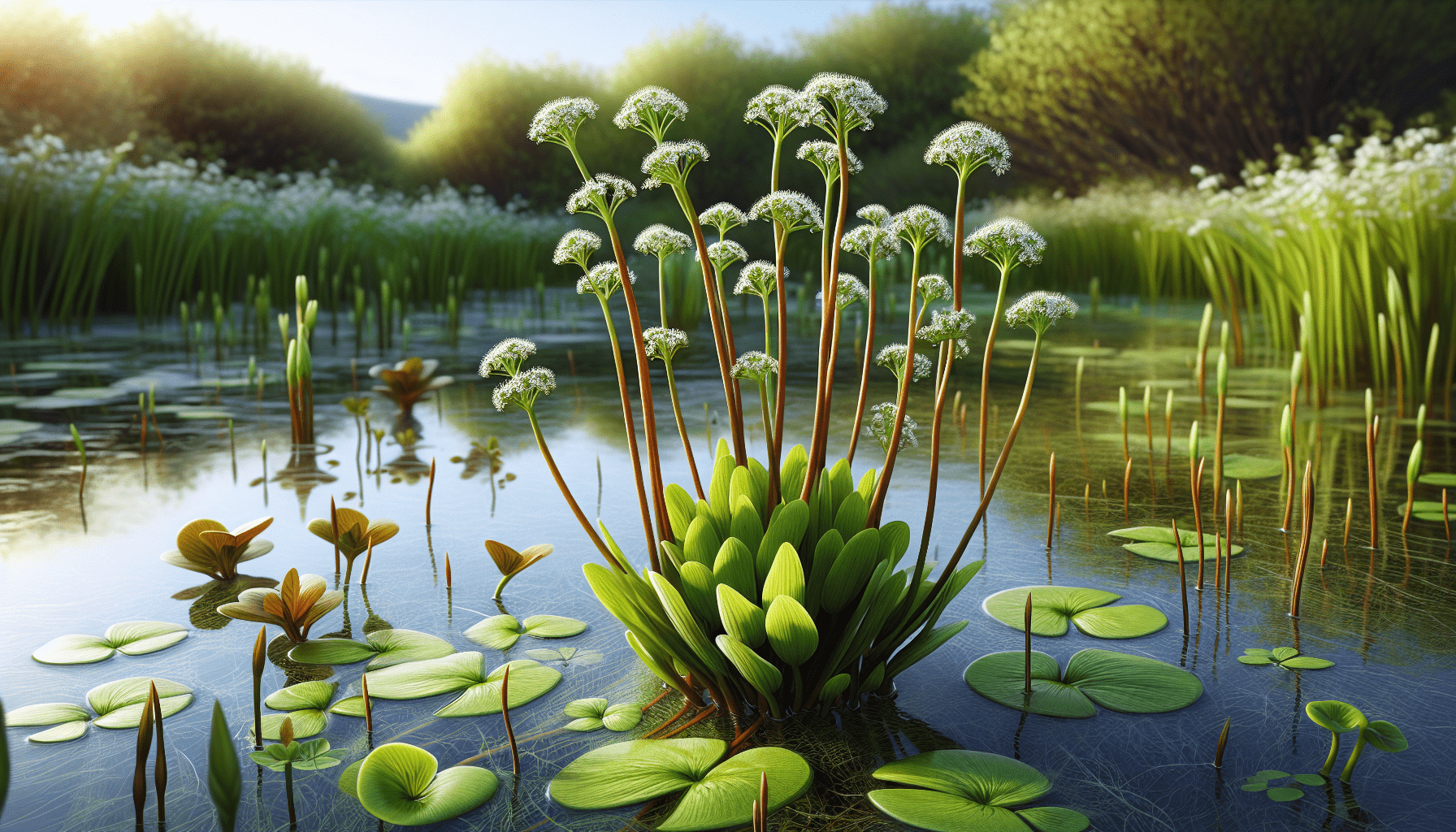
The American Water Plantain is a relatively large plant, with heights reaching up to 1 meter or more. It has long and broad leaves that are usually unequal in size. These leaves can be completely submerged, floating or rising above the water surface depending on the water depth. The plant also bears small white or pink flowers during its blooming period.
Natural habitat and geographic distribution
This plant can be found in most parts of the United States except for some regions in the west. It favors the edges of ponds, streams, and creeks, as well as marshes and swamps. The plant is also found in similar habitats in other parts of North America, Central America, and South America.
Morphological Characteristics of the American Water Plantain
The American Water Plantain is distinguished by certain morphological characteristics that help it survive in its aquatic habitat.
Root system and growth
The American Water Plantain has a fibrous root system that anchors it to the bottom of a body of water. The plant sprouts from a tuber-like corm that permits it to endure periods of drought or cold.
Stem and leaf structure
The plant’s green, fleshy leaves emanate from a basal rosette and stand erect above the water. The leaf blades are up to 12 inches long and 6 inches wide, and they have pointed tips and heart-shaped bases.
Flower and fruiting details
The flowers of the American Water Plantain appear as panicles on a tall, single stem that can reach up to a meter high. After pollination, the flowers form seed pods that contain numerous small seeds.
Growth Habit of the American Water Plantain
Understanding the growth habit of this plant is crucial for its effective cultivation and management.
Life cycle and growth season
American Water Plantain is a perennial plant. It begins to grow in late spring or early summer and flowers throughout the summer months. The plant dies back in winter but returns in spring from the corm.
Growth rate
The plant has a moderate growth rate and can reach its full size within one growing season.
Common cultivation methods
American Water Plantain is usually propagated through its seeds or by dividing the corms. It can thrive in a variety of water bodies including ponds, streams, and marshes.
Propagation and Cultivation of the American Water Plantain
Growing American Water Plantain successfully requires understanding its propagation and cultivation methods.
Typical propagation techniques
Seeds can be collected in the late summer or early fall and directly sown in shallow water or wet soil. The corms can be divided in spring or fall and replanted in a new location.
Soil requirements and preparation
The American Water Plantain prefers loamy to sandy soil. The soil should be wet or, ideally, submerged under shallow water.
Light, water, and temperature needs
This plant grows best in full sun to partial shade. It requires a good amount of water but can also tolerate some degree of seasonal dryness. It is generally tough and can tolerate a wide range of temperatures as long as the roots do not dry out.
Pruning and maintenance
Since this plant naturally grows in wetland areas, it requires very little maintenance. If needed, dead leaves and flowers can be removed to keep the plant looking attractive.
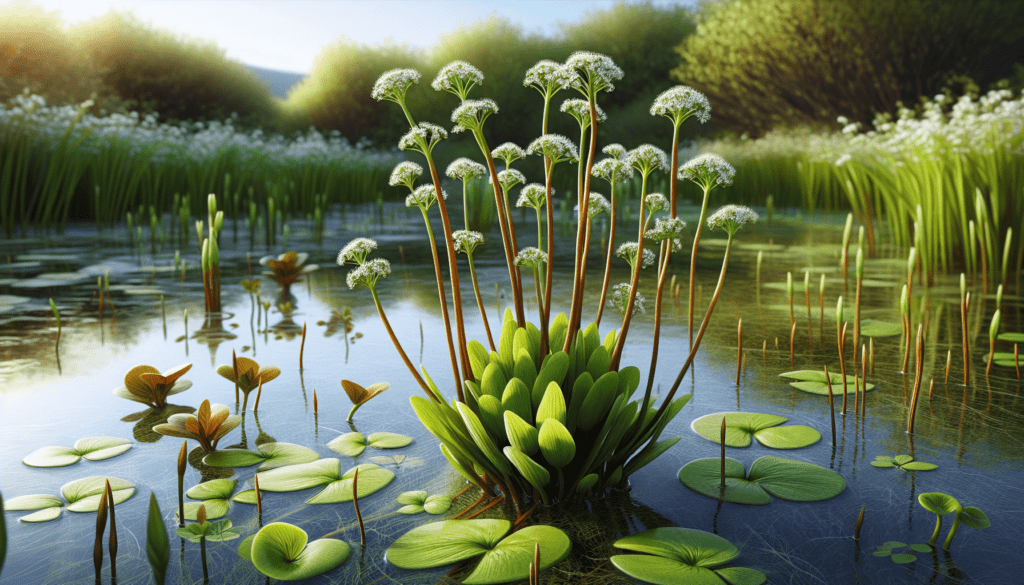

Ecological Role of the American Water Plantain
This plant plays an essential role in aquatic ecosystems.
Use in water purification
Its roots absorb pollutants from the water, helping to purify it. Furthermore, the plant helps in oxygenating water and preventing algae bloom, thereby promoting a healthy aquatic environment.
Role in providing aquatic habitat
The American Water Plantain provides shelter for small aquatic creatures, including insects, snails, and small fish. Its leaves and stems above the water surface are also useful for certain bird species.
Contribution to the food chain
Various parts of the plant, including seeds, leaves, and tubers, serve as a source of food for some animals. These include waterfowl and other birds, as well as certain species of mammals and insects.
Pests and Diseases affecting the American Water Plantain
Like most plants, the American Water Plantain is susceptible to certain pests and diseases.
Common pests and their management
Common pests include aphids and leafhoppers. Washing the plants with a strong jet of water can dislodge these pests. In severe cases, insecticidal soaps or oils can be used.
Typical diseases and ways to treat them
Fungal diseases like leaf spots and powdery mildew may infect the leaves. These can be controlled by improving air circulation and avoiding overhead watering.
Effect of environmental conditions on health
Fluctuating water levels, poor water quality, and exposure to extreme temperatures can stress the plant and make it more susceptible to pests and diseases.
Medicinal Uses of the American Water Plantain
Historically, the American Water Plantain has been used medicinally by native peoples.
Historic medicinal uses
Traditionally, it has been used to treat conditions such as stomach aches, wounds, and sores.
Current research and medicinal benefits
Current research suggests potential benefits of this plant for conditions like kidney stones and urinary tract infections due to diuretic properties.
Preparation and dosage of plant extracts
Typically, the roots are dried and crushed into a powder, then taken in capsule form or as a tea.
Possible side effects and precautions
As with many herbal remedies, it’s important to take with caution as it may cause allergic reactions in some people.
American Water Plantain in Landscape Design
The American Water Plantain adds beauty and biodiversity to a water garden or pond.
Ways to incorporate into water gardens
It can be planted in the shallow edges of a pond or stream, where its tall stems with white or pink flowers can add a visual appeal.
Pairing with other plants
It can be paired with other aquatic or marginal plants, like rushes or irises.
Handling challenges in landscape use
If grown without constraints, it can become competitive and might overshadow less vigorous plants. Therefore, it is important to monitor its growth and spread.
Conservation Status of the American Water Plantain
While not currently considered threatened or endangered, the American Water Plantain is vulnerable to habitat destruction.
Current conservation status
At present, it is not on any endangered or threatened species lists.
Threats to survival
The main threat comes from habitat loss due to urbanization and drainage of wetlands. Pollutants like pesticides and heavy metals can also affect the plant’s health and growth.
Conservation efforts and preservation tactics
Preserving wetland habitats, promoting the use of this plant in water gardens, and reducing the use of harmful pollutants can contribute to its conservation.
Interesting Facts about the American Water Plantain
Finally, here are some interesting facts about this beautiful and versatile plant.
Historical significance
Native American tribes found multiple uses for this plant, from food to medicine.
Unique adaptations
The plant can adjust to fluctuating water levels, and its leaves can vary depending on the depth of water.
Trivia and fun facts
The plant’s flowers only open in the afternoon and close in the evening, and each flower lasts for only a single day.